Why Mobile Testing Feels Like an Uphill Battle (And How to Win)
In the hyper-competitive world of mobile apps, a flawless user experience is no longer a luxury, it’s the baseline for survival. Yet, achieving this standard is fraught with complexity. Developers and QA teams grapple with a constantly shifting landscape of devices, operating systems, and user expectations. The path from code to a successful app store launch is paved with numerous, often formidable, mobile testing challenges. These hurdles can drain resources, delay releases, and ultimately impact your app’s ratings and user retention.
This article dives deep into the 8 most significant mobile testing challenges that teams face today. We will go beyond the surface to explore the root causes, illustrate them with real-world scenarios, and provide actionable, expert-level strategies to overcome them. From managing device fragmentation and OS compatibility to mastering performance under fluctuating network conditions, you will gain practical insights to refine your testing processes. We will also cover the nuances of security, battery consumption, and the ongoing debate of real devices versus emulators. By understanding and addressing these core issues, you can ensure your application is not just functional, but exceptional, ready to meet the high demands of modern users.
1. Device Fragmentation
Device fragmentation is arguably the most foundational of all mobile testing challenges. It describes the vast and ever-expanding universe of devices, operating systems, screen sizes, and hardware configurations your app must support. Unlike desktop environments, the mobile ecosystem is not standardized. This diversity creates a complex testing matrix, making it financially and logistically impossible to guarantee flawless performance on every single device your users might own. The sheer scale of this problem means that without a smart strategy, teams can easily drown in an endless cycle of testing and bug fixing.
The Root Cause and Real-World Impact
The core of the issue lies in the open nature of the Android ecosystem and the rapid evolution of both iOS and Android hardware. For instance, while Apple maintains tight control over its hardware, an app like Instagram must still optimize for different iPhone screen sizes and resolutions, from the smaller iPhone SE to the larger Pro Max models. The challenge is magnified exponentially for Android. A company like Samsung must ensure its Samsung Pay app works flawlessly not only on its flagship models but across its entire range of devices, each with unique hardware and software customizations. This creates significant overhead and risk for developers.
