Why Strong App Security Standards Are Non-Negotiable Today
Implementing recognized app security standards is now essential for safeguarding user data, maintaining trust, and meeting compliance obligations amid escalating cyber threats. This listicle directly presents 8 crucial app security standards to consider for 2025. Understanding these frameworks enables developers, security professionals, and product teams to effectively strengthen their applications against attacks and improve overall security posture, ensuring your software remains resilient.
1. OWASP Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS)
In the ever-evolving landscape of mobile technology, ensuring the security of applications is paramount. The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS), formally known as project masvs, stands as a cornerstone among app security standards. It offers a community-driven, comprehensive framework that defines security requirements for mobile applications. This standard is crucial for developers, security testers, and organizations aiming to build and maintain secure mobile experiences, providing a clear, industry-recognized benchmark for mobile app security.
What is MASVS and How Does It Work?
The OWASP MASVS is a detailed set of security requirements that mobile applications should adhere to. It’s designed to be platform-agnostic, providing a unified standard applicable to both iOS and Android applications. The core of MASVS lies in its structured approach, categorizing security controls across 14 distinct domains (V1-V14). These domains cover essential aspects such as:
- V1: Architecture, Design and Threat Modeling Requirements: Focusing on secure design principles from the outset.
- V2: Data Storage and Privacy Requirements: Addressing how sensitive data is stored on the device and handled to protect user privacy.
- V3: Cryptography Requirements: Ensuring proper use of cryptographic APIs and algorithms.
- V4: Authentication and Session Management Requirements: Verifying user identities and managing sessions securely.
- V5: Network Communication Requirements: Securing data in transit.
- V6: Environmental Interaction Requirements: Managing interactions with platform features and other apps.
- V7: Code Quality and Build Setting Requirements: Promoting secure coding practices and build configurations.
- V8: Resiliency Against Reverse Engineering and Tampering Requirements: Making apps harder to analyze and modify illicitly.
MASVS defines three distinct security verification levels (L1, L2, and L3), allowing organizations to choose the appropriate level based on their application’s risk profile.
- MASVS-L1: Standard Security: This level is recommended for all mobile applications. It covers basic security hygiene, addressing common vulnerabilities and ensuring a baseline level of security. It focuses on protecting user data and ensuring the app functions as intended without introducing significant security flaws.
- MASVS-L2: Defense-in-Depth: This level is for applications that handle more sensitive data or perform critical functions, such as mobile banking or healthcare apps. MASVS-L2 builds upon L1 by requiring additional security controls that provide defense-in-depth against more sophisticated attacks. This includes protections against client-side threats like tampering and reverse engineering.
- MASVS-L3: Advanced Security: This level is reserved for applications with the highest security requirements, often those handling extremely sensitive data or facing significant threats (e.g., high-value financial transactions, critical infrastructure control). MASVS-L3 includes stringent requirements for resiliency against advanced reverse engineering and tampering techniques.
The following infographic illustrates the hierarchical structure of the OWASP MASVS framework, showcasing its three progressive security levels.
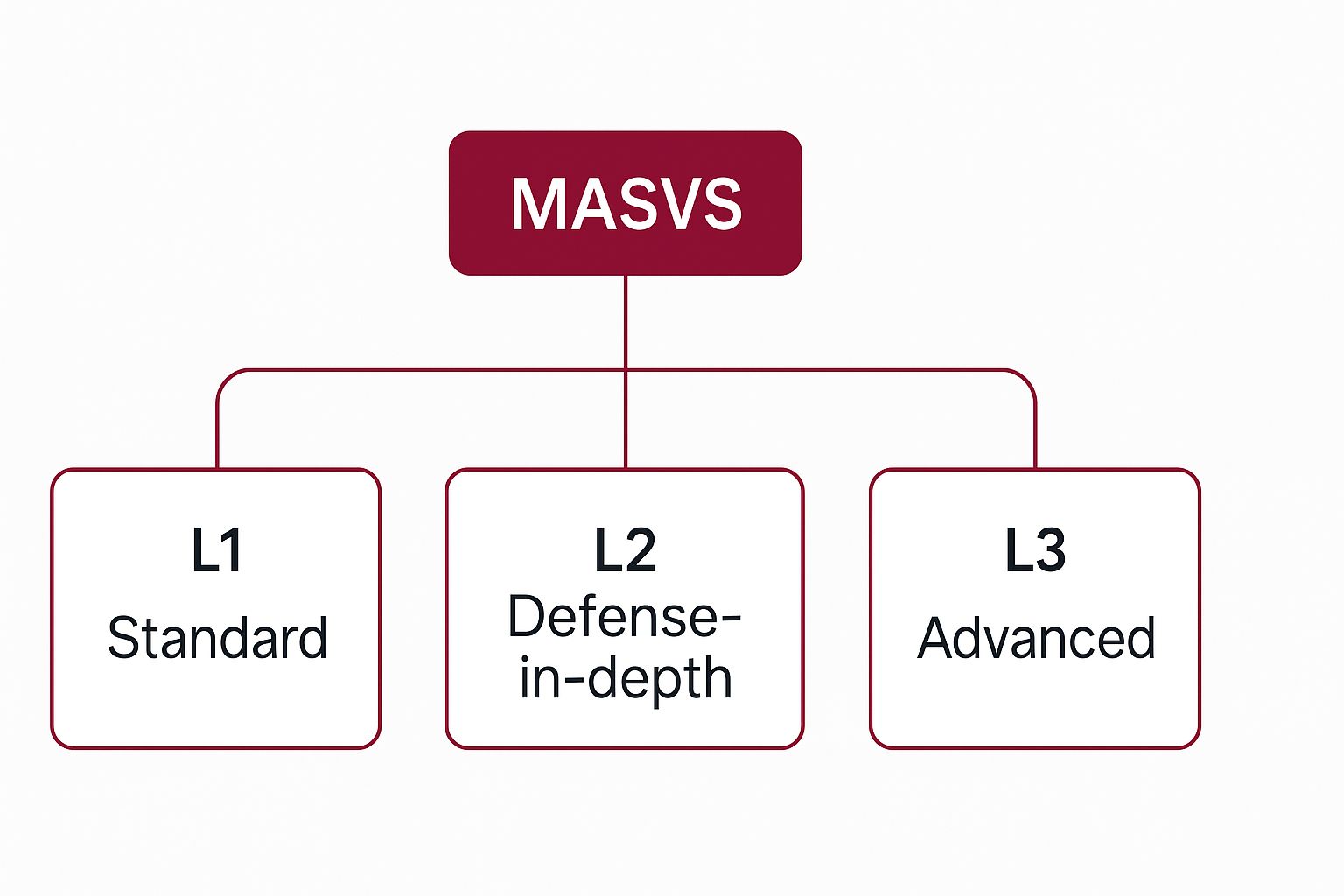
This hierarchical structure clearly shows ‘MASVS’ as the overarching standard, branching into ‘L1 Standard’, ‘L2 Defense-in-depth’, and ‘L3 Advanced’, indicating a progression in security stringency. Each level builds upon the previous, allowing organizations to select a target that aligns with their specific security needs and risk assessment, making MASVS a flexible and scalable app security standard.
Why MASVS Deserves its Place
MASVS is widely recognized as an industry-standard framework, making it an indispensable tool for any organization serious about mobile application security. Its comprehensive nature, regular updates reflecting the current threat landscape, and alignment with the OWASP Mobile Top 10 risks ensure its continued relevance. Being free and open-source, it’s accessible to everyone, from individual developers to large enterprises. This transparent and collaborative approach, championed by leaders like Sven Schleier and Jeroen Willemsen of the OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide (MSTG) project, has solidified its position. The MSTG, in fact, serves as a practical guide for implementing MASVS requirements, offering detailed testing procedures.
Features and Benefits:
- Three-tiered Security Levels: Offers flexibility (L1, L2, L3) to match varying risk appetites.
- Platform-Agnostic: Applicable to both iOS and Android, simplifying cross-platform security strategies.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Addresses 14 security categories, from authentication to data storage and cryptography.
- Aligned with OWASP Mobile Top 10: Directly tackles the most critical mobile security risks.
- Measurable Criteria: Provides clear, verifiable security requirements, aiding in testing and validation.
- Industry Standard: Widely recognized and respected globally.
- Free and Open-Source: Accessible to all, fostering community contributions and widespread adoption.
