Demystifying CI/CD: Core Concepts That Drive Modern DevOps
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) are essential practices in modern software development. These interconnected processes automate the steps involved in building, testing, and deploying software, creating a streamlined workflow known as a CI/CD pipeline. This pipeline acts as a digital assembly line, transforming code from its initial commit to production-ready software.
Continuous Integration: Building a Solid Foundation
Continuous Integration (CI) focuses on integrating code changes frequently into a shared repository. This practice encourages developers to commit code multiple times a day, rather than waiting for large, infrequent merges. Think of it like building a house. With CI, each developer adds their piece (code) to the house (repository) regularly, checking that everything fits together seamlessly.
This frequent integration relies on automated build processes and testing. Every time a developer commits code, the CI system automatically builds the software and runs a suite of tests. This ensures that new code doesn’t introduce errors or break existing functionality.
Continuous Delivery: Preparing for Launch
Continuous Delivery (CD) begins where CI ends. Once the code has been integrated and tested, CD automates the process of preparing the software for release. This might involve packaging the application, deploying it to a staging environment, and running further tests. It’s like our house construction team ensuring all inspections are passed and the house is ready for the new owners.
With Continuous Delivery, a release-ready version of the software is always available, allowing teams to deploy updates quickly and efficiently.
Continuous Deployment: Automating the Final Mile
Continuous Deployment automates the final step by automatically deploying code changes to production after they pass all tests. This removes the need for manual deployments, further accelerating the release cycle. Returning to our house analogy, this is like the construction team handing over the keys and the new owners moving in – automatically.
This high level of automation requires robust testing and monitoring to ensure that any issues are identified and addressed quickly. The adoption of CI/CD pipelines has significantly changed the software development process, enabling faster and more reliable release cycles. This shift towards CI/CD is driven by the need for agility and speed in software delivery, a critical competitive advantage for businesses.
By automating testing and deployment, companies can reduce development risks and costs while increasing the value of each software release. For example, high-performing teams using CI/CD can ship updates three times faster than lower-performing teams. This translates into significant savings and allows for strategic resource allocation. Learn more about CI/CD trends here: CI/CD Pipeline Trends. For real-world examples, see these success stories.
You might also be interested in: How to master…
Building Your First Pipeline: From Zero to Continuous Integration

Now that we understand the core concepts of CI/CD, let’s explore how to build your first pipeline. This section provides a practical guide to creating a CI/CD environment that adapts and grows alongside your project, empowering you to build a robust and efficient development workflow.
Choosing the Right Tools for the Job
Selecting the right CI/CD tool is paramount. Several platforms offer diverse features and capabilities. A careful evaluation of these tools, based on your project’s specific requirements, is crucial for pipeline success. Consider these popular options: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and CircleCI.
-
Jenkins: This open-source automation server offers a high degree of flexibility and a vast plugin ecosystem. Jenkins is powerful for complex projects, but it does have a steeper learning curve.
-
GitHub Actions: Tightly integrated with GitHub repositories, GitHub Actions offers a streamlined workflow. Its simplicity makes it ideal for smaller teams and projects.
-
GitLab CI: Integrated within GitLab, this CI/CD tool simplifies setup and configuration for projects already using the GitLab ecosystem. It boasts robust features, including a built-in container registry and Kubernetes integration.
-
CircleCI: This cloud-based CI/CD platform offers fast build times and easy scalability. CircleCI is a popular choice for projects demanding rapid iteration and frequent deployments.
For a comprehensive understanding of building effective pipelines, review these CI/CD pipeline best practices.
From Cloud-Based Simplicity to Self-Hosted Control
A key decision involves choosing between cloud-based and self-hosted CI/CD solutions. Cloud-based platforms provide convenience and rapid setup, freeing you to focus on building your pipeline. Self-hosting, however, offers greater control and can be more cost-effective for larger teams with specific security or compliance needs.
The best choice depends on project size, team structure, and organizational policies. A small startup might prioritize the speed of a cloud-based solution, while a large enterprise might choose the control of a self-hosted setup.
Integrating with Your Version Control Workflow
Integrating with your version control system (VCS) is essential for a smooth CI/CD workflow. Most CI/CD tools integrate with popular VCS platforms like Git. Connecting your repository allows for automated triggers, ensuring every code commit initiates the pipeline. This automation is fundamental to continuous integration.
For example, with each code push, the pipeline can automatically build the application, run tests, and deploy to a staging environment. This automatic validation catches errors early and ensures code stability. Read also: How to master…
Scaling Your Pipeline for Growth
Building a scalable CI/CD pipeline is crucial for long-term success. As your team and project grow, your pipeline must adapt. Consider parallel testing, caching mechanisms, and infrastructure automation to handle increasing demands.
