Feature flagging is a powerful technique that lets you turn parts of your application on or off without shipping new code. The simplest way to think about it is like having a set of remote-controlled light switches for your app’s features. This gives you the power to decide who sees what and when, completely separating the act of deploying code from the act of releasing a feature.
Breaking Down Feature Flagging

So, what’s really going on under the hood? At its core, feature flagging is about wrapping new functionality inside a conditional block—the “flag.” This simple if statement gives your team the ability to activate or deactivate the feature from a central dashboard, changing the user experience on the fly. No new build, no app store submission, just a flip of a switch.
This kind of control is no longer a “nice-to-have.” The pressure to ship faster is intense. In fact, 97% of organizations feel an urgent need to get new features out the door more quickly. The problem? 65% admit they can’t do it safely. This is precisely the gap feature flagging is designed to fill, bridging the divide between development speed and production stability. You can see this trend reflected in many recent DevOps adoption reports where it’s becoming a mainstream practice.
The Core Components
A feature flagging system isn’t black magic; it’s just a few key pieces working in harmony. Once you understand them, the whole “light switch” concept makes perfect sense.
To help visualize how these parts work together, here’s a quick breakdown.
Core Concepts of Feature Flagging at a Glance
| Concept | Analogy | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| The Flag | A light switch | The if/else statement in your code that shows or hides the feature. |
| Targeting Rules | The person flipping the switch | The logic that decides who the flag is “on” for (e.g., only beta testers). |
| Management Dashboard | The remote control | The UI where your team manages all flags and rules without touching code. |
These components create a system that empowers everyone on the team, from product managers to engineers.
By decoupling feature releases from code deployments, teams gain an incredible amount of control over their development pipeline. You can push unfinished code to production safely hidden behind a flag, test new ideas with real users, and roll out features with confidence.
How It Works in Practice
Let’s walk through a real-world scenario. Say your team is building a new chat function for your React Native app. The code gets merged into your main branch, but it’s wrapped in a feature flag that’s turned off by default for everyone.