- Regular Updates: Maintained by security experts to reflect the evolving threat landscape.
- Supports Compliance: Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements like HIPAA or GDPR by providing a structured security baseline.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Establishes a clear, industry-recognized benchmark for mobile app security.
- Comprehensive and detailed, covering a wide array of mobile security aspects.
- Free, open-source, and regularly updated by a global community of experts.
- Provides a structured approach to security testing and verification.
- Supports compliance with various regulatory and audit requirements.
Cons:
- Can be complex to implement, especially for smaller development teams or those new to security.
- Requires a good understanding of mobile security concepts and expertise to apply effectively.
- MASVS-L3 requirements might be overly stringent and costly for many applications not dealing with extremely high-risk scenarios.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Banking Applications: Institutions like Chase Mobile often implement requirements aligning with MASVS-L2 or even elements of L3 to protect sensitive financial data and transactions. They focus heavily on strong authentication, secure data storage, and robust anti-tampering measures.
- Healthcare Apps: Mobile apps that handle Protected Health Information (PHI) leverage MASVS to meet HIPAA compliance. They focus on V2 (Data Storage and Privacy) and V5 (Network Communication) to ensure patient data confidentiality and integrity.
- Government Applications: Secure government communication or citizen service apps often require advanced security verification akin to MASVS-L2/L3, ensuring data integrity and resilience against state-level actors.
Actionable Tips for Readers:
- Start with L1: Begin by assessing your application against MASVS-L1 requirements. This provides a solid foundation and addresses the most common vulnerabilities.
- Progressively Implement: Based on your application’s risk profile and data sensitivity, gradually incorporate requirements from L2 and, if necessary, L3.
- Use OWASP MSTG: The Mobile Security Testing Guide (MSTG) is an invaluable companion to MASVS. It provides detailed testing procedures and implementation guidance for each MASVS requirement.
- Integrate Early: Embed MASVS requirements into your development lifecycle (SDLC) from the design phase. This “shift-left” approach is more cost-effective than fixing vulnerabilities later.
- Risk-Based Approach: Don’t aim for L3 if your app doesn’t warrant it. Conduct a thorough risk assessment to determine the appropriate MASVS level for your specific application.
When and Why to Use MASVS:
MASVS should be used whenever an organization aims to develop or maintain secure mobile applications. It’s particularly beneficial when:
- Handling sensitive user data (e.g., PII, financial information, health records).
- Needing to comply with industry regulations or legal requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS).
- Seeking a standardized and verifiable method to assess and improve mobile app security posture.
- Developing applications for industries with high security demands, such as finance, healthcare, or government.
- Wanting to protect brand reputation and user trust by proactively addressing security vulnerabilities.
By adopting MASVS, developers and organizations can systematically enhance their mobile app security standards, reduce the likelihood of security breaches, and build more resilient applications.
To delve deeper into the nuances of mobile app security, you can explore further resources. Learn more about OWASP Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS) for additional insights.
For a visual and auditory explanation, consider this overview:
Ultimately, MASVS provides a roadmap for achieving robust mobile application security, making it an essential standard for any modern development practice.
2. NIST Cybersecurity Framework for Mobile Devices
When organizations seek to establish gold-standard app security standards, particularly for mobile ecosystems, the guidance from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a cornerstone. While NIST doesn’t offer a single, monolithic “Mobile Framework,” its comprehensive suite of publications, most notably Special Publication (SP) 800-124 (“Guidelines for Managing the Security of Mobile Devices in the Enterprise”) and the broader SP 800-53 (“Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations”), provides a robust, risk-based approach to mobile security. This collection of guidelines, often collectively referred to in the context of the overarching NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), offers a structured methodology for securing mobile devices and the applications they run.
The core of NIST’s approach to cybersecurity, applicable to mobile environments, revolves around five concurrent and continuous functions:
- Identify: This foundational step involves developing an organizational understanding to manage cybersecurity risk to systems, assets, data, and capabilities. For mobile app security, this means identifying mobile assets (devices, apps, data), understanding business needs, mapping data flows, identifying vulnerabilities in apps (e.g., insecure data storage, weak authentication), and assessing risks specific to the mobile platform. React Native developers and QA teams play a crucial role here by helping to identify potential weaknesses in the app’s architecture and dependencies.
- Protect: This function focuses on developing and implementing appropriate safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services. In the mobile context, this translates to implementing security controls such as strong authentication for app users, encryption of data at rest and in transit, secure coding practices for app development, mobile device management (MDM) policies, network security measures, and user training.
- Detect: The Detect function enables the timely discovery of cybersecurity events. For mobile apps, this involves implementing logging and monitoring for suspicious activities, intrusion detection systems for mobile networks, and tools that can identify compromised devices or malicious app behavior. Continuous monitoring is key to quickly identifying security incidents.
- Respond: This involves developing and implementing appropriate activities to take action regarding a detected cybersecurity incident. Should a mobile security incident occur (e.g., a data breach via an app, malware infection), a well-defined response plan is crucial. This includes containment, eradication, and communication strategies.
- Recover: The Recover function supports timely recovery to normal operations to reduce the impact of a cybersecurity incident. This involves restoring affected mobile services and devices, implementing lessons learned to prevent future occurrences, and updating security policies and app configurations.
This framework is not merely a checklist but a strategic approach that encourages organizations to tailor security controls based on their specific risk appetite, operational environment, and regulatory obligations. Its alignment with federal security requirements gives it significant credibility, making it a preferred choice for government agencies and enterprises in regulated sectors.
Why NIST Guidance Deserves Its Place in App Security Standards
NIST’s guidance is pivotal for several reasons. Firstly, its government backing lends it unparalleled credibility and ensures it’s widely accepted across industries. Secondly, it offers a truly comprehensive risk management approach, moving beyond technical fixes to encompass governance, processes, and people. This holistic view is essential for establishing durable app security standards. Furthermore, NIST regularly updates its publications based on emerging threats and evolving technologies, ensuring the guidance remains relevant. For organizations, especially those developing or deploying applications like React Native apps that handle sensitive enterprise data, adopting NIST principles provides a strong, defensible security posture.
Pros:
- Government-backed credibility: Widely trusted and often a baseline for regulatory compliance.
- Flexible and adaptable: While comprehensive, its risk-based nature allows tailoring to diverse organizational needs.
- Comprehensive risk management: Addresses security from multiple angles – technical, procedural, and human.
- Regular updates: Stays current with the evolving threat landscape.
- Strong focus on governance: Emphasizes policy, oversight, and accountability.
Cons:
- Potential complexity: Can seem overwhelming, especially for smaller organizations or startups without dedicated security teams.
- Enterprise-focused: Primarily designed for larger enterprises and government agencies, requiring adaptation for smaller contexts.
- Can be perceived as bureaucratic: The thoroughness can sometimes lead to slower implementation cycles if not managed pragmatically.
When and Why to Use the NIST Approach
Organizations should consider leveraging NIST’s mobile security guidance when:
- Handling sensitive or regulated data (e.g., PII, PHI, financial data) on mobile devices or through mobile apps.
- Needing to comply with federal regulations (like FISMA) or industry-specific mandates that align with NIST standards (e.g., elements of HIPAA security).
- Aiming to integrate mobile security seamlessly into an existing enterprise-wide cybersecurity program based on the NIST CSF.
- Seeking a mature, well-documented, and widely respected framework to build a robust mobile security program.
The “why” is straightforward: NIST provides a proven path to systematically reduce mobile security risks, enhance resilience, and demonstrate due diligence in protecting information assets.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- U.S. Federal Agencies: Many federal agencies are mandated to follow NIST guidelines, using them to secure government-issued mobile devices and applications handling official data.
- Large Enterprises (e.g., IBM): Global corporations often adopt or align with NIST frameworks to standardize their mobile security policies, manage Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) risks, and secure enterprise mobile applications.
- Healthcare Organizations: To meet HIPAA’s Security Rule requirements, healthcare providers often map their mobile security controls (protecting ePHI on tablets and smartphones used by clinicians) to NIST guidelines, particularly SP 800-53 controls.
Actionable Tips for Readers:
- Start with a Risk Assessment: Before diving into specific controls, conduct a thorough risk assessment focused on your mobile apps and devices. Identify your most critical mobile assets, data, and potential threats.