This proactive approach prevents bottlenecks and maintains efficiency as the project evolves. Your team can continue delivering value quickly and reliably, even as the project expands. Proper scaling also improves pipeline performance, reducing build times and accelerating the feedback loop.
Core Pipeline Components: Building Blocks of Reliable Delivery
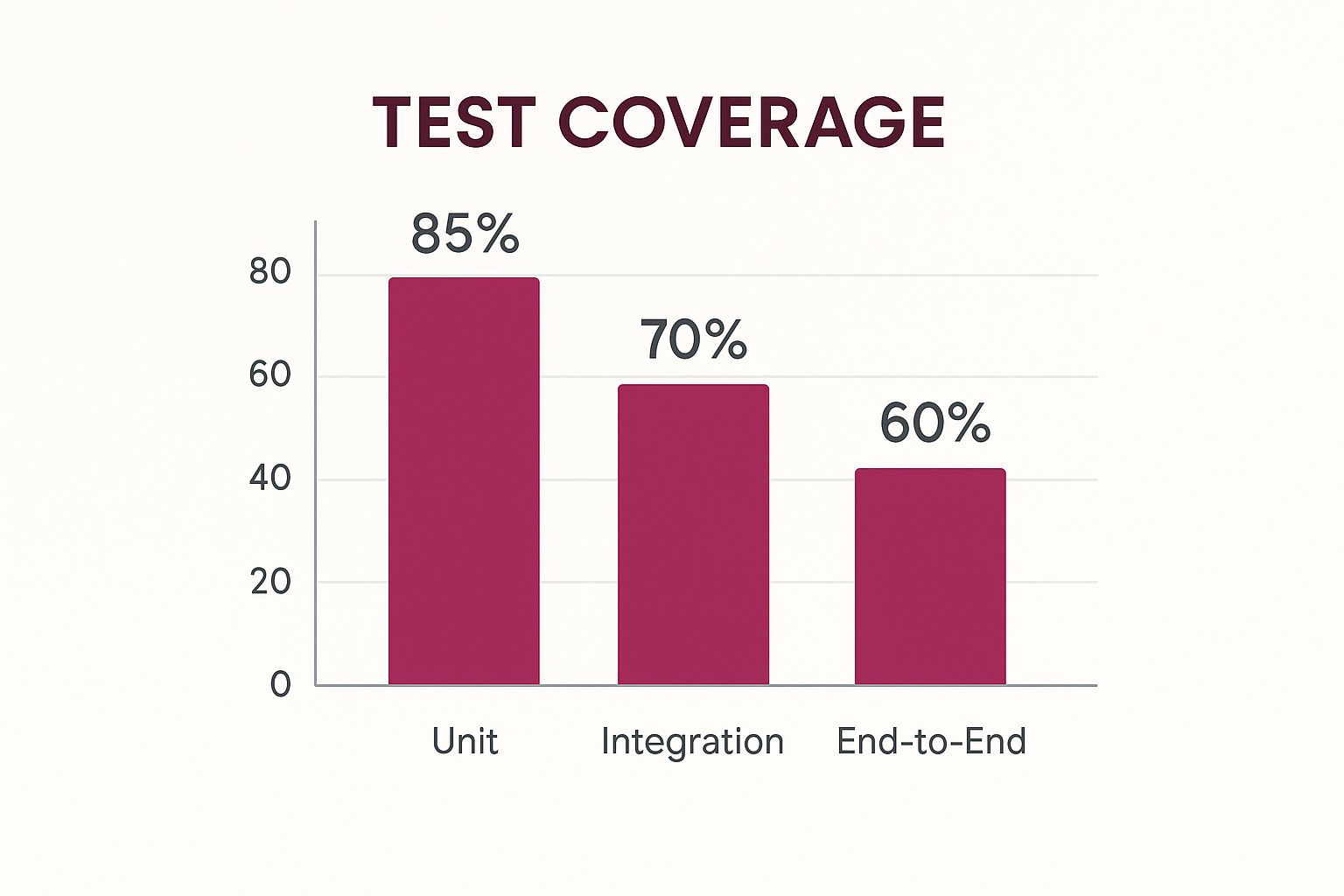
The infographic above visualizes typical test coverage at different CI/CD pipeline stages. It shows coverage for Unit, Integration, and End-to-End tests. Unit tests often have the highest coverage, followed by integration tests, then end-to-end tests. This emphasizes a balanced testing strategy, with strong unit tests and progressively broader integration and end-to-end test coverage. A well-structured CI/CD pipeline comprises key components that automate and streamline software delivery. These components work together to ensure code changes are integrated, tested, and deployed reliably and efficiently.
