The Android CI Revolution: Why It Changes Everything
Android’s widespread adoption has made it a dominant force in the mobile market. This popularity, however, presents developers with a unique set of challenges. Successfully navigating the fragmented world of devices, OS versions, and screen sizes demands a robust and efficient development process. This is where Android Continuous Integration (CI) comes in, changing how teams build, test, and release apps. It represents a shift from traditional manual processes to automated workflows.
Why CI Is Crucial for Android Development
Traditional integration methods often involve infrequent code merges, leading to difficulties. These can include “integration nightmares,” late-stage bug discoveries, and lengthy release cycles. Android CI tackles these problems directly. By automating the build, test, and integration processes, CI enables developers to merge code frequently, even several times a day. This means integration issues are identified and fixed earlier in the development process, reducing the cost and time needed for bug fixes.
Imagine a team working on various app features. Without CI, integrating these features could be a complex, manual merge. With Android CI, each feature branch is automatically integrated into a main branch, allowing for continuous testing and validation. This streamlined process reduces the risk of errors and speeds up development.
Real-World Impacts of Android CI Adoption
The benefits of Android CI extend beyond bug detection. Teams using CI experience advantages like faster releases, better product quality, and increased developer satisfaction. Faster release cycles help companies respond to market demands quicker. Improved quality leads to better user reviews and greater customer loyalty. Businesses can therefore deliver value to users faster and more consistently.
The Android operating system holds a significant global market share of 72.15% as of January 2025, up from 12% in 2010. This dominance is particularly strong in areas like Africa and South America, where Android’s market share is over 85%. Find more detailed statistics here. The widespread use of Android highlights the importance of CI and CD. CI automates tedious tasks, letting developers focus on building great apps. This improves the developer experience, boosting team morale and productivity. Developers can dedicate their time to creating new features and improving user experience, rather than manually integrating code and troubleshooting merge conflicts.
CI and the Broader DevOps Ecosystem
Android CI isn’t a standalone practice. It plays a key role within the larger DevOps ecosystem, which emphasizes collaboration and automation throughout the software development lifecycle. CI is a core component of this approach, enabling teams to achieve continuous delivery and deployment. This means CI is not just a technical practice, but a cultural shift towards shared responsibility and streamlined workflows. By automating the integration process, CI builds the foundation for a more efficient and reliable delivery pipeline. This creates a more robust and responsive development process, empowering teams to deliver high-quality apps to the growing Android market.
Choosing Your Android CI Arsenal: Tools That Actually Work
So, you’re ready to take advantage of Android continuous integration (CI). Finding the right CI platform for your Android project can be tough with so many options available. This section helps you focus on CI platforms that perform well in challenging development environments. We’ll explore how these tools handle the specific needs of Android, offering honest assessments of their strengths and weaknesses.
Top Contenders in the Android CI Arena
Let’s look at some key players: Jenkins, CircleCI, GitHub Actions, and Bitrise. Each has its own advantages. Jenkins is known for its flexibility and extensive plugin ecosystem, offering significant customization, but may require more setup and maintenance. CircleCI is easy to use and cloud-based, ideal for teams seeking rapid setup and scalability. GitHub Actions tightly integrates with your existing GitHub repositories, simplifying workflows. Bitrise specializes in mobile CI, offering Android-specific features and integrations that can really improve developer productivity.
Choosing the right tools means understanding what you can automate. For example, you can automate your Jira Cloud processes. Learn more about this here. The CI tools market is growing rapidly, from $2.37 billion in 2024 to a projected $2.9 billion in 2025. This represents a 22.6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). This growth is fueled by increasing software adoption, the need for simplified development, and cost optimization. You can discover more insights about continuous integration tools here.
To help you choose the right CI tool for your needs, we’ve put together a comparison table:
To help you choose the right CI tool for your Android projects, let’s look at a comparison of some popular options:
Popular CI Tools for Android Development Comparison of leading continuous integration platforms for Android development
| CI Tool | Android-Specific Features | Learning Curve | Pricing Model | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | Extensive plugin ecosystem, highly customizable | Steep | Open Source (costs associated with infrastructure) | Teams needing maximum flexibility and control |
| CircleCI | Cloud-based, easy setup, excellent scalability | Moderate | Tiered, free tier available | Teams prioritizing speed and ease of use |
| GitHub Actions | Tight GitHub integration, simplified workflows | Moderate | Pay-as-you-go, free tier available | Projects hosted on GitHub, focused on streamlined workflows |
| Bitrise | Mobile-first approach, Android-specific integrations, device testing | Moderate | Tiered, free trial available | Mobile-focused teams, prioritizing Android-specific features |
This table highlights some key differences between these popular CI tools. While Jenkins offers great flexibility, it requires more effort to set up and maintain. CircleCI and Bitrise provide more streamlined experiences, with Bitrise focusing specifically on mobile development needs. GitHub Actions is a strong choice for projects already using GitHub.