- Customize, Don’t Just Copy-Paste: Use NIST guidelines as a baseline. React Native developers, for instance, should focus on controls relevant to JavaScript vulnerabilities, native module security, and secure API integrations, tailoring NIST’s principles to their specific tech stack.
- Focus on Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: The mobile threat landscape is dynamic. Implement mechanisms for ongoing monitoring of your mobile apps and environment, and regularly review and update your security measures.
- Integrate, Don’t Isolate: Mobile app security should be an integral part of your overall cybersecurity strategy, not a standalone effort. Ensure it aligns with your enterprise risk management framework.
- Leverage Specific NIST Publications: Begin by exploring NIST SP 800-124 and relevant controls from SP 800-53. These documents offer detailed guidance.
For those looking to deepen their understanding of how these principles apply broadly, you can Learn more about NIST Cybersecurity Framework for Mobile Devices and related security topics. Adopting or adapting NIST’s guidance can significantly elevate your organization’s app security standards and overall mobile resilience.
3. ISO/IEC 27001 Mobile Security Controls
In the landscape of robust app security standards, ISO/IEC 27001 stands out as a globally recognized framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). Developed jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), with its origins in BS 7799 from the British Standards Institution (BSI), ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive, risk-based approach to information security that naturally extends to the complexities of mobile environments. While not exclusively a mobile security standard, its holistic nature ensures that mobile device security, Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies, and mobile application security are integral components of an organization’s overall security posture.
How ISO/IEC 27001 Addresses Mobile Security
ISO/IEC 27001 operates on the principle that effective information security is achieved by identifying risks and implementing appropriate controls to mitigate them. For mobile security, this translates into a systematic process:
- Risk Assessment and Treatment: The journey begins with a thorough risk assessment specific to mobile devices and applications. This involves identifying assets (mobile devices, sensitive app data), threats (device loss/theft, malware, insecure Wi-Fi, data leakage from apps), vulnerabilities (unpatched OS, weak app code, poor user practices), and the potential impact of these risks materializing. Based on this assessment, organizations select relevant controls from ISO 27001’s Annex A or define their own.
- Relevant Annex A Controls: While ISO 27001 is broad, several control areas in Annex A are particularly pertinent to mobile security:
- A.6.2 Mobile devices and teleworking: Directly addresses policies and security measures for mobile device usage and teleworking, crucial for managing BYOD and corporate-owned devices.
- A.8 Asset Management: Includes inventorying mobile devices that access corporate data.
- A.12 Operations Security: Covers malware protection and data backup, essential for mobile endpoints.
- A.13 Communications Security: Focuses on network security and protecting data in transit, vital for mobile apps communicating over various networks. Key controls often address mobile data protection, including strong encryption for data at rest on the device and data in transit during app communications. Learn more about data encryption strategies, a vital aspect of mobile security within the ISO 27001 framework.
- A.14 System acquisition, development and maintenance: Encompasses secure development practices for mobile applications, critical for React Native developers and DevOps teams aiming to build secure apps from the ground up. This involves secure coding standards, security testing, and managing vulnerabilities in the development lifecycle.
- A.18 Compliance: Ensures adherence to legal, statutory, regulatory, and contractual requirements related to mobile data processing.
- Policy Development: Clear, enforceable policies are fundamental. This includes BYOD policies, acceptable use policies for mobile devices, mobile application security guidelines, and incident response procedures for mobile-related breaches.
- Continuous Improvement (PDCA Cycle): The standard promotes a Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle:
- Plan: Establish the ISMS, including mobile security objectives, policies, processes, and controls.
- Do: Implement and operate the ISMS controls, train staff, and manage mobile devices and apps securely.
- Check: Monitor and review the ISMS’s effectiveness, conduct internal audits, and assess mobile security performance against policies.
- Act: Take corrective and preventive actions to continually improve the ISMS based on review results and evolving mobile threats.
This risk-based, cyclical approach ensures that mobile security measures are not static but adapt to new technologies, threats, and business requirements, making it a dynamic component of app security standards.
Why ISO/IEC 27001 Deserves its Place
ISO/IEC 27001 is a cornerstone for organizations, including security-conscious enterprises and product managers, aiming for a high level of validated security. Its inclusion in this list is merited by its comprehensive, internationally recognized framework that fosters trust and operational excellence.
-
Features:
- International Standard with Global Recognition: Provides credibility and facilitates international business.
- Integration with Broader Information Security Management: Ensures mobile security isn’t siloed but part of a holistic strategy.
- Specific Mobile Device Policy Requirements: Guides the creation of robust policies for mobile use.
- Risk-Based Approach: Tailors mobile security controls to actual organizational risks rather than a one-size-fits-all checklist.
- Continuous Improvement Methodology: Employs the PDCA cycle for ongoing refinement.
-
Benefits (Pros):
- Internationally Recognized Certification: Achieving ISO 27001 certification can significantly build customer trust, enhance brand reputation, and provide a competitive edge.
- Comprehensive Security Management: Offers a structured and all-encompassing approach to managing information security risks, including those posed by mobile technologies.
- Strong Audit and Compliance Framework: Facilitates internal and external audits, demonstrating due diligence and adherence to security best practices and legal requirements.
- Regular Updates and Improvements: The standard itself is periodically reviewed, and the ISMS framework drives continuous internal security enhancements.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Systematically identifies, analyzes, and treats mobile-related security risks, reducing the likelihood and impact of incidents.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Organizations should consider adopting ISO 27001 when:
- Handling sensitive customer, financial, or proprietary data via mobile applications or devices.
- Operating in regulated industries (e.g., finance, healthcare, telecommunications).
- Aiming to provide a high assurance of security to stakeholders, crucial for enterprise clients.
- Managing a significant fleet of mobile devices (corporate or BYOD).
- Seeking a structured, internationally accepted framework to manage overall information security, with mobile security as a key component.
The primary “why” is to establish a mature, demonstrable, and continuously improving security posture that addresses the evolving mobile threat landscape. It moves an organization beyond ad-hoc fixes towards a strategic and resilient approach to information security.
Examples of Successful Implementation
- Telecommunications Companies (e.g., Vodafone): Many telcos achieve ISO 27001 certification, encompassing security for their mobile networks, customer data handled via mobile services, and internal mobile device usage.
- Financial Services Firms: Implement stringent mobile security controls within their ISO 27001 ISMS to protect mobile banking applications, transaction data, and customer PII accessed or processed on mobile platforms.
- Cloud Service Providers: Secure mobile access points to their cloud services, ensuring that management and user access from mobile devices are governed by their certified ISMS.
- Software Development Companies: For development teams, including React Native developers, integrating secure SDLC practices as part of A.14 within an ISO 27001 framework ensures mobile apps are designed and built with security in mind.
Actionable Tips for Readers
- Conduct a Thorough Mobile-Specific Risk Assessment: Before implementing controls, identify your specific mobile threats, vulnerabilities (e.g., in-app permissions, data storage, API interactions), and potential business impacts.
- Focus on Documentation and Process Standardization: ISO 27001 mandates documented policies and procedures. Ensure your mobile security policies (BYOD, secure mobile app development, incident response for lost devices) are clear, communicated, and consistently applied.
- Integrate Security into the Mobile App Lifecycle: For development (React Native, etc.) and DevOps teams, embed security into every phase: secure coding training, use of secure libraries, vulnerability scanning (SAST/DAST) in CI/CD pipelines, and rigorous QA security testing.
- Train Staff on Mobile Security Policies: Regular awareness training for all employees, especially those developing, testing, or using mobile apps and devices with access to corporate data, is crucial.
- Regular Internal Audits: Don’t rely solely on external certification audits. Conduct frequent internal audits focusing on the effectiveness of your mobile security controls to ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Start with a Defined Scope: If a full organizational ISMS is too ambitious initially, consider scoping your ISO 27001 implementation to critical systems or departments that heavily utilize mobile technology or handle sensitive mobile data.
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Internationally recognized certification, comprehensive security management approach, strong audit and compliance framework, regular updates and improvements, builds customer trust and credibility.
- Cons: The certification and maintenance process can be expensive and time-consuming. Implementation is complex and requires significant organizational resources (personnel, budget, time). For organizations only focused on a very narrow aspect of mobile app security without broader information security needs, it might seem overly comprehensive, though its true strength lies in this holistic integration.
By leveraging ISO/IEC 27001, organizations can significantly elevate their mobile app security standards, fostering a culture of security that protects valuable data and builds lasting trust with users and partners.