Source Control Integration: The Foundation of Traceability
A CI/CD pipeline begins with source control integration. This connects the pipeline to your Version Control System (VCS), like Git. This integration lets the pipeline automatically detect and respond to code changes, triggering subsequent stages. It also provides complete traceability, tracking every change from commit to deployment. This is invaluable for debugging, auditing, and understanding your application’s history.
Automated Builds: Preventing Integration Headaches
The pipeline initiates an automated build process when a code change is detected. This compiles the code, runs linters and formatters, and packages the application into a deployable artifact. Automating builds ensures consistent build environments and catches compilation errors early, preventing integration issues. It also frees developers from manual tasks, allowing them to focus on coding.
Dependency Management: Eliminating the “Works on My Machine” Problem
Effective dependency management is crucial for reproducible builds. A CI/CD pipeline should automatically resolve and install project dependencies. This ensures consistency across environments and eliminates the “works on my machine” problem, where code behaves differently due to local environment variations. Using tools like package managers (npm, pip, etc.) within the pipeline guarantees consistent library and framework versions.
Comprehensive Testing Suites: Catching Issues Early
Robust CI/CD pipelines incorporate various automated tests. These include unit tests (verifying individual components), integration tests (testing interactions between modules), and end-to-end tests (validating the entire application flow). These tests act as a safety net, catching issues before they reach production.
Automated Quality Gates: Maintaining Code Standards
Automated quality gates enforce coding standards and best practices. Tools like static analyzers and code formatters, integrated into the pipeline, check for code quality and ensure consistent style. This maintains code quality without manual reviews and prevents code with known vulnerabilities from being deployed.
To understand the effectiveness and benefits of incorporating CI/CD tools, let’s look at a comparison of some popular options:
CI/CD Tool Comparison
Comparison of popular CI/CD tools with their key features, pricing, and best use cases.
| Tool | Key Features | Hosting Options | Learning Curve | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | Highly extensible, open-source, large community | Self-hosted, Cloud | Moderate | Versatile, complex pipelines |
| CircleCI | Cloud-native, strong Docker support | Cloud | Easy | Quick setup, containerized applications |
| GitLab CI | Integrated with GitLab, easy configuration | Self-hosted, Cloud | Easy | GitLab users, streamlined workflows |
| GitHub Actions | Tight GitHub integration, growing ecosystem | Cloud | Easy | GitHub users, open-source projects |
This table highlights some key differences between popular CI/CD tools. Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs and project requirements.
The 2025 State of Software Delivery Report by CircleCI showed that top-performing teams using CI/CD automation were five times faster than lower-performing teams. This efficiency gain allows for focusing on strategic initiatives. More details can be found here: CircleCI Report.
Deployment Automation: Delivering Value Faster
Deployment automation is the final CI/CD pipeline stage. This automatically deploys the tested application to various environments (staging, production). This minimizes manual intervention, reduces errors, and enables faster value delivery. Deployment strategies like blue/green deployments and canary releases enhance deployment reliability and safety. Check out our guide on How to master….
Deployment Strategies That Minimize Risk, Maximize Value

Building a CI/CD pipeline is more than just automating steps. It’s about strategically deploying code changes to minimize disruptions and get the most value. This means carefully choosing and implementing deployment strategies that fit your application and user base. Techniques like blue-green deployments, canary releases, and feature toggles are key to this process.
Blue-Green Deployments: Seamless Switching for Zero Downtime
Blue-green deployments use two identical environments: “blue” (live) and “green” (staging). New code goes to the green environment for testing. Once tested, traffic switches from blue to green. This switch is usually fast, minimizing downtime. If problems pop up in green, traffic quickly reverts back to blue. This safety net protects users from faulty deployments.
Canary Releases: Gradual Rollouts for Controlled Testing
Canary releases deploy new code to a small group of users. This real-world test lets you monitor performance and find potential issues before they affect everyone. If the new code works well with this canary group, the rollout gradually expands until all users have the update.
Feature Toggles: Enabling and Disabling Features On-Demand
Feature toggles (also called feature flags) separate deployment from release. You can deploy code with inactive new features until they’re toggled on. This offers a lot of flexibility. You can enable a feature for a specific group for A/B testing or quickly turn off a feature in production if a bug is found, all without redeploying.