The following bar chart illustrates the scale of Android fragmentation, showing the massive number of device models compared to the typical testing coverage.
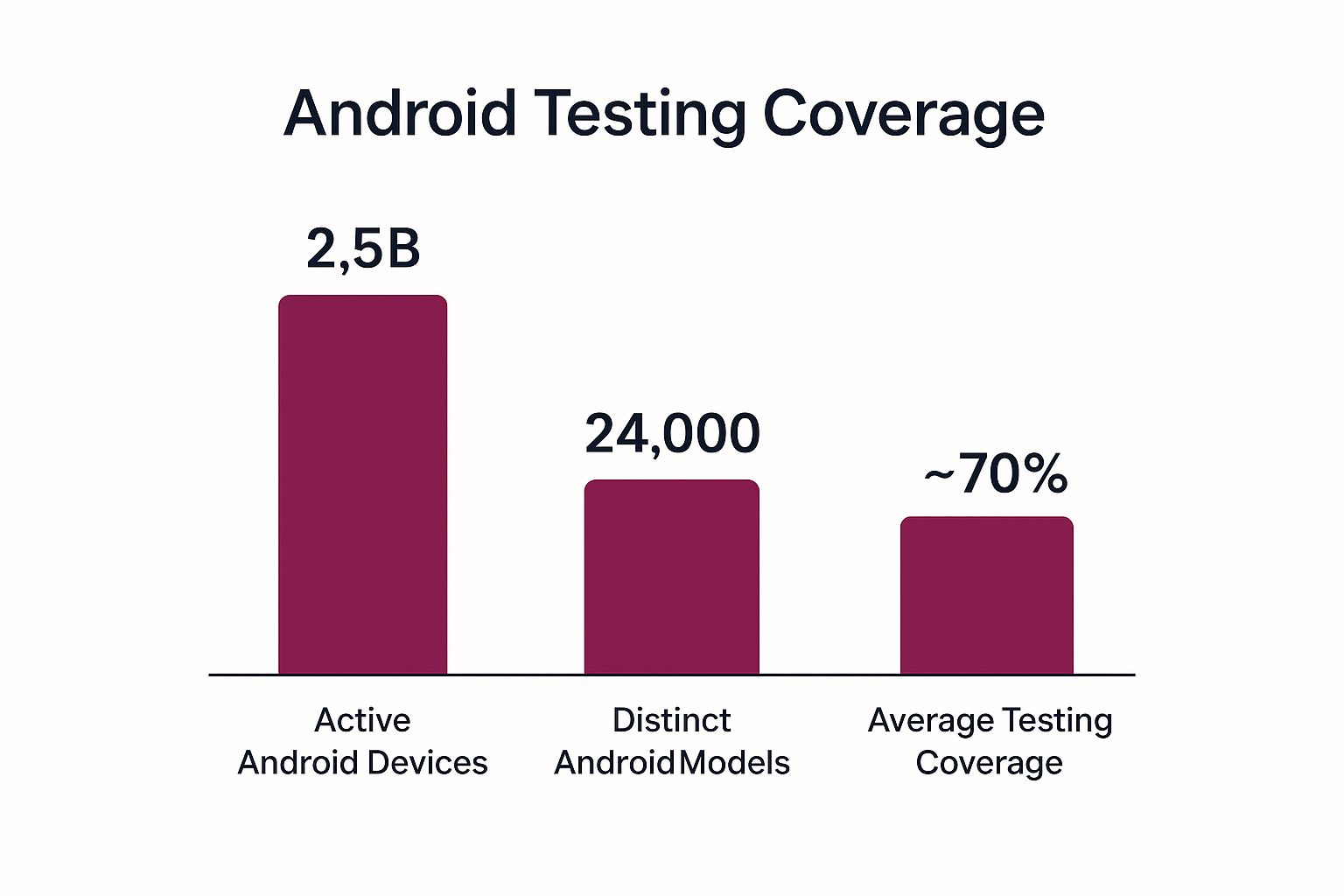
The visualization starkly contrasts the 24,000+ distinct Android models with the average team’s testing coverage, highlighting a significant gap where critical bugs can go undetected.
How to Mitigate Fragmentation Challenges
Confronting this mobile testing challenge requires a data-driven, strategic approach rather than attempting to test everything.
- Prioritize with Analytics: Use analytics data to identify the most popular devices, OS versions, and screen sizes among your target audience. Create a device test matrix that focuses coverage on these segments, ensuring you address the majority of your user base.
- Leverage Cloud Device Farms: Services like AWS Device Farm and Firebase Test Lab provide access to hundreds of real physical devices without the cost of purchasing and maintaining them. This allows you to run automated tests on a representative sample of devices, catching hardware-specific bugs.
- Embrace Responsive Design: Implement responsive design principles from the start. Using flexible grids and layouts in your code ensures your UI adapts gracefully to various screen dimensions, reducing the need to create custom layouts for every possible size.
2. Operating System Version Compatibility
Operating System (OS) version compatibility is a persistent mobile testing challenge that stems from the rapid and continuous evolution of iOS and Android. This issue requires teams to ensure their app functions seamlessly not just on the latest OS release, but also on several older versions still used by a significant portion of their audience. OS updates often introduce critical changes, such as new security protocols, deprecated APIs, or modified user permissions, which can break existing app functionality without warning. This forces development and QA teams into a constant cycle of validation and adaptation to prevent alienating users on both legacy and cutting-edge OS versions.

The visualization highlights the fragmented OS landscape, showing how users are spread across multiple versions, each requiring dedicated testing efforts.