4. Common Criteria (CC) for Mobile Applications
For organizations developing mobile applications where security is paramount, particularly those in government, defense, or critical infrastructure sectors, the Common Criteria (CC) for Information Technology Security Evaluation (commonly referred to as Common Criteria or CC) represents one of the most rigorous international app security standards. It is formally standardized as ISO/IEC 15408 and provides a comprehensive framework for specifying, evaluating, and certifying the security features of IT products, including mobile applications.
How Common Criteria Works
The Common Criteria process is meticulous and structured. It revolves around several key concepts:
- Protection Profile (PP): This document defines a standard set of security requirements for a specific type of product (e.g., a mobile operating system, a database, or even a class of mobile application). PPs are often developed by user communities or government bodies to address common security needs. For mobile applications, specific PPs like those for “Application Software” or more granular profiles can be used or adapted. Developers can also create their own PPs if existing ones aren’t suitable, though this adds complexity.
- Security Target (ST): The developer of the mobile application (the “Target of Evaluation” or TOE) creates the Security Target. This document specifies the security functions of their particular app, the threats it’s designed to counter, and how it meets the security objectives. The ST can claim conformance to one or more PPs, or it can define a unique set of security requirements.
- Evaluation Assurance Levels (EALs): CC defines seven EALs, from EAL1 (lowest) to EAL7 (highest), representing increasing levels of rigor and assurance in the evaluation process.
- EAL1: Functionally Tested: The app’s functions are tested.
- EAL2: Structurally Tested: Includes analysis of high-level design and developer testing.
- EAL3: Methodically Tested and Checked: Adds more rigor to design review and testing.
- EAL4: Methodically Designed, Tested, and Reviewed: Requires a more comprehensive analysis of security design, often a target for commercial products needing strong, independently verified security.
- EAL5: Semiformally Designed and Tested: Introduces formal methods in design and testing.
- EAL6: Semiformally Verified Design and Tested: Increases the scope of formal verification.
- EAL7: Formally Verified Design and Tested: The highest level, involving formal proof of correctness, typically reserved for extremely high-risk environments. The choice of EAL depends on the application’s risk profile and target market.
- Evaluation and Certification: Independent, accredited third-party laboratories conduct the evaluation. They meticulously examine the ST, the mobile application itself, and the developer’s processes against the claimed EAL and any PPs. If successful, a certificate is issued by a national certification body.
- Common Criteria Recognition Arrangement (CCRA): This international agreement means that certificates issued by one member nation are recognized by others, simplifying global market access for certified products.
Why Common Criteria Deserves its Place in App Security Standards
Common Criteria is included in this list because it offers an unparalleled level of security assurance through a standardized, internationally recognized methodology. For mobile apps handling highly sensitive data or operating in regulated environments, CC validation provides a high degree of confidence in the app’s security posture, making it a critical component of a comprehensive app security standards strategy.
Features and Benefits
-
Features:
- Seven Evaluation Assurance Levels (EAL1-EAL7): Allows for a graded approach to security assurance based on risk.
- Custom Protection Profiles: Enables tailoring security requirements to specific mobile app functionalities, such as secure data storage, biometric authentication, or encrypted communications.
- International Mutual Recognition (CCRA): Certificates are often recognized across dozens of countries, reducing redundant testing.
- Formal Security Evaluation Methodology: Provides a structured, repeatable, and objective evaluation process.
- Independent Third-Party Validation: Offers unbiased confirmation of security claims, building trust.
-
Benefits (Pros):
- High Level of Security Assurance: Provides strong confidence that the mobile app meets its stated security claims.
- International Recognition and Acceptance: Facilitates entry into global markets, especially in regulated sectors.
- Rigorous Evaluation Process: The depth of analysis can uncover vulnerabilities that other testing methods might miss.
- Suitable for High-Security Applications: Essential for apps in government, military, finance, and healthcare.
- Government and Military Acceptance: Often a prerequisite for procurement by these entities.
Considerations (Cons)
- Extremely Expensive and Time-Consuming: The certification process can cost hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars and take 12-24 months, or even longer, involving significant internal resources and lab fees.
- Complex Certification Process: Requires extensive documentation, meticulous preparation, and ongoing interaction with evaluation labs.
- May Not Reflect All Real-World Threats: CC evaluates against the threats and security functions defined in the ST and PP. Agile, zero-day, or rapidly evolving threats might not be fully addressed if the PPs are outdated or the ST isn’t forward-looking. Certification is a snapshot in time.
- Limited to Specific Evaluated Configurations: The certification applies only to the exact version of the mobile app and its specified operating environment that was evaluated. Any significant change typically requires re-evaluation or an assurance continuity process.
When and Why to Use Common Criteria for Your Mobile App
CC certification is not for every mobile application. It’s typically pursued when:
- Mandated by Requirements: Government agencies, military branches, or specific industry regulations (e.g., some critical infrastructure sectors) explicitly require CC certification, often at a specific EAL (like EAL4+).
- Handling Extremely Sensitive Data: If your mobile app processes classified information, high-value financial transactions, or life-critical data, CC can provide the necessary assurance.
- Seeking a Strong Competitive Differentiator: In security-conscious markets, CC certification can significantly enhance your product’s credibility and trustworthiness.
- Ultimate Security Validation is Needed: When the consequences of a security breach are catastrophic, CC offers the most thorough validation available.
Examples of Successful Implementation
- Samsung Knox: Samsung’s mobile security platform, Knox, has consistently achieved Common Criteria certifications for its various components, underpinning its suitability for enterprise and government use.
- Government Mobile Applications: Many custom-developed mobile apps used by government employees for secure communication, accessing sensitive databases, or fieldwork often require EAL4+ certification or conformance to specific PPs (e.g., NIAP-approved PPs in the USA).
- Military-Grade Communication Apps: Secure voice and messaging applications designed for military and intelligence use frequently undergo CC validation to ensure confidentiality and integrity in hostile environments.
Actionable Tips for Mobile App Developers and Organizations
- Assess Necessity and EAL: Carefully evaluate if CC is truly required. If so, determine the appropriate EAL based on your risk assessment, budget, and market requirements. Don’t aim for EAL7 if EAL4 is sufficient and more attainable.
- Plan Extensively and Early: Integrate CC requirements into your development lifecycle from the outset. The process is lengthy (12-24+ months), so early planning for resources, documentation, and timelines is crucial.
- Engage Accredited Labs: Select an accredited Common Criteria Testing Laboratory (CCTL) with experience in mobile application evaluations and your target EAL. They can provide guidance throughout the process.
- Prioritize Protection Profiles: Investigate existing PPs relevant to mobile applications or mobile application software. Conforming to an established PP can streamline the process.
- Focus on Assurance Continuity: Certification applies to a specific version. Establish processes for managing software updates and changes to maintain your certified status, which may involve delta evaluations or re-certification.
Common Criteria, while demanding, provides a robust and internationally respected benchmark for organizations serious about implementing the highest app security standards for their mobile solutions.
For more information, visit the official Common Criteria portal: https://www.commoncriteriaportal.org/
5. PCI Mobile Payment Acceptance Security Guidelines
In an era where mobile commerce is booming, ensuring the security of payment transactions on mobile devices is paramount. The Payment Card Industry Mobile Payment Acceptance Security Guidelines, established by the PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC), provide a critical framework for safeguarding sensitive cardholder data within mobile applications and point-of-sale (POS) systems. These guidelines are not merely suggestions but form a vital component of comprehensive app security standards, especially for any application that processes, stores, or transmits payment card information. They aim to ensure that mobile payment solutions adhere to the same stringent security benchmarks as traditional payment systems, thereby fostering trust and protecting consumers and businesses alike from financial fraud.

These guidelines work by establishing a comprehensive security posture for the entire mobile payment ecosystem. They meticulously outline specific, auditable requirements that cover every touchpoint of payment data within a mobile environment. This holistic approach begins from the secure development and deployment of the mobile application itself, extends to how it captures and handles card data during a transaction, and dictates how that data is securely transmitted to payment processors. It’s a defense-in-depth strategy crucial for robust app security standards.