Environment Parity: Ensuring Consistent Behavior Across Stages
Environment parity—making your development, staging, and production environments as similar as possible—is critical for successful deployments. This consistency reduces unexpected issues as code moves through the pipeline. Using Infrastructure as Code helps achieve this, ensuring identical environment provisioning.
The continuous delivery market is growing fast, fueled by agile development and the need for quicker releases. This market is expected to hit $12.31 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 23.6%. For more statistics, see this Continuous Delivery Market Report.
Robust Rollbacks and Deployment Monitoring: Essential Safeguards
Minimizing risk also means having robust rollback mechanisms. If a deployment goes wrong, you need a fast, reliable way to go back to the previous stable version. Automated rollbacks, often tied to monitoring systems, can quickly revert changes if metrics show problems. Deployment monitoring offers real-time data on application performance after deployment. This lets you proactively find and fix issues before users report them, ensuring a positive user experience. These strategies make your pipeline more than just automation; they become a business advantage, speeding up value delivery and keeping your system stable.
Securing Your Pipeline: Protection Beyond Production Code

Automating software delivery with a CI/CD pipeline offers incredible efficiency. However, it also presents potential security risks that must be addressed to ensure the integrity and safety of your applications. This section explores how to fortify your pipeline, creating a robust defense for your code, data, and users.
Comprehensive Scanning: Securing the Entire Supply Chain
Modern CI/CD pipelines often incorporate numerous third-party components and dependencies. This creates a complex software supply chain, making it susceptible to malicious code and security flaws. Comprehensive scanning tools are essential for early identification of these vulnerabilities.
This includes scanning your codebase for security issues, analyzing dependencies for known vulnerabilities, and verifying the integrity of container images and infrastructure definitions. Tools like Snyk and Anchore can automate these security checks within your pipeline.
Credential Management and Secrets Protection: Keeping Your Keys Safe
Protecting sensitive information, such as API keys, database credentials, and other secrets, is paramount. Hardcoding these values directly into code or configuration files presents a significant security risk.
A dedicated secrets management solution, like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager, is essential. These tools allow secure storage and management of secrets, granting access only to authorized processes and users within the CI/CD pipeline. This follows the principle of least privilege, minimizing the potential damage from a security breach.
Automating Compliance Validation: Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Many industries operate under strict regulatory requirements for software development and deployment. Automating compliance validation within your CI/CD pipeline ensures consistent adherence to these standards without hindering delivery speed.
This might include automated checks for license compliance, security configuration audits, and vulnerability assessments. Integrating these checks directly into the pipeline allows early identification and resolution of compliance issues, preventing costly delays and potential penalties.
Addressing Emerging Threats to the Software Supply Chain
The software supply chain is an increasingly common target for attacks. Staying informed about emerging threats and best practices for mitigation is critical. Code signing and provenance verification can help ensure the integrity of components moving through your pipeline.
These techniques verify that software artifacts come from trusted sources and haven’t been tampered with, strengthening your pipeline’s security posture.
Practical Security Measures at Each Stage
The following checklist outlines essential security measures for each stage of your CI/CD pipeline:
To illustrate the practical implementation of these security measures, consider the following table:
CI/CD Security Checklist
Essential security measures to implement at each stage of your CI/CD pipeline.
| Pipeline Stage | Security Measures | Implementation Tools | Common Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code Commit | Static code analysis, secret scanning | SonarQube, Snyk | Insecure coding practices, secrets leakage |
| Build | Dependency vulnerability scanning | OWASP Dependency-Check, Snyk | Vulnerable dependencies |
| Test | Security testing (e.g., penetration testing) | OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite | Application vulnerabilities |
| Deploy | Infrastructure security scanning, access control | Checkov, Terraform Cloud | Misconfigurations, unauthorized access |
This table provides a practical guide to implement security measures at each stage, using appropriate tools to mitigate common vulnerabilities. This structured approach helps to build a robust and secure CI/CD pipeline.
By integrating these security practices, your CI/CD pipeline transforms from a potential vulnerability into a powerful defense. This proactive approach protects your code and applications, safeguards your users, and protects your organization’s reputation. Remember, security is not a one-time implementation but a continuous process of improvement and adaptation.
Pipeline Optimization: Achieving Speed Without Sacrificing Quality
A functional CI/CD pipeline is a good starting point, but optimizing it is crucial for high-performance delivery. This section explores techniques to reduce execution times and improve reliability, boosting developer productivity and application quality.
Parallelization: Running Tasks Concurrently
Parallelization dramatically reduces execution time. Think of it like building a car: a single worker takes much longer than a team working on different parts simultaneously. Similarly, running tests in parallel, using tools like Jenkins, significantly shortens the feedback loop and enables faster issue identification.