The Root Cause and Real-World Impact
The core of this challenge is the dual pressure of supporting old technology while embracing new features. Apple and Google release major OS updates annually, along with frequent minor security patches. For example, when Apple introduced more stringent location tracking permissions in iOS 14, apps like Uber had to adapt their code to handle the new “Precise” and “Approximate” location options or risk losing essential functionality. Similarly, Android’s shift to Scoped Storage from Android 10 onwards required developers, such as those at Spotify, to completely refactor how their apps handle file access, a significant undertaking to maintain features like offline downloads across Android 7.0 to Android 14. For banking apps, this is even more critical, as an OS update can introduce security vulnerabilities or break compliance if the app isn’t updated in lockstep.
How to Mitigate OS Compatibility Challenges
Effectively managing OS compatibility demands a proactive and analytical testing strategy.
- Define a Support Policy: Use analytics from tools like Google Play Console or Firebase to understand your user base’s OS distribution. Define a clear policy for the minimum supported OS version, focusing your resources on the versions used by over 95% of your audience.
- Automate Regression Testing: Establish a robust automated testing suite that runs against different OS versions on both emulators and real devices. This ensures that new features or bug fixes don’t unintentionally break functionality on an older, supported OS.
- Use Feature Flags for OS-Specific Code: When implementing features that rely on new OS APIs, wrap them in feature flags. This allows you to safely deploy new code and enable it only for users on the compatible OS version, preventing crashes or broken experiences for those on older systems.
- Monitor OS Adoption Rates: Keep a close watch on public OS adoption data and your own user analytics. As users migrate to newer versions, you can adjust your testing priorities and eventually deprecate support for outdated versions, freeing up valuable engineering resources.
3. Performance Testing Across Network Conditions
One of the most unpredictable variables in mobile app usage is network quality. Unlike stable, high-speed office WiFi, users interact with apps on the move, facing a spectrum of network conditions: from strong 5G and WiFi to spotty 3G, congested public hotspots, and even complete offline periods. Performance testing across network conditions is a critical mobile testing challenge that involves verifying an app remains responsive, functional, and reliable regardless of network speed, latency, or stability. Neglecting this can lead to frustrated users experiencing slow load times, failed actions, and a generally poor user experience.

This visualization highlights the direct correlation between app performance and user retention, underscoring the business impact of ensuring your app performs well even on slower networks.
The Root Cause and Real-World Impact
The core of this challenge is the inherent mobility of users. An app that works perfectly on a developer’s high-speed connection can become unusable for a commuter in a tunnel or a user in a region with underdeveloped network infrastructure. For example, YouTube’s adaptive video quality streaming is a direct solution to this; it detects bandwidth and adjusts the video resolution to prevent buffering. Similarly, banking apps must handle transaction submissions over unstable networks, ensuring a transaction either completes successfully or fails gracefully with clear user feedback, preventing duplicate charges or data loss. Facebook’s “2G Tuesdays” initiative, where they internally throttled their own network, was born from the need to understand and build for users in emerging markets.
How to Mitigate Network Performance Challenges
Tackling this mobile testing challenge requires simulating real-world network chaos in a controlled environment and building resilience directly into your app. For a deeper dive into measuring these factors, you can explore our guide on application performance monitoring best practices.
- Utilize Network Simulation Tools: Tools like Chrome DevTools’ network throttling feature, Apple’s Network Link Conditioner, or Charles Proxy allow you to simulate various network profiles. You can test app behavior under conditions like high latency, low bandwidth, and packet loss without leaving your desk.
- Implement Graceful Degradation and Offline-First: Design your app to function in low-connectivity states. This includes caching critical data, allowing offline access to key features (like Google Maps’ offline maps), and gracefully disabling features that require a strong connection.
- Optimize Payloads and Assets: Minimize the size of data requests and media assets. Use efficient data formats like WebP for images and implement content delivery networks (CDNs) to cache assets closer to the user, reducing latency and load times on all network types.