Key features and components of the PCI Mobile Payment Acceptance Security Guidelines include:
- Specific Requirements for Mobile Payment Applications: The PCI SSC doesn’t offer a one-size-fits-all solution. Instead, it provides a suite of dedicated guidance documents. For instance, the PCI Mobile Payment on COTS (MPoC) standard addresses solutions using commercial off-the-shelf devices like smartphones and tablets for payment acceptance, often with an external Secure Card Reader. Software-based PIN Entry on COTS (SPoC) covers solutions where PIN entry occurs on the touchscreen of a COTS device, while Contactless Payments on COTS (CPoC) focuses on solutions that enable contactless payment acceptance using a COTS device with embedded NFC. Each standard details controls for application security (e.g., preventing tampering, ensuring secure coding), device security (e.g., monitoring for jailbreaking/rooting), data protection, and transaction processing specific to the mobile context.
- Rigorous Card Data Protection Standards: A fundamental tenet of PCI DSS, which extends to its mobile guidelines, is the unwavering protection of cardholder data. This primarily involves never storing Sensitive Authentication Data (SAD) – such as full magnetic stripe data, CVV2, or PIN data – after authorization. Furthermore, if the Primary Account Number (PAN) must be stored, it must be rendered unreadable (e.g., through strong, industry-accepted encryption). When displaying PANs, only the first six and last four digits can be shown; the middle digits must be masked. These measures drastically reduce the value of any data compromised in a breach.
- Secure Transmission Protocols: The journey of cardholder data from the mobile app to the payment processor is a critical vulnerability point. Therefore, all transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks (like the internet or cellular networks) must be encrypted using strong cryptography and robust security protocols. Transport Layer Security (TLS), specifically version 1.2 or higher, is mandated to protect data in transit from eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks, and data interception.
- Point-to-Point Encryption (P2PE) Requirements: For many mobile payment solutions that utilize external card reading hardware, P2PE is a highly effective security measure that is often mandated or strongly recommended. PCI-validated P2PE solutions encrypt card data at the precise point of interaction (i.e., within the secure card reader itself) before it ever reaches the mobile application or device. This encrypted data can only be decrypted by a secure Hardware Security Module (HSM) in the payment processor’s trusted environment. The significant advantage here is that it devalues the data for attackers and dramatically reduces the PCI DSS compliance scope for the merchant’s application and mobile device, as they never handle clear-text cardholder data.
- Regular Security Testing and Monitoring Mandates: Security is not a one-time setup; it’s an ongoing process. The guidelines mandate continuous vigilance through regular security testing. This includes quarterly external vulnerability scans by an Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV), annual (or post-significant change) penetration testing, application code reviews, and continuous monitoring of security controls. This proactive approach to identifying and remediating vulnerabilities is a cornerstone of effective app security standards and helps organizations stay ahead of evolving threats.
The PCI Mobile Payment Acceptance Security Guidelines unequivocally deserve their place in any discussion of critical app security standards because mobile payments are a high-value target for cybercriminals. Adherence to these guidelines is not just about compliance; it’s about fundamental risk management. By implementing these standards, developers and organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of data breaches, which can lead to severe financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. The guidelines provide a clear, globally recognized benchmark for securing mobile payment channels, ensuring a consistent level of security across the industry. For any application venturing into the realm of mobile payments, these standards are non-negotiable.
While indispensable, navigating PCI compliance for mobile applications comes with its own set of considerations:
Pros:
- Industry-Mandated Standard: Provides a clear, authoritative framework for securing payment processing, recognized and enforced by major card brands.
- Clear Compliance Requirements: The PCI SSC offers detailed documentation and guidance, outlining specific controls and validation procedures.
- Regular Updates Addressing New Threats: The standards are periodically updated to address emerging threats and evolving technologies in the mobile payment landscape.
- Wide Industry Acceptance: Adherence is expected by payment processors, acquirers, and card brands, facilitating interoperability and trust.
- Detailed Implementation Guidance: Alongside the core standards, the PCI SSC publishes supporting documents, FAQs, and glossaries to aid in implementation.
Cons:
- Complex Compliance Requirements: Achieving and maintaining compliance can be a complex and resource-intensive undertaking, especially for smaller organizations or those new to PCI DSS.
- Expensive Implementation and Maintenance: Costs can include specialized hardware (like P2PE-validated devices), software, security assessments, and dedicated personnel.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to comply can result in significant fines, increased transaction fees, or even revocation of the ability to accept card payments.
- Limited to Payment-Related Applications: While critically important for payment apps, these specific guidelines do not cover all aspects of general mobile application security beyond the payment transaction itself.
The impact and successful adoption of PCI Mobile Payment Acceptance Security Guidelines can be seen in various widely used solutions:
- Square Mobile Payment Readers: Solutions like Square’s card readers are designed to meet PCI standards, often incorporating P2PE to ensure that sensitive card data is encrypted immediately upon swipe, dip, or tap.
- Apple Pay and Google Pay: These mobile wallets leverage tokenization, a key PCI recommendation. Instead of transmitting the actual PAN, a unique device-specific token is used for transactions.
- Banking Mobile Apps with Integrated Payment Features: Banks developing mobile apps that allow customers to make payments must ensure these features comply with relevant PCI requirements, protecting card data.
For developers and organizations aiming to navigate PCI compliance for their mobile applications, here are some actionable tips:
- Implement Tokenization: Utilize tokenization services to replace sensitive card data with a unique token, significantly reducing your PCI DSS scope.
- Use Certified Payment Processors and P2PE Solutions: Partner with PCI-validated payment processors and use certified P2PE solutions to offload compliance burdens.
- Regular Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing: Conduct frequent security tests to proactively identify and fix weaknesses.
- Maintain Detailed Documentation for Audits: Keep meticulous records of security controls, policies, and procedures for PCI assessments.
- Stay Updated on PCI Standards: Regularly review updates from the PCI SSC. Learn more about PCI Mobile Payment Acceptance Security Guidelines and related encryption best practices to bolster your security posture.
The PCI Mobile Payment Acceptance Security Guidelines are mandatory for any entity developing or using mobile applications to accept payment cards from major brands like Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover, and JCB. If your mobile app handles cardholder data, these guidelines apply.
These crucial app security standards have been established and are continuously promoted by the PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC). Their adoption and enforcement are driven by the major payment card brands (Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover, JCB), and further supported by payment processors and acquirers who require compliance from their clients.
6. SANS Mobile Application Security Guidelines
In the dynamic landscape of mobile application development, establishing robust app security standards is paramount. While formal standards provide a necessary framework, the practical application of security principles often requires a more hands-on, continuously evolving approach. This is where the SANS (SysAdmin, Audit, Network, and Security) Institute’s Mobile Application Security Guidelines come into play, offering a vital resource for organizations and individuals seeking to build and maintain secure mobile applications.
The SANS Institute is a globally recognized leader in cybersecurity training and certification. Its Mobile Application Security Guidelines are not a singular, static document but rather a comprehensive ecosystem of training courses, research publications, certifications, and best practice documentation. This approach focuses on the practical implementation of security controls throughout the entire mobile application development lifecycle, from initial design to post-deployment maintenance. The core philosophy is to empower developers, security professionals, and even product managers with the actionable knowledge needed to defend against real-world mobile threats.
How SANS Mobile Application Security Guidelines Work
SANS’s methodology is deeply rooted in practicality and experiential learning. Instead of merely prescribing rules, it emphasizes understanding the “why” and “how” behind mobile vulnerabilities and defenses. This is achieved through:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: SANS offers a range of intensive, hands-on courses specifically targeting mobile security, such as SEC575: Mobile Device Security and Ethical Hacking. These courses immerse participants in real-world attack scenarios, teaching them to think like an attacker to better defend mobile applications. For React Native developers, this means understanding platform-specific vulnerabilities (iOS and Android) and common pitfalls in cross-platform development. DevOps engineers learn to embed security into automated pipelines, and QA teams gain skills to perform more than just functional testing.
- Cutting-Edge Research and Best Practices: The SANS Institute continually publishes research, whitepapers, security cheat sheets, and blog posts that reflect the latest mobile threat landscape and defensive strategies. This ensures that the guidance remains current and relevant, a critical factor in the fast-evolving mobile ecosystem.
- Hands-On Security Testing and Vulnerability Management: A significant emphasis is placed on practical security testing. SANS teaches methodologies for mobile application penetration testing, reverse engineering, static and dynamic analysis, and identifying vulnerabilities in areas like data storage, network communication, and authentication mechanisms. This empowers teams to proactively uncover and remediate weaknesses.