Integrating Testing Frameworks for a Robust CI Pipeline
A strong CI pipeline needs seamless testing integration. Effective Android CI relies heavily on testing frameworks like Espresso, JUnit, and Robolectric. Espresso is designed for UI testing and lets you simulate user interactions and validate UI behavior. JUnit is essential for unit testing, helping ensure individual components work correctly. Robolectric offers a fast and efficient way to test Android code without a physical device or emulator.
Think of it like building a house: unit tests are like inspecting individual bricks, while UI tests ensure the whole structure is sound. Combining these frameworks gives you comprehensive test coverage.
Visualizing the Impact of Android CI
The infographic below shows the benefits of using Android CI, comparing key metrics before and after implementation. It looks at builds per day, average bug resolution time, and releases per week.
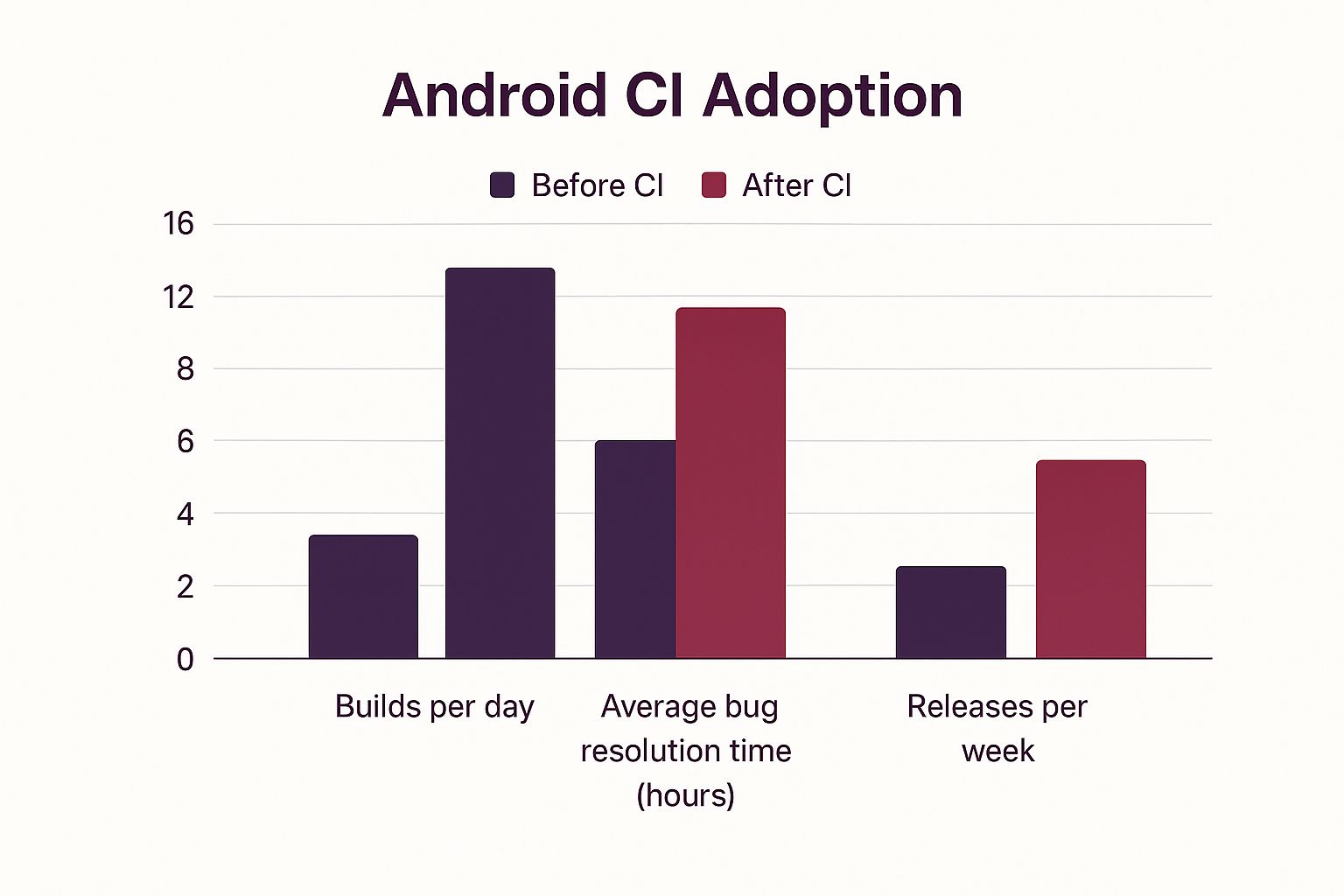
The data shows that Android CI significantly increases builds per day and releases per week, while reducing the average bug resolution time. This means faster development cycles, quicker feature delivery, and better quality apps.