4. User Interface and User Experience Testing
A flawless user interface (UI) and intuitive user experience (UX) are non-negotiable for mobile app success. However, achieving this is a significant mobile testing challenge due to the interactive and personal nature of mobile devices. UI/UX testing validates everything a user sees, touches, and feels, from visual elements and gesture controls to screen orientations and accessibility features. Unlike backend testing, which deals with data and logic, UI/UX testing is deeply subjective and context-dependent, making it difficult to automate and measure effectively.

This process must ensure that interactive elements are not just functional but also feel responsive and natural to the user, a standard heavily influenced by platform-specific guidelines like Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines and Google’s Material Design.
The Root Cause and Real-World Impact
The core challenge stems from translating design concepts into a functional, tactile experience that works consistently across a fragmented device landscape. A gesture that works perfectly on one device might be clunky or unresponsive on another due to different screen sensitivities or OS interpretations. For example, Tinder’s iconic swipe-right/left mechanic required extensive testing to feel equally satisfying and accurate on countless devices. Similarly, a banking app must undergo rigorous accessibility testing with screen readers like VoiceOver and TalkBack to ensure visually impaired users can navigate critical functions, a process that is both time-consuming and technically demanding.
The following video from the Nielsen Norman Group explains the key differences between UI and UX, highlighting why both are critical to test.
Failing to address these UI/UX challenges can lead to user frustration, negative reviews, and ultimately, app abandonment.
How to Mitigate UI/UX Testing Challenges
A comprehensive UI/UX testing strategy blends automated checks with essential human-centric evaluation.
- Validate Touch Target Sizes: Ensure all interactive elements meet platform guidelines for size (e.g., at least 44x44 points on iOS and 48x48 dp on Android). This simple check prevents user frustration from mistaps and improves usability, especially for users with motor impairments.
- Conduct Real-User Usability Testing: Go beyond your internal team and test with real users from your target demographics. Observe them performing key tasks, like an e-commerce checkout, to uncover unexpected pain points and usability bottlenecks that automated scripts would miss.
- Test Dynamic UI Changes: Methodically test how the UI reacts to interruptions. This includes checking for layout breaks during screen orientation changes (portrait to landscape) and ensuring the interface adapts correctly when the on-screen keyboard appears and disappears. You can explore more articles about improving user experience to deepen your understanding.
5. Battery Life and Power Consumption Testing
Excessive battery drain is a silent app killer. This mobile testing challenge involves measuring, analyzing, and optimizing your application’s impact on a device’s power resources. Unlike a UI glitch, which is an annoyance, an app that rapidly drains a user’s battery can render their device useless, often leading to immediate uninstallation. It requires a dedicated testing focus because high power consumption is rarely caused by a single bug; it’s typically the result of inefficient network requests, aggressive GPS usage, high CPU cycles, or unoptimized background processes.
The Root Cause and Real-World Impact
The core of this problem lies in the finite power supply of mobile devices and the increasing demand apps place on hardware components like the CPU, GPU, GPS, and network radio. For example, a navigation app like Waze must continuously use the GPS, which is notoriously power-hungry. The challenge is to provide accurate, real-time directions without depleting the user’s battery before they reach their destination. Similarly, a fitness tracking app that constantly polls for sensor data can drain a battery in hours. Facebook faced this issue with its Messenger app, where frequent background syncs to fetch new messages and updates led to significant battery consumption complaints, forcing them to re-architect their data fetching strategy.
The impact is direct and severe. Users consistently cite poor battery performance as a top reason for deleting an app. This makes power consumption not just a technical issue but a critical factor in user retention and product success.
How to Mitigate Power Consumption Challenges
Tackling this mobile testing challenge requires proactive monitoring and optimization throughout the development lifecycle, not just as a final check.
- Profile with Platform Tools: Utilize native profiling tools to pinpoint energy hotspots. For iOS, Apple’s Xcode Instruments (Energy Log) provides detailed insights into CPU, network, and GPS usage. For Android, Android Studio’s Profiler and the Battery Historian tool help visualize system events and their impact on battery life.