- Development Lifecycle Integration (DevSecOps): SANS champions the integration of security into every phase of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). This aligns perfectly with DevSecOps principles, encouraging developers (including those using React Native) to write secure code from the start, QA teams to incorporate security testing early, and operations teams to maintain secure configurations.
- Incident Response Procedures: Understanding that breaches can still occur, SANS provides guidance and training on developing and implementing effective incident response plans specifically tailored for mobile security incidents. This helps organizations minimize damage and recover quickly.
Why SANS Deserves its Place in App Security Standards
While SANS guidelines may not be a formal, certifiable standard like ISO 27001, they are an indispensable component of a comprehensive app security standards strategy. Their strength lies in:
- Operationalizing Formal Standards: SANS provides the critical “how-to” for implementing the principles outlined in more formal standards. It bridges the gap between theoretical requirements and practical execution.
- Industry-Wide Influence: The knowledge and skills imparted by SANS are highly respected and have shaped the practices of countless security professionals and organizations globally. SANS-trained individuals often become key drivers of security within their teams.
- Adaptability: The mobile threat landscape changes rapidly. SANS’s commitment to continuous updates ensures that its guidance remains at the forefront of mobile security, making it an essential resource for maintaining relevant app security standards.
- Skill Development: Ultimately, security relies on skilled individuals. SANS focuses on building deep, practical expertise that enables teams to effectively secure mobile applications, a crucial element that complements documented standards.
Features and Benefits
The SANS approach offers distinct advantages:
- Practical, Hands-on Guidance: Training involves extensive lab work using real tools and techniques, ensuring participants can immediately apply what they’ve learned.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Courses cover a wide spectrum of mobile security topics, from secure coding and testing to forensics and incident response.
- Real-World Attack Scenarios and Defenses: Learning is based on actual attack vectors and proven defensive measures, making the knowledge directly applicable.
- Development Lifecycle Integration: Promotes a “security-by-design” culture, reducing vulnerabilities and the cost of remediation later in the development cycle.
- Incident Response Procedures: Equips teams to handle security incidents effectively, minimizing impact.
- Benefit: The overarching benefit is the development of more resilient mobile applications, a significant reduction in security risks, and highly skilled, confident security and development teams. For product managers, this translates to increased user trust and protection of brand reputation.
Pros:
- Highly practical and actionable guidance: Focuses on real-world skills and immediate applicability.
- Regular updates based on current threats: Curriculum and resources stay relevant to the evolving threat landscape.
- Strong training and certification programs: GIAC certifications (like GMOB - GIAC Mobile Device Security Analyst) are industry-recognized and validate expertise.
- Industry-respected expertise: SANS is a trusted name in cybersecurity education and research.
- Focus on real-world implementation: Emphasizes doing security, not just talking about it.
Cons:
- Training and certification costs: SANS courses and certifications represent a significant financial investment.
- May require significant security expertise for advanced topics: While foundational courses exist, some advanced mobile security topics assume a baseline understanding of security concepts.
- Less formal than other standards: It’s a framework for building expertise and implementing practices rather than a compliance checklist.
Examples of Successful Implementation
- Enhanced Security Teams: Organizations regularly send their developers, QA testers, and security analysts to SANS mobile security courses. These individuals return with advanced skills to secure mobile app code (e.g., in React Native projects), conduct thorough penetration tests, and better assess third-party library risks.
- Robust Penetration Testing: Penetration testing teams adopt SANS methodologies (like those taught in SEC575) to conduct comprehensive assessments of mobile applications, identifying vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss.
- Effective Incident Response: Enterprise security teams leverage SANS incident handling frameworks to develop and drill mobile-specific incident response plans, ensuring they are prepared to tackle breaches involving mobile devices and applications. For instance, a financial institution might refine its mobile banking app’s incident response based on SANS guidelines after a training exercise.
When and Why to Use SANS Mobile Application Security Guidelines
Consider leveraging SANS resources when your organization:
- Needs to elevate the practical mobile security skills of its development, QA, DevOps, or security teams.
- Aims to establish or enhance a robust mobile application penetration testing program.
- Is committed to integrating security throughout the mobile app SDLC (adopting DevSecOps).
- Needs to ensure its app security standards are not just documented but actively and effectively implemented by knowledgeable personnel.
- Wants to build a proactive defense against emerging and sophisticated mobile threats.
- Is developing or refining its mobile security incident response capabilities.
The “why” is clear: SANS empowers your teams with the practical knowledge and skills to build, test, and maintain secure mobile applications, directly supporting and enhancing your overall app security standards.
Actionable Tips for Readers
- Start with Foundational Knowledge: If new to security, consider SANS’s foundational courses before diving into advanced mobile topics.
- Combine Training with Hands-on Practice: Encourage teams to apply learned SANS techniques in internal projects, capture-the-flag (CTF) exercises, or SANS’s own NetWars tournaments to solidify skills.
- Focus on Continuous Learning: The mobile threat landscape is ever-changing. Leverage SANS webcasts, whitepapers, and summits to stay updated. Encourage GIAC certification renewal as a means of demonstrating ongoing competence.
- Implement Security Testing Early and Often: Use SANS methodologies to guide security testing activities from the design phase through to post-release for your mobile apps, including those built with React Native.
- Build Security into Development Processes: For React Native developers and DevOps engineers, integrate secure coding principles and automated security checks (inspired by SANS teachings) into your CI/CD pipelines.
- For Product Managers: Utilize SANS’s research on mobile threats to inform risk assessments and prioritize security features in your product roadmap.
By investing in the knowledge and practices promoted by the SANS Institute, organizations can significantly strengthen their mobile application security posture, ensuring their app security standards translate into tangible, real-world protection.
For more information on SANS mobile security training and resources, visit: https://www.sans.org/cyber-security-courses/?focus-area=mobile-security
7. Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Mobile Security Guidelines
In an era where mobile applications are increasingly intertwined with powerful cloud backends, ensuring robust security across this distributed architecture is paramount. The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Mobile Security Guidelines emerge as a critical resource and a significant component of modern app security standards. These guidelines offer a comprehensive framework specifically designed to address the unique security challenges posed by the integration of mobile applications with cloud services. They move beyond traditional, siloed security approaches by providing a holistic view of the mobile-cloud ecosystem.

The CSA’s framework works by dissecting the complex interactions between mobile endpoints and cloud platforms. It identifies potential vulnerabilities and provides best practices for securing data in transit and at rest, managing identities and access, safeguarding APIs, and ensuring secure data synchronization. This guidance is crucial for developers, DevOps engineers, and security teams building or managing applications that, for example, store user data in the cloud, leverage cloud-based authentication, or use cloud services for processing and analytics. The guidelines are a product of an industry-driven, collaborative effort, meaning they are shaped by experts from various sectors, including major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, as well as enterprise cloud adoption leaders. This collaborative nature ensures the guidelines remain relevant and practical in the face of rapidly evolving cloud technologies.
Key Features and Benefits:
The CSA Mobile Security Guidelines stand out due to their specific focus and comprehensive nature:
- Cloud-Mobile Integration Security Focus: This is the cornerstone of the CSA guidelines. They specifically tackle the nuanced security implications that arise when mobile apps communicate with and rely on cloud services, a common pattern in today’s app development.
- API Security Best Practices: APIs are the lifelines between mobile apps and cloud backends. The CSA provides detailed recommendations for securing these critical interfaces, covering aspects like authentication (e.g., OAuth 2.0), authorization, input validation, rate limiting, and secure communication protocols (TLS).
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Guidelines: Proper IAM is vital. The guidelines emphasize principles like least privilege, strong multi-factor authentication (MFA), secure credential storage, and federated identity management to ensure only authorized users and services can access resources.
- Data Protection in Cloud-Mobile Scenarios: The framework addresses data security comprehensively – protecting data while it’s being transmitted between the mobile device and the cloud, while it’s stored on the mobile device, and while it resides in cloud storage. This includes guidance on encryption, tokenization, and data classification.
- Multi-tenant Security Considerations: Many cloud services operate on a multi-tenant model. The CSA guidelines help organizations understand and mitigate the risks associated with shared environments, ensuring data isolation and preventing cross-tenant vulnerabilities.
- Regular Updates and Practical Guidance: The cloud landscape is dynamic. The CSA consistently updates its guidance to reflect new threats, technologies, and best practices, offering practical and actionable advice that can be implemented by development and security teams.