Building a Cohesive Android CI Workflow
Effective Android CI requires more than just the right tools; it requires a well-planned workflow. Consider setup complexity, maintenance, and scalability when choosing your CI tools. For example, Jenkins is flexible, but can be resource-intensive. CircleCI, being cloud-based, simplifies setup and scaling. The best tool combination depends on your team’s needs and resources. This strategic approach will ensure a smooth, efficient, and impactful Android CI pipeline.
Building Your First Android CI Pipeline That Actually Works
Stop getting lost in endless tutorials. This guide provides clear, actionable steps to set up a working Android continuous integration (CI) pipeline. We’ll break down the process, from connecting your repository to configuring builds, with practical code examples.
Connecting Your Repository and Configuring Builds
The first step in Android CI is connecting your code repository to your CI platform. This usually means giving the platform access to your repository so it can track changes and start builds automatically. This connection is the base of your automated workflow.
Next, configure your build process. This defines the steps the CI platform takes when it detects a change. This configuration usually lives in a file (.yaml for GitHub Actions, Jenkinsfile for Jenkins). A well-structured configuration file specifies the environment, dependencies, build commands, and testing procedures. For Android, this includes the Android SDK version, build tools, and any needed libraries.
Handling Android SDK Dependencies and Signing
Experienced Android developers structure their CI configurations to handle Android SDK dependencies and signing efficiently. A best practice is using Gradle. Gradle lets you declare dependencies, and the CI platform automatically downloads and manages them, ensuring consistent builds.
Another key aspect is signing. Android apps must be signed before installation or distribution. Your CI configuration should securely manage your signing keys and certificates, automating the signing process during the build.
Practical Templates for .yaml and Jenkinsfiles
Here are some proven templates to get you started:
- .yaml (GitHub Actions):
name: Android CI
on: push: branches: [ main ] pull_request: branches: [ main ]
jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up JDK 11
uses: actions/setup-java@v2
with:
java-version: '11'
distribution: 'adopt'
- name: Build with Gradle
run: ./gradlew assembleDebug- Jenkinsfile:
pipeline { agent any stages { stage(‘Build’) { steps { sh ’./gradlew assembleDebug’ } } } }
These templates provide a starting point you can customize. They handle basic tasks like checking out the code, setting up the Java Development Kit (JDK), and running the Gradle build command. For iOS developers with similar CI/CD setups, automating your Jira Cloud can further streamline workflows.
Implementing Effective Notifications and Interpreting CI Reports
Effective notifications keep you updated on build status and test results without overwhelming you. Configure your CI platform to send notifications for key events like build failures, test failures, or successful deployments.
CI reports offer valuable data on your build process and code quality. Learning to interpret these reports helps you quickly find and fix problems. Focus on key metrics like build time, test coverage, and failed test counts. Analyzing CI reports helps you find bottlenecks and address code quality early, improving efficiency and ensuring app stability.
Balancing Thoroughness and Real-World Performance
A critical part of successful Android CI is balancing thorough testing with fast build times. While comprehensive testing is crucial, excessively long builds can slow down development. For example, Duolingo cut their Android and iOS build times by 68%, from 50 minutes to 16 minutes, by upgrading build machines and using caching. Implement Gradle optimizations like caching and parallel execution to minimize build time while keeping adequate test coverage. This keeps your CI process efficient and effective.

Testing Strategies That Prevent Production Nightmares
Beyond simple unit tests, robust testing methodologies are crucial for shielding your Android apps from critical failures. This section explores how strategic testing prevents embarrassing bugs from reaching your users.
The Android Testing Pyramid: Balancing Speed and Coverage
Successful mobile teams often utilize the testing pyramid to balance test coverage and execution speed. Think of the pyramid with unit tests forming the base. These tests are numerous, fast, and focused on small code units.
The middle layer consists of integration tests, which verify interactions between different components.