Once that code is deployed, the QA team can log in, turn the flag on just for their own accounts, and start testing the new chat in the actual production environment. No more trying to replicate production on a staging server.
Later, a product manager might create a special test group of early adopters. They can enable the feature for just that small segment of users to collect real-world feedback before a big launch. The beauty of this is that each step—testing, beta release, full launch—happens without a single new deployment. A well-planned strategy for managing a test group is crucial to getting the most out of this process.
How Feature Flags Transform Your Development Workflow
Grasping the basic concept of a feature flag is one thing, but the real magic happens when you see how it completely overhauls the way your team builds and ships software. It’s a shift away from slow, high-stakes deployments toward a much more fluid, controlled, and data-informed process.
This infographic breaks down the three massive benefits that feature flags introduce into a modern development workflow.
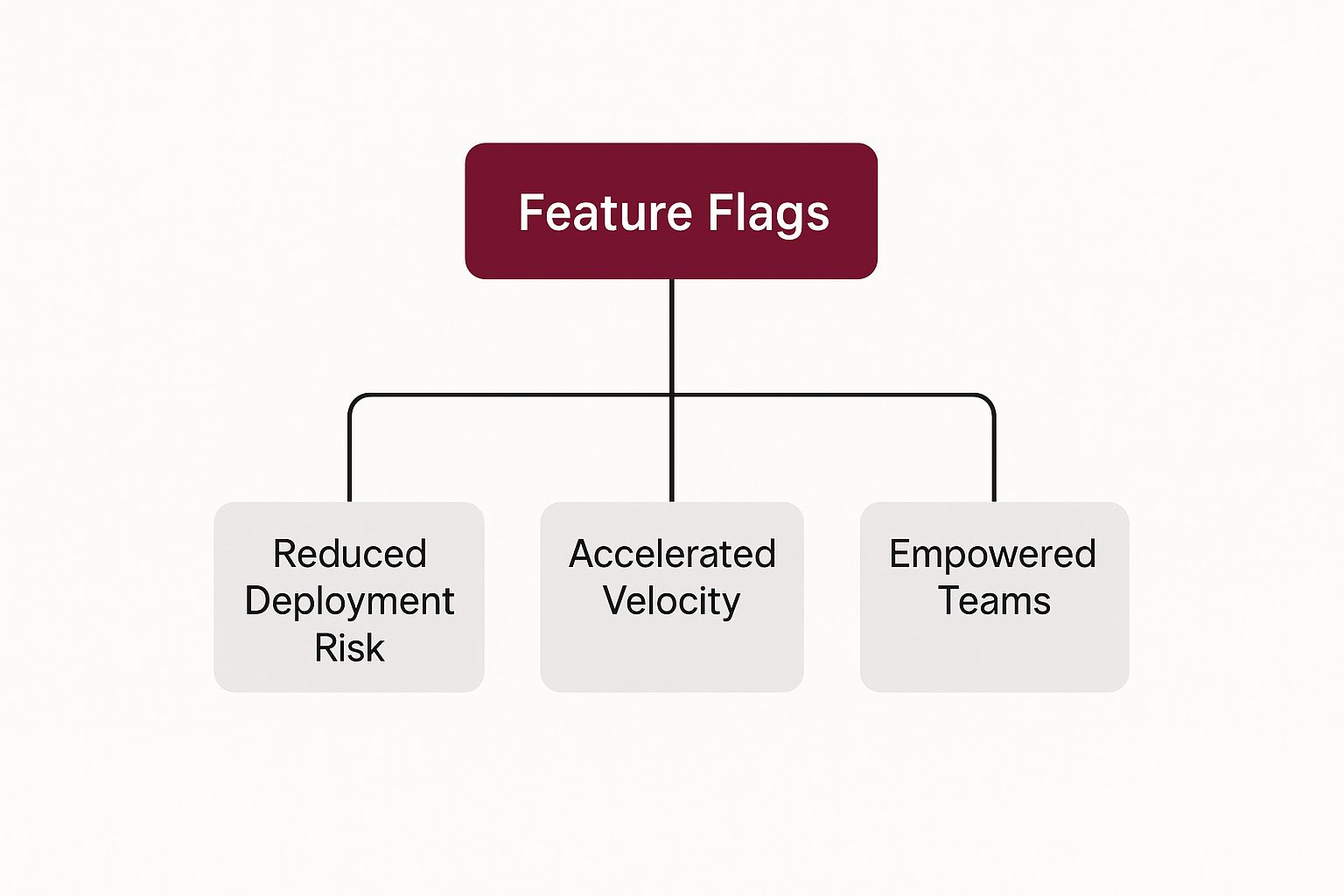
As you can see, feature flags make a direct impact on managing risk, speeding up your team, and helping everyone collaborate more effectively, no matter their role.
Drastically Reduce Deployment Risk
Think about traditional deployments. They’re often tense, “all-or-nothing” events. You push the new code, hold your breath, and just hope for the best. Feature flags completely flip that script by decoupling code deployment from the actual feature release.
This separation is what enables controlled rollouts. You can start small and expand with confidence using techniques like:
- Canary Releases: Roll out a new feature to just 1% of your users. This small group becomes your “canary in the coal mine,” letting you watch performance metrics and catch bugs without affecting everyone. The blast radius is tiny if something goes wrong.
- A/B Tests: Want to know which button color converts better? Release two different versions to separate user groups at the same time. You get real, hard data to back up your decisions before a full launch.
By testing new code with a small, specific audience in the live production environment, you can confirm your ideas work and squash bugs before they ever become a widespread problem. This makes deployments safer and a whole lot less stressful.
Accelerate Your Team’s Velocity
One of the biggest bottlenecks in development is the headache of managing multiple long-running feature branches. When it’s finally time to merge, you’re often stuck in a swamp of code conflicts and integration problems. It slows everything down.