- Focus on Emerging Technologies: The guidelines are forward-looking, often incorporating considerations for emerging technologies like IoT and serverless architectures as they intersect with mobile and cloud.
Why CSA Mobile Security Guidelines Deserve a Place in App Security Standards:
These guidelines are indispensable in the current technological landscape. As more applications adopt a hybrid architecture—mobile frontends powered by cloud backends—a specialized set of app security standards that specifically addresses this convergence is essential. Traditional mobile security standards might not adequately cover the cloud backend vulnerabilities, and traditional cloud security standards might overlook mobile-specific risks. The CSA Mobile Security Guidelines bridge this gap, providing a unified approach. Their industry-backed, collaborative development also lends them significant credibility and relevance, making them a trusted resource for organizations aiming to build secure and resilient mobile-cloud solutions.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Enterprise Mobile Apps using Office 365 or Google Workspace: Companies developing mobile apps that integrate with these productivity suites rely on CSA principles to secure API calls for accessing emails, documents, and calendars, ensuring proper authentication and data synchronization protection.
- Mobile Banking Apps with Cloud Backend Services: Financial institutions leverage CSA guidance to secure transactions, protect sensitive customer data stored and processed in the cloud, and implement robust IAM for mobile users accessing cloud-hosted banking services.
- IoT Mobile Applications with Cloud Data Processing: For mobile apps controlling IoT devices and sending data to the cloud for analysis, CSA guidelines help secure the device-to-cloud communication channels, protect large volumes of telemetry data, and manage device identities.
Actionable Tips for Readers:
When applying the CSA Mobile Security Guidelines, consider the following:
- Prioritize API Security and Authentication: Implement strong authentication mechanisms (e.g., OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect) for all APIs. Use API gateways for centralized security policy enforcement, traffic management, and threat protection.
- Implement Proper Data Classification and Protection: Identify and classify data based on sensitivity. Apply appropriate encryption mechanisms for data in transit (TLS) and data at rest (both on the device and in the cloud).
- Leverage Cloud-Native Security Services: Utilize security services offered by your cloud provider, such as AWS IAM, Azure Active Directory, Google Cloud Identity, Key Management Services (KMS), and Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), as they are often optimized for the cloud environment.
- Conduct Regular Security Assessments: Perform thorough security assessments, including penetration testing and code reviews, specifically focusing on the integration points between the mobile app and cloud services.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Organizations should adopt or refer to the CSA Mobile Security Guidelines whenever they are developing or managing mobile applications that interact with cloud services for any significant function—be it data storage, backend logic, authentication, or analytics. This is especially crucial for applications handling sensitive user data, performing critical transactions, or forming part of a larger enterprise ecosystem.
The “why” is compelling: these guidelines help build more secure, resilient, and trustworthy applications. By addressing the specific vulnerabilities inherent in mobile-cloud architectures, organizations can reduce their risk exposure, protect user data, comply with regulatory requirements, and maintain customer confidence. While they can be complex to implement, especially for teams new to cloud security, the comprehensive protection they offer is invaluable for modern applications.
Pros:
- Addresses modern cloud-mobile architectures comprehensively.
- Industry-driven collaborative approach ensures relevance and practicality.
- Regularly updated to reflect the evolving cloud landscape.
- Provides practical implementation guidance for developers and security teams.
- Strong focus on emerging technologies and their security implications.
Cons:
- Being relatively new and constantly evolving means practitioners need to stay updated.
- Effective implementation often requires a good understanding of both mobile and cloud security expertise.
- May seem complex for organizations with very simple, traditional mobile apps that have minimal cloud interaction.
For React Native app developers, DevOps and release engineers, QA teams, security-conscious enterprises, and product managers, understanding and applying these guidelines is a step towards building more robust and secure mobile experiences. To delve deeper into this area, you can Learn more about Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Mobile Security Guidelines and explore the resources available directly from the Cloud Security Alliance.
8. FIDO Alliance Mobile Authentication Standards
In the evolving landscape of mobile application security, moving beyond traditional passwords is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day necessity. The FIDO (Fast IDentity Online) Alliance is at forefront of this shift, developing open authentication standards designed to reduce, and ultimately eliminate, the world’s over-reliance on passwords. For mobile applications, where user experience and robust security must go hand-in-hand, FIDO standards represent a significant leap forward in establishing stronger app security standards.
What are FIDO Standards and How Do They Work?
The FIDO Alliance champions a set of open and interoperable authentication standards—primarily FIDO UAF (Universal Authentication Framework), FIDO U2F (Universal Second Factor), and the more recent FIDO2 (comprising WebAuthn and CTAP). These standards enable passwordless or multi-factor authentication that is both more secure and easier to use than traditional passwords, particularly in mobile environments.
The core principle behind FIDO authentication is public-key cryptography. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Registration: When a user registers with a FIDO-enabled mobile application or service, their device (or a connected FIDO authenticator) creates a new, unique cryptographic key pair. The private key is securely stored on the user’s device (e.g., within a Secure Element, Trusted Platform Module (TPM), or protected by the device’s screen lock like a PIN or biometrics). The public key is sent to the online service and associated with the user’s account. Crucially, the private key never leaves the user’s device.
- Authentication: To log in, the service sends a challenge (a random piece of data) to the user’s device. The FIDO authenticator on the device uses the stored private key to sign this challenge. This step typically requires user verification – a biometric scan (fingerprint, face), a PIN entry on the device, or pressing a button on a hardware key. The signed challenge is then sent back to the service.
- Verification: The service uses the previously registered public key to verify the signature on the challenge. If the signature is valid, authentication is successful.
This mechanism prevents phishing attacks (as credentials are bound to specific origins), replay attacks (due to unique challenges), and server-side credential breaches (as servers only store public keys, not shared secrets like passwords).
The key FIDO specifications relevant to mobile are:
- FIDO UAF (Universal Authentication Framework): Designed for passwordless experiences. It allows users to register their device’s local authenticators (like fingerprint sensors or facial recognition) with an online service. Subsequent logins are as simple as a biometric scan.
- FIDO U2F (Universal Second Factor): Focuses on providing a strong second factor of authentication, typically using hardware security keys (e.g., YubiKey) that connect via USB, NFC, or Bluetooth.
- FIDO2 (WebAuthn and CTAP): This is the latest generation and arguably the most impactful.
- WebAuthn (Web Authentication): A W3C standard API that allows web applications to utilize FIDO authentication directly in browsers. This is highly relevant for Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and hybrid mobile apps using web views.
- CTAP (Client to Authenticator Protocol): Enables external authenticators (like hardware keys or even other mobile devices) to communicate with the user’s device (e.g., a laptop or desktop) over USB, NFC, or Bluetooth to perform FIDO authentication.
Why FIDO Standards are Crucial App Security Standards
FIDO standards directly address the most pervasive vulnerabilities in the digital world: those stemming from passwords. Weak, reused, and stolen passwords are the leading cause of data breaches. By offering a path to passwordless authentication or significantly stronger multi-factor authentication, FIDO implementations elevate app security standards by:
- Mitigating Phishing: FIDO credentials are scoped to specific domains, making them inherently resistant to phishing attacks.
- Preventing Credential Stuffing: Since unique cryptographic keys are used per service, stolen credentials from one breach cannot be used elsewhere.
- Protecting Against Server Breaches: Servers store public keys, which are not sensitive, rather than password hashes or shared secrets.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Passwordless Authentication Protocols: Offers the option to completely remove passwords from the user flow for supported services.
- Biometric Authentication Support: Seamlessly integrates with on-device biometrics (fingerprint, face, iris) for user-friendly and secure authentication on mobile.
- Hardware-based Security Key Integration: Supports the use of phishing-resistant hardware security keys for the highest level of assurance.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: FIDO2 and WebAuthn are increasingly supported across major operating systems (Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, Linux) and browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari).
- Privacy-Preserving Authentication Methods: Biometric data never leaves the user’s device. FIDO is designed to prevent tracking of users across different services, as key pairs are unique per service.
Pros:
- Eliminates password-related vulnerabilities: Drastically reduces risks from phishing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and credential database breaches.
- Improved user experience: Faster and more convenient login processes compared to typing complex passwords, especially on mobile devices.
- Strong cryptographic security: Leverages proven public-key cryptography for robust protection.