- Test on Degraded Devices: Do not limit testing to new devices with pristine batteries. Run tests on older models with degraded battery capacity to simulate a more realistic, worst-case user scenario. This helps uncover performance issues that only become apparent on less-capable hardware.
- Optimize Background and Network Activity: Implement intelligent data-syncing strategies. Instead of constant polling, batch network requests, use push notifications to trigger updates, and leverage platform APIs like Android’s
WorkManager. This minimizes how often the app wakes the device from a low-power sleep state.
6. Security and Privacy Testing
In an era of frequent data breaches and heightened privacy awareness, security and privacy testing has become a non-negotiable mobile testing challenge. This discipline involves a comprehensive validation of your app’s defenses against malicious attacks and its adherence to data protection regulations. It covers everything from data encryption at rest and in transit to secure authentication, API protection, and safeguarding against common mobile threats like man-in-the-middle attacks or reverse engineering. A single vulnerability can lead to catastrophic consequences, including financial loss, reputational damage, and legal penalties.
The Root Cause and Real-World Impact
The core issue stems from the mobile device itself being a complex and often untrusted environment. Apps store sensitive information, access personal data, and communicate over public networks, creating numerous attack vectors. For example, a healthcare app must go beyond basic functionality testing to rigorously validate its HIPAA compliance, ensuring that patient data is encrypted and transmitted securely. Similarly, a banking app must test its multi-factor authentication and transaction security protocols to prevent unauthorized access and financial fraud. Failure in these areas can expose user data, erode trust, and render an application unusable.
The increased scrutiny from regulators and app stores, such as Apple’s App Transport Security requirements and Google Play Protect scanning, places the burden of security squarely on developers. This makes robust security testing an essential part of the development lifecycle, not an afterthought.
How to Mitigate Security and Privacy Challenges
Addressing security requires a proactive, multi-layered approach that integrates testing throughout the development process.
- Conduct Penetration Testing: Regularly engage security experts to perform penetration tests (pen tests). These simulated attacks identify vulnerabilities in your app, APIs, and backend infrastructure before malicious actors can exploit them. Tools like OWASP ZAP and Burp Suite can be used for initial assessments.
- Implement Secure Coding and Validation: Perform both static (SAST) and dynamic (DAST) code analysis to find security flaws early. Critically, validate transport layer security by implementing certificate pinning to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and ensure all data is encrypted over TLS/SSL.
- Test Authentication and Authorization: Rigorously test all authentication mechanisms, including password policies, biometric systems (like Face ID or fingerprint), and token-based access. Ensure that user roles and permissions are correctly enforced, preventing unauthorized access to data or features. For a deeper dive into this area, you can learn more about key app security standards.
7. Real Device vs Simulator/Emulator Testing
Deciding between real physical devices and virtualized environments like simulators or emulators is a persistent mobile testing challenge. Each approach presents a trade-off between accuracy, cost, and scalability. Real devices provide the most authentic testing environment, perfectly replicating user interactions with hardware components. However, acquiring and maintaining a diverse lab of physical devices is expensive and difficult to scale. Simulators and emulators offer a cost-effective, scalable alternative but can fail to capture real-world performance nuances and hardware-specific bugs.
The Root Cause and Real-World Impact
The core of this challenge is the gap between software simulation and physical reality. Simulators are software programs that mimic an OS’s behavior, while emulators replicate both the hardware and software. Neither can perfectly reproduce network fluctuations, battery drain, CPU throttling, or the precise behavior of sensors like GPS, accelerometers, and cameras. For an app like Uber, testing its location services on a simulator would be inadequate, as it cannot replicate the real-world GPS signal variability a user experiences. Similarly, a banking app that relies on biometric authentication must be validated on real devices to ensure the fingerprint or facial recognition hardware functions correctly.