Feature flags make trunk-based development a practical reality. All developers commit their code directly to the main branch—the “trunk.” Any features that aren’t quite finished are simply wrapped in a flag and turned off. This means you can merge and deploy incomplete work safely, knowing it won’t be visible to users.
This workflow gets rid of those painful, complex merges and keeps the whole team aligned and moving quickly on a single codebase. It’s a key part of effective https://codepushgo.com/blog/code-release-management-best-practices/, promoting short, iterative development cycles.
Empower Non-Technical Teams
Feature flags also hand the release controls over to people outside the engineering team. Product managers, marketers, or sales teams can turn features on or off through a simple UI. Suddenly, you don’t need to pull an engineer away from their work just to make a feature live.
This is a huge advantage that top companies lean on heavily. A great example is Netflix’s approach to experimentation, where they constantly test and refine the user experience. This setup gives the business side the agility to react to user feedback or market shifts instantly, without having to wait for the next scheduled deployment.
Practical Feature Flagging Strategies and Patterns

Feature flagging isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s more like a versatile toolkit, with different tools designed for specific jobs. Once you get the hang of these common patterns, you can pick the right strategy for any situation, moving beyond just hiding new code and toward making truly data-driven product decisions.
Each pattern has a distinct job to do, whether it’s protecting your app during a release or running sophisticated user tests. Mastering them gives your team precise control over the entire development lifecycle.
Release Toggles for Safe Deployments
The most common and straightforward pattern is the Release Toggle. Its main purpose is simple: to separate deploying new code from releasing a new feature. This lets developers merge incomplete work into the main branch and push it all the way to production, safely tucked behind a flag that’s off for everyone.
This approach is the backbone of trunk-based development and continuous integration. For instance, if you’re overhauling the checkout flow, your team can merge small pieces of it daily, confident that it won’t affect a single user until you’re ready to flip the switch. For many teams, this is the first “aha!” moment when they start using feature flags in their workflow.
Release Toggles are your safety net. They make deploying code a non-event, giving your team the freedom to ship smaller changes more often without that constant fear of breaking production.
Experiment Toggles for A/B Testing
If release toggles are all about safety, Experiment Toggles are all about learning. These flags are built to show different versions of a feature to specific user segments at the same time—the core idea behind A/B testing. You might show 50% of your users a green “Buy Now” button and the other 50% a blue one, just to see which one converts better.
This pattern is a game-changer for product teams because it replaces gut feelings with real data. You can measure exactly how a change affects key metrics like user engagement or revenue before you decide to roll it out to everyone. This data-first mindset is a huge part of a smart canary deployment strategy, allowing you to test and measure the impact in a controlled environment.
Operational and Permission Toggles
Beyond deployments and experiments, a couple of other patterns offer essential control over your application.
-
Ops Toggles: Think of this as the big red emergency stop button. If a new feature suddenly starts causing performance problems or making the app unstable, an Ops Toggle lets you shut it down for everyone instantly. No frantic code rollbacks needed. This buys your engineering team critical time to figure out what went wrong and fix it properly.
-
Permission Toggles: These flags manage who gets to see certain features based on who they are. This is perfect for rolling out premium functionality to paid subscribers, giving beta testers an early peek, or even enabling special tools just for your internal team. You can create very specific rules to target precise groups of users.
When you first start using feature flags, it feels like a superpower. Suddenly, you can ship faster and with less risk. But as your team grows and your app gets more complex, that clean, simple system can spiral into a tangled mess of forgotten flags. This is what we call flag debt, and it’s a real headache.
This buildup of old, obsolete flags adds a ton of unnecessary complexity and risk to your codebase. To keep things from getting out of hand, you have to treat feature flags like any other piece of software—they have a lifecycle. You need a solid plan for managing them from the moment they’re created to the day they’re retired. You wouldn’t let dead code rot in your repository, so don’t let old flags pile up either.
Establish a Clear Naming Convention
Your first line of defense against flag debt is a good naming convention. A flag named new-button-test might make sense today, but six months from now? It’s completely meaningless. No one will remember who made it, what it does, or if it’s even safe to remove.