Caching: Leveraging Stored Information
Caching is another key strategy. Just as a web browser caches websites, a CI/CD pipeline can cache dependencies, build artifacts, and test results. This avoids redundant work, saving valuable time during each run, especially for large and complex projects.
Self-Healing Mechanisms: Automating Problem Resolution
Self-healing mechanisms add resilience by automating recovery from common failures. A self-healing pipeline might restart a failed service, retry a flaky test, or revert to a stable version, minimizing manual intervention and allowing developers to focus on building features.
Performance Monitoring and Identifying Bottlenecks
Understanding pipeline bottlenecks is crucial. Pipeline monitoring tools offer insights into execution times, resource usage, and potential bottlenecks. Analyzing this data allows teams to target optimization efforts for maximum impact. For further insights, read our article about How to master…
Pipelines as Code: Managing Pipelines Like Software
Treating pipelines as code, using formats like YAML or JSON, allows for version control, code reviews, and automated testing of the pipeline itself. This ensures changes are tracked and tested, minimizing errors and enabling iterative enhancement alongside application development.
Optimizing for Specific CI/CD Tools
Different tools have unique optimization strategies. With Jenkins, optimizing Groovy scripts and managing plugins is important. With GitHub Actions, optimizing workflow YAML and leveraging built-in caching are key. With platforms like CircleCI, understanding the pricing model and optimizing resource usage can significantly impact cost and efficiency.
By implementing these optimization techniques, your CI/CD pipeline becomes a sophisticated delivery platform, accelerating developer productivity and enhancing software quality and reliability at every stage. This empowers your team to deliver value faster and with greater confidence.
Real-World Success Stories: Pipeline Transformations That Delivered
Moving from theoretical concepts to practical application, let’s explore how CI/CD pipelines have driven tangible improvements for organizations in various sectors. These real-world examples showcase the transformative potential of pipeline modernization for enhanced delivery and business growth.
Startups Leveraging Automation for Competitive Advantage
Startups frequently face limitations in resources. Early implementation of a CI/CD pipeline enables them to compete effectively with larger, more established companies by optimizing efficiency.
For instance, a small team can leverage a cloud-based CI/CD platform like CircleCI to automate testing and deployment processes. This allows for rapid iteration on new features and swift responses to changing market demands. This speed and agility can be a critical competitive advantage.
Enterprise Organizations Navigating Complex Compliance
Large enterprises often grapple with intricate compliance requirements. CI/CD pipelines can play a vital role in automating compliance checks and ensuring consistent adherence to regulations.
Integrating automated security scanning and policy enforcement within the pipeline can streamline audits and minimize the risks associated with non-compliance. This empowers organizations to maintain security and regulatory compliance without compromising delivery speed.
Measuring and Communicating Business Value
Demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of CI/CD implementation is essential for securing ongoing support and resources. Tracking key metrics provides quantifiable data to showcase the pipeline’s impact.
Some of these important metrics include deployment frequency, lead time for changes, and change failure rate. This data-driven approach helps communicate the value of CI/CD investments to stakeholders and justifies further optimization efforts.
Common Success Patterns and Overcoming Pitfalls
Several key patterns contribute to the successful adoption of CI/CD:
-
Starting small and scaling gradually: Begin with a pilot project to gain practical experience and refine processes before expanding pipeline usage across the organization.
-
Prioritizing automated testing: Robust automated tests are fundamental for maintaining high code quality and identifying issues early in the development cycle.
-
Embracing a culture of continuous improvement: Regularly review and optimize your pipeline based on performance metrics and feedback from development teams.
Even with meticulous planning, teams may still encounter obstacles. Common pitfalls to be aware of include:
-
Lack of clear ownership and responsibility: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities for pipeline management are crucial for success.
-
Insufficient training and support: Providing adequate training ensures teams can effectively utilize the CI/CD system and resolve any issues that may arise.
-
Resistance to change: Addressing concerns and emphasizing the advantages of CI/CD can help overcome resistance from team members accustomed to traditional workflows.
By learning from the experiences of others, organizations can adapt proven strategies and avoid common mistakes, leading to a smoother and more successful CI/CD implementation. These real-world examples offer practical guidance and inspiration, regardless of your current stage in the CI/CD journey.
Ready to enhance your React Native deployments? CodePushGo provides a robust platform for streamlined over-the-air updates, enabling faster and more reliable releases. Explore the benefits of CodePushGo today and transform your release process: https://codepushgo.com
Article created using Outrank