A gaming company, on the other hand, might run thousands of automated regression tests on emulators to quickly check for code-level bugs after a new commit, saving real device testing for performance-critical or user experience validation. The risk of relying solely on virtual environments is launching an app that works in the lab but fails in the user’s hand due to unforeseen hardware or environmental factors.
How to Mitigate Testing Environment Challenges
The most effective strategy is not to choose one over the other but to create a hybrid model that leverages the strengths of both.
- Embrace a “Pyramid” Strategy: Use simulators and emulators for the broad base of your testing pyramid. This includes unit tests, component tests, and a large portion of your automated regression suite, which can run quickly and inexpensively during early development cycles. A robust CI/CD pipeline benefits greatly from this approach, and you can explore this further by learning about continuous integration for Android.
- Reserve Real Devices for Critical Paths: Allocate real device testing for user acceptance testing (UAT), performance benchmarking, and validating features that interact directly with hardware. This includes camera functions, Bluetooth connectivity, NFC, and biometric sensors.
- Leverage Cloud Device Platforms: Services like Sauce Labs, BrowserStack, and AWS Device Farm offer a powerful middle ground. They provide access to hundreds of real, physical devices on demand, allowing you to run automated and manual tests at scale without the overhead of maintaining your own device lab. This is ideal for broad compatibility and fragmentation testing.
8. Test Automation Complexity
While automation is often presented as the ultimate solution to testing bottlenecks, its implementation in the mobile landscape introduces its own significant set of mobile testing challenges. Test automation complexity arises from the need to create, manage, and maintain robust test scripts that can reliably execute across a volatile mobile environment. Challenges include handling dynamic UI elements that change with app updates, managing test data across different app states, and synchronizing tests with asynchronous operations like network requests. This complexity can make automation a resource-intensive endeavor that, if not managed correctly, fails to deliver its promised ROI.
The Root Cause and Real-World Impact
The core of this challenge stems from the inherent dynamism and platform-specific nature of mobile apps. A single user flow, like a checkout process on Shopify, must be automated separately for iOS and Android, often using different underlying frameworks like XCUITest and Espresso. Furthermore, frequent OS updates and app releases can break existing test scripts, leading to “flaky” tests that fail unpredictably. For an app like Slack, automated regression tests for messaging functionality must account for real-time updates and asynchronous message delivery, which are notoriously difficult to synchronize with automated scripts. This constant maintenance cycle can consume more time than manual testing if not architected properly from the start.
How to Mitigate Automation Complexity Challenges
Tackling automation complexity requires a strategic, architectural approach focused on stability and maintainability.
- Implement the Page Object Model (POM): Adopt the POM design pattern to separate UI interaction logic from test case logic. This makes your test code cleaner, more reusable, and significantly easier to maintain when the UI changes, as updates only need to be made in one place.
- Develop Robust Wait Strategies: Instead of using fixed delays, which lead to flaky tests, implement explicit and dynamic wait strategies. Configure your tests to wait for specific UI elements to become visible or interactive before proceeding, making them more resilient to variations in app performance and network speed.
- Prioritize Critical User Journeys: Start your automation efforts by focusing on high-value, critical-path test cases, such as user login, core feature usage, and payment flows. This ensures that you get the most immediate value from your automation suite while building a stable foundation. You can find many tools to help with this in our detailed guide on mobile app test automation tools.