A solid naming scheme should give you all the important context at a glance. Think about baking key details right into the name itself. Here’s a format that works well:
- Team or Project:
[checkout-team] - Feature Name:
[apple-pay-support] - Flag Type:
[release] - Creation Date:
[2024-10-26]
Putting it all together, a name like [checkout-team]-[apple-pay-support]-[release]-[2024-10-26] tells a complete story. Anyone can see what the flag is for, who owns it, and how old it is. This simple habit makes your system so much easier to audit and manage down the line.
Practice Proactive Flag Hygiene
Let’s be clear: old feature flags are technical debt. They clutter your code, increase the mental overhead for developers, and can even trigger bizarre bugs if someone flips the wrong switch by accident. The only way to deal with this is through proactive flag hygiene—making cleanup a regular, routine part of your workflow.
A feature flag’s job isn’t permanent. Once a feature is rolled out to 100% of your users and you know it’s stable, the flag has served its purpose. The very next step should be scheduling its removal from both your feature flag dashboard and your codebase.
A great habit to get into is setting a cleanup reminder or an expiration date the moment you create a flag. This forces you to think about its entire lifecycle from the start. By making flag cleanup a standard part of your sprint planning or code reviews, it becomes a small, consistent task instead of a massive, painful project you have to tackle once a year. This kind of discipline is what separates the pros from the amateurs when it comes to feature flagging at scale.
How to Implement Feature Flags in React Native
Alright, let’s move from theory to reality. This is where you see just how powerful feature flagging can be. For React Native teams, getting a system like this up and running is surprisingly simple, and it’s the key to managing your app’s features without waiting for app store approvals.
Let’s walk through a real-world example: controlling a new UI element in your app.
The first move is to bring a feature flagging service into your project. This usually means installing an SDK and firing it up in your app’s main entry point. For a service like CodePushGo, you’d add their package and plug in your unique API key. That one-time setup is all it takes to link your app to a central dashboard where the real magic happens.
A Practical Implementation Example
Imagine you’ve just built a shiny new “Get a Quote” button, but you’re not quite ready to unleash it on everyone. The old way would be to comment out the code or juggle a separate branch. With a feature flag, you just wrap the component. This simple action decouples the button’s visibility from the code that’s already deployed.
The logic couldn’t be more straightforward: the app checks if a specific flag is “on” for the current user. If it is, the button appears. If not, it stays hidden. Simple as that.
Here’s what a central dashboard for managing these flags often looks like.

This kind of clean, intuitive interface is your new command center. With your button’s code already wrapped, you can log in, create a new flag—let’s call it show-quote-button—and take control.
The single biggest win for mobile development here is skipping the app store review process for every little change. Once the code is in the app, a product manager can flip the
show-quote-buttonflag from “off” to “on” and instantly show it to a specific group of users—or everyone.
This immediate control lets you build dynamic experiences and iterate incredibly fast based on real user feedback. If you’re itching to see more of the code, our guide on how to implement feature toggles has more detailed examples to get you started.
Controlling Feature Rollouts
With the flag in place, you now have fine-grained control over who sees what and when. You’re no longer stuck with an all-or-nothing release. Instead, you can set specific rules right from your dashboard to target users based on almost any attribute.
Here are just a few ways you could roll out that new button:
- Internal Testing: Flip the switch only for users with email addresses ending in
@yourcompany.com. - Staged Rollout: Start small. Enable the feature for just 10% of your user base, watch the analytics, and then slowly dial it up.
- Regional Release: Make the button visible only to users in a specific country, like Canada or the UK, before a global launch.
This level of precision turns risky, high-stress releases into controlled, data-backed processes. And if something goes wrong? You can instantly disable the flag. It’s a “kill switch” that contains any negative impact immediately, all without begging for an emergency hotfix from the app stores.
Measuring Success with Feature Adoption Metrics
Shipping a new feature is really just the first step. The real win comes when you can prove it’s making a difference for your users and your business. This is where feature flags truly shine—they’re not just for deploying code, but for measuring real-world impact.