- Industry-wide adoption and support: Backed by major tech companies (Google, Microsoft, Apple) and increasingly adopted by financial institutions and enterprises. This widespread support ensures longevity and interoperability.
- Privacy-focused design: Biometric templates are processed locally and never transmitted. No linkable identifiers are shared between services.
Cons:
- Requires compatible hardware/software: While support is growing rapidly, older devices or browsers might lack FIDO capabilities.
- Implementation complexity: Integrating FIDO, especially the server-side components, can be more complex than traditional password systems, though SDKs and platform support are easing this.
- User education and adoption challenges: Users accustomed to passwords may need education on how FIDO works and its benefits to encourage adoption.
- Backup authentication method still needed: Users need a way to recover access if they lose their device or FIDO authenticator (e.g., recovery codes, alternative registered devices).
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Google: Android has robust FIDO2 support, allowing users to authenticate to websites and apps using their device’s screen lock or fingerprint sensor. Google accounts themselves support FIDO security keys.
- Microsoft: Windows Hello for Business utilizes FIDO2 principles for passwordless sign-in to Windows devices and Azure AD services.
- Apple: iOS and macOS support FIDO authentication, including “Passkeys,” which are FIDO credentials that can sync across a user’s devices via iCloud Keychain.
- Banking Apps: Many banking and financial apps leverage on-device biometrics, often aligning with FIDO UAF principles, for secure and quick access.
- Enterprise Applications: Companies are deploying FIDO security keys to protect access to sensitive internal systems and cloud services.
When and Why to Use FIDO Standards:
Mobile app developers, DevOps teams, and product managers should consider FIDO standards when:
- Handling sensitive user data: Essential for financial, healthcare, e-commerce, and enterprise applications.
- Seeking to improve user experience: To reduce login friction and password fatigue.
- Aiming for top-tier phishing resistance: Particularly important for services targeted by sophisticated attacks.
- Modernizing authentication infrastructure: To align with current and future app security standards and move away from legacy password-based systems.
- Targeting security-conscious users and enterprises: Demonstrates a commitment to robust security practices.
Implementing FIDO is a proactive step towards building more secure, user-friendly mobile applications that meet the high expectations of modern app security standards.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Start with Platform Authenticators: Leverage built-in platform capabilities first (e.g., Android’s
BiometricPromptwith FIDO2 APIs, iOS’s support for Passkeys). This often provides the easiest path to passwordless login for many users. - Educate Your Users: Clearly explain the benefits of FIDO authentication (security, convenience) and provide simple instructions on how to set it up and use it.
- Provide Robust Fallback and Recovery Options: Users may lose devices or authenticators. Ensure secure account recovery mechanisms are in place (e.g., recovery codes, verified email/phone recovery, or alternative FIDO authenticators).
- Thoroughly Test Across Devices and Platforms: Given the diversity of mobile hardware and OS versions, comprehensive testing is crucial to ensure a consistent and reliable experience. QA teams should focus on different biometric sensor types, OS versions, and form factors.
- Evaluate Server-Side Requirements: FIDO relies on server-side logic to manage public keys, store registration data, and validate authentication assertions. DevOps and backend teams need to plan for these infrastructure changes. Consider using FIDO-certified servers or libraries.
- Explore Passkeys: For consumer-facing applications, “Passkeys” (FIDO credentials that can sync across a user’s devices) offer a highly user-friendly approach to passwordless. Investigate platform support for Passkeys.
- For React Native Developers: Look into native modules or community packages that bridge to native FIDO APIs. For web-centric parts of your app, WebAuthn can be used within web views.
By embracing FIDO standards, organizations can significantly enhance their mobile application security posture, reduce fraud, and provide a superior user experience, solidifying their commitment to cutting-edge app security standards.
For more detailed information and technical specifications, visit the FIDO Alliance website.
8 Key App Security Standards Comparison
| Standard | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OWASP MASVS | Moderate to High; requires security expertise | Medium to High; depends on security level (L1-L3) | Measurable mobile app security levels aligned with OWASP risks | Banking, Healthcare, Government apps needing strong mobile security | Widely recognized, free, comprehensive coverage |
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework | High; extensive governance and process-driven | High; suited for enterprise and organizational scale | Robust risk management and incident response | Federal agencies, large enterprises, healthcare orgs | Flexible, government-backed, strong compliance focus |
| ISO/IEC 27001 Mobile Security Controls | High; complex ISMS integration | High; certification and audit resources | Internationally certified mobile security management | Telecom, finance, cloud service providers | Globally recognized, builds trust, audit focus |
| Common Criteria (CC) for Mobile Applications | Very High; lengthy and costly certification process | Very High; requires third-party evaluation labs | High-assurance security certification | Government, military, high-security mobile applications | Rigorous, internationally recognized, strong assurance |
| PCI Mobile Payment Acceptance Guidelines | High; strict compliance and security requirements | High; specialized for payment processing apps | Secure payment apps meeting card data protection mandates | Mobile payment apps and POS systems | Industry-mandated, clear payment security standards |
| SANS Mobile Application Security Guidelines | Moderate; practical and hands-on approach | Medium; training and expertise required | Enhanced security testing and vulnerability management | Security teams, penetration testers, developers | Practical, up-to-date, strong training programs |
| CSA Mobile Security Guidelines | Moderate to High; cloud and mobile integration focus | Medium to High; cloud security expertise needed | Secured mobile-cloud applications and APIs | Cloud-backed mobile apps, IoT, enterprise cloud usage | Addresses modern cloud-mobile challenges, collaborative |
| FIDO Alliance Mobile Authentication Standards | Moderate; requires hardware/software compatibility | Medium; hardware/software integration efforts | Strong passwordless, biometric mobile authentication | Mobile apps needing strong authentication, enterprises | Eliminates password risks, privacy-focused, widely adopted |
Building a Secure Future: Implementing These Standards
Adopting the diverse array of app security standards we’ve explored in this article is not just a recommendation—it’s a foundational pillar for building resilient, trustworthy, and successful mobile applications. From the comprehensive guidelines of OWASP MASVS and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework for Mobile Devices, to specific controls in ISO/IEC 27001 and PCI Mobile Payment Acceptance Security Guidelines, and specialized insights from SANS, the Cloud Security Alliance, and the FIDO Alliance, each standard offers invaluable frameworks for fortifying your app against evolving threats.
The crucial takeaway is that robust app security isn’t achieved by a single silver bullet, but through a committed, ongoing effort to integrate these established app security standards into every phase of your development lifecycle. It’s about cultivating a proactive security culture within your teams, from React Native developers and DevOps engineers to QA testers and product managers. This commitment ensures you’re not just meeting compliance checkboxes, but genuinely safeguarding user data and maintaining application integrity.
Here are actionable next steps to consider:
- Assess and Prioritize: Evaluate which of the discussed standards (OWASP MASVS, NIST, ISO/IEC 27001, Common Criteria, PCI Mobile, SANS, CSA, FIDO) are most pertinent to your application’s functionality, data sensitivity, and regulatory environment.
- Integrate into SDLC: Embed security considerations and relevant standard checks directly into your software development lifecycle (SDLC), from design and coding to testing and deployment.
- Educate and Train: Ensure your development, QA, and DevOps teams are knowledgeable about these app security standards and best practices.
- Regular Audits & Updates: Implement a schedule for regular security audits, penetration testing, and, crucially, timely patching of identified vulnerabilities.
Mastering and consistently applying these concepts is immensely valuable. It directly translates into protecting your users’ sensitive information, significantly reducing the risk of costly data breaches, and enhancing your application’s reputation and reliability. In an increasingly security-conscious world, demonstrating a steadfast commitment to these principles not only builds crucial user trust but also provides a competitive advantage for enterprise organizations.
While the landscape of mobile security can seem complex, embracing these standards proactively paves the way for innovation with confidence. By continuously applying these frameworks, you ensure your applications are not only functional and engaging but also fundamentally secure, contributing to a safer digital ecosystem for everyone.
Maintaining these high app security standards in an agile development environment requires the ability to respond swiftly to new vulnerabilities. For React Native developers, DevOps teams, and release engineers looking to streamline the delivery of critical security patches and updates directly to users, explore how CodePushGo can significantly aid in this continuous security effort. CodePushGo facilitates rapid hot-fixes and real-time updates, helping you uphold your commitment to security and maintain the integrity of your app security standards without compromising development velocity.