Mobile Testing Challenges Comparison Matrix
| Aspect | Device Fragmentation | OS Version Compatibility | Network Performance Testing | UI/UX Testing | Battery Life Testing | Security & Privacy Testing | Real Device vs Simulator Testing | Test Automation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Very high due to many device variants | High, due to many OS versions & regressions | High, requires complex network simulations | Moderate to high; manual & automated mix | High, needs specialized tools & long sessions | High, needs expert penetration testing | Moderate; balancing real & simulated devices | High; complex UI handling & test flakiness |
| Resource Requirements ⚡ | High: multiple physical/cloud devices needed | High: devices/emulators for OS versions | High: network simulation tools & setups | Moderate: real users, diverse devices | High: profiling tools & extended testing | High: security tools, expert auditors | Moderate: combo of real devices & emulators | Moderate to high: tooling & maintenance |
| Expected Outcomes 📊 | Broad compatibility, device-specific issue detection | Compatibility across OS, reduces user churn | Reliable app under variable networks | Improved UX, accessibility, better retention | Optimized battery usage, less uninstall rate | Strong security, compliance, trust | Balanced test coverage, cost vs accuracy | Faster releases, greater coverage, reduced manual effort |
| Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Apps targeting large, diverse device base | Apps supporting multiple OS versions | Apps in areas with poor/variable connectivity | Apps focusing on UX and accessibility | Apps with heavy battery impact | Apps handling sensitive data or payments | Early dev vs final validation & scalability | Apps with frequent updates and UI changes |
| Key Advantages ⭐ | Ensures wider user compatibility | Supports legacy & latest OS features | Optimizes performance across network types | Identifies usability & accessibility issues | Improves app retention via battery optimization | Protects user data & meets regulations | Cost control and testing efficiency | Speeds up regression testing & improves quality |
Turning Testing Challenges into Competitive Advantages
Navigating the complex landscape of mobile testing is no longer just about fixing bugs; it’s a strategic imperative for success in a crowded marketplace. As we’ve explored, the journey is filled with significant hurdles, from the ever-expanding universe of device fragmentation and OS versions to the nuanced demands of performance, user experience, and security testing. Each of these mobile testing challenges represents a potential pitfall that can derail an app’s launch, erode user trust, and damage brand reputation.
The core lesson is that a reactive, last-minute approach to quality assurance is destined to fail. Instead, the most successful development teams adopt a proactive, integrated, and continuous testing culture. They don’t just find problems; they anticipate them. They leverage a combination of real devices and emulators, implement robust automation frameworks, and rigorously test under a variety of real-world network and battery conditions. This shift in mindset transforms testing from a costly bottleneck into a powerful engine for innovation and user satisfaction.
Key Takeaways for a Resilient Testing Strategy
Mastering these challenges requires more than just good intentions. It demands a concrete action plan built on the insights discussed throughout this article. Your primary takeaways should be:
- Embrace a Hybrid Approach: Acknowledge that neither real devices nor emulators alone are sufficient. Use emulators for early-stage, rapid testing and a diverse, real-device cloud for validating compatibility, performance, and user experience on the hardware your audience actually uses.
- Automate Intelligently: Don’t try to automate everything. Focus automation efforts on repetitive, high-value test cases like regression suites and performance benchmarks. This frees up your manual testers to focus on exploratory testing and complex UX validation, where human intuition is invaluable.
- Integrate Security Early and Often: Shift security testing left. Instead of a final-gate check, integrate static and dynamic security analysis (SAST/DAST) tools into your CI/CD pipeline. This ensures vulnerabilities are caught and remediated when they are cheapest and easiest to fix.
The Post-Testing Advantage: Agility in Deployment
Ultimately, even the most thorough testing process will uncover issues that need immediate attention. Your ability to respond to these discoveries is just as critical as your ability to find them. The final, crucial piece of the puzzle is closing the loop between identifying a critical bug and deploying a fix to your users. Waiting days or weeks for a traditional app store review can be devastating, especially for a security patch or a crash-inducing bug.
This is where over-the-air (OTA) update solutions become a game-changer for React Native developers. By decoupling your JavaScript and asset updates from the native binary, you gain the power to deliver critical changes almost instantly. This agility fundamentally changes the dynamic of your response to mobile testing challenges, turning a potential crisis into a demonstration of your team’s responsiveness and commitment to quality.
Ready to transform your development cycle and deliver flawless user experiences faster? Implement a powerful OTA update solution to complement your rigorous testing strategy. With CodePushGo, you can push hotfixes, security patches, and feature updates directly to your users’ devices, bypassing the app store delay and turning your testing insights into immediate action.