By linking your feature flags to analytics, you can stop guessing and start tracking hard numbers. This feedback loop, fueled by data, is exactly what you need to make smart, confident product decisions.
What to Track: The Metrics That Matter
So, how do you know if a feature is a hit? You need to watch how people are actually using it. A few core metrics will give you a surprisingly clear picture of your feature’s performance right out of the gate.
When you’re rolling out something new, you need a way to quantify its success. The table below breaks down the essential metrics that tell you whether users are finding, using, and getting value from your feature.
Key Feature Adoption Metrics
| Metric | What It Measures | Example Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption Rate | The percentage of targeted users who tried the feature within a set time. This shows initial awareness and appeal. | (Number of users who used the feature / Total number of targeted users) x 100 |
| Time-to-Adopt | The average time it takes for a new user to use the feature for the first time. Shorter is usually better! | Average of (Time of first feature use - User sign-up time) for a group of new users. |
| Feature Retention | The percentage of users who continue to use the feature over time. This is your best indicator of long-term value. | (Number of users who used the feature in Week 4 / Number who used it in Week 1) x 100 |
Tracking these numbers helps you see the complete story, from initial curiosity to sustained engagement. High retention, in particular, is a fantastic sign that you’ve built something that delivers ongoing value.
These metrics are all part of the bigger picture of user engagement. If you want to go deeper, it’s worth exploring the key app engagement metrics that fuel sustainable product growth.
Using Feature Flags to Get Clear Answers
Feature flags are the perfect tool for gathering this kind of precise data. Think about it: when you roll out a feature to a specific group of users, you’ve created a natural experiment. You can track their behavior and compare it directly against a control group who doesn’t have the feature.
This is how you get undeniable proof.
While the average software feature sees an adoption rate of around 24.5%, using feature flags for a targeted rollout can blow that number out of the water. One team used this exact strategy to hit an 85% feature adoption rate, backed by a 92% customer satisfaction score. You can read more about these feature adoption findings on userpilot.com.
This isn’t just about good data; it’s about empowering your team to prove the value of their work and make smarter decisions based on what users actually do.
A Few Common Questions About Feature Flagging
Even after getting the hang of the basics, a few questions always seem to come up when teams first start looking into feature flags. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones head-on.
Will Feature Flags Slow Down My App?
This is probably the number one concern we hear, but the short answer is no. Modern feature flagging systems are built for speed. A good SDK can evaluate a flag in milliseconds because it isn’t hitting a network every single time.
Instead, the system grabs the ruleset once and keeps it cached locally on the device. That means every check after the initial one is practically instant, so there’s no performance hit that your users would ever notice.
Are Feature Flags Just for Big Companies?
Absolutely not. It’s true that large companies depend on them, but the tools and practices have become so accessible that teams of any size can benefit. Safer releases, quicker iteration, and targeted rollouts are just as valuable for a team of five as they are for a team of five hundred.
Feature flags level the playing field. They give smaller teams access to the same powerful deployment strategies that were once exclusive to the tech giants. It’s a practice that grows right alongside your company.
How Is a Feature Flag Different From a Config File?
It’s easy to mix these two up. A simple config file can definitely turn a feature on or off, but it’s missing the dynamic, real-time control that makes feature flags so powerful. Changing a config file almost always means you have to deploy your app all over again.
Feature flags, on the other hand, are controlled from a dashboard and can be toggled instantly without a new release. Even better, they support sophisticated targeting rules. You can roll out a new feature to just your beta testers, or only to users in a specific country—something you just can’t do with a static config file.
This kind of real-time control is a game-changer. For example, Slack managed to boost the adoption of new integrations by 15% just by using segmented rollouts. You can dig deeper into how data-driven insights optimize user experience on zigpoll.com.
Ready to ship faster and with more confidence? CodePushGo offers instant, over-the-air updates for your React Native apps, complete with powerful feature flagging capabilities. Take control of your release cycle and start delivering features on your terms. Learn more and get started at https://codepushgo.com.