Finally, the peak represents UI tests, fewer in number but crucial for validating user interactions. This approach ensures comprehensive testing without sacrificing speed.
Writing Maintainable Tests: Handling UI Changes
A common challenge is writing tests that don’t break with every UI update. Focus on testing functionality, not specific UI elements.
For example, instead of checking for a button’s specific ID, test the action triggered by the button press. This approach makes your tests more resilient to UI changes, reducing maintenance overhead.
Tackling Android Device Fragmentation: Emulators vs. Real Devices
Android’s notorious device fragmentation poses a unique testing challenge. While emulators offer cost-effectiveness and ease of use, real devices provide more accurate insights into performance and compatibility across different hardware and software configurations.
A blended approach, using emulators for initial testing and real devices for final verification, offers the best balance. To build an effective Android CI pipeline, it’s helpful to review established CI/CD approaches.
Conquering Flaky Tests: Enhancing CI Reliability
Flaky tests, tests that sometimes pass and sometimes fail without code changes, undermine CI reliability. Identify and address flaky tests proactively.
Strategies include retry mechanisms, improved test isolation, and mocking external dependencies. This enhances the trustworthiness of your CI system. Duolingo, for instance, focused on optimizing their Android and iOS CI builds, resulting in a dramatic reduction in build times from 50 minutes to 16 minutes. Their efforts included upgrading build machines and leveraging caching.
Android Test Types in CI Environments
To further understand different testing approaches within continuous integration, the following table provides a comparison of various test types and their characteristics. This table helps clarify the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
| Test Type | Coverage Level | Execution Speed | Resources Required | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Tests | Individual components | Very Fast | Minimal | Test core logic, mock dependencies |
| Integration Tests | Interactions between components | Fast | Moderate | Verify data flow, ensure component compatibility |
| UI Tests | End-to-end user flows | Slow | High (emulators or real devices) | Test critical user journeys, validate UI behavior |
| End-to-End Tests | Complete system flow | Slowest | Highest (integrated environment) | Verify interactions across all systems and services |
Key takeaways from this comparison include the trade-offs between coverage, speed, and resources. Unit tests offer fast and efficient testing of individual components, while end-to-end tests provide comprehensive system validation but require significant resources.
Real-World Examples and Performance Metrics
By studying case studies of successful app releases, we can learn how strategic testing catches critical issues early on. These case studies often highlight the effectiveness of different test types and their impact on preventing production nightmares. This information is invaluable for shaping a comprehensive and effective testing strategy within your Android continuous integration workflow.

Remember, thorough testing isn’t an obstacle; it’s a safeguard for your app’s success. Imagine preventing a critical bug from reaching thousands of users – that’s the power of a robust Android continuous integration and testing strategy.
Automating Delivery: From Commits to Google Play Store
Releasing a successful Android app means transforming your release process from a chaotic scramble into a smooth, predictable operation. This involves automating everything from the initial code commit to the final release on the Google Play Store. Let’s explore how leading mobile teams achieve this seamless automation.
Versioning and Build Variants: Managing Complexity
Effective Android continuous integration relies on robust versioning and build variant management. Practical versioning strategies, like semantic versioning, are key. Semantic versioning uses a three-part number (e.g., 1.2.3) representing major, minor, and patch updates. This helps developers and users understand the significance of each release.
A new feature increases the minor version, a bug fix increases the patch number, and major changes update the major version.
Managing multiple build variants (like free vs. paid, or different CPU architectures) is also crucial for Android’s diverse ecosystem. Techniques such as product flavors in Gradle let you define different build configurations without redundant code.
Securely Handling Sensitive Signing Credentials
Protecting your signing credentials is paramount. Never store them directly in your repository. Instead, use dedicated secret management systems offered by CI platforms. These systems securely store and inject credentials during the build process, preventing unauthorized access while keeping your builds automated.
Phased Rollouts and Beta Distribution: Minimizing Risk
Phased rollouts minimize risk by initially releasing updates to a small percentage of users. This lets you monitor stability in a real-world environment before full release, detecting and fixing problems early on.
Automating beta distribution further streamlines feedback. Platforms like CodePushGo simplify getting updates to beta testers and collecting valuable feedback early. This feedback loop helps identify and address bugs before they impact your wider audience. CodePushGo’s support for channel-based systems facilitates staged rollouts and targeted beta testing, offering granular control and real-time monitoring.
Post-Release Monitoring and the Feedback Loop
Post-release monitoring tools close the feedback loop. By tracking crashes, ANRs (Application Not Responding), and other performance metrics, you can quickly identify and resolve any post-release issues.
This continuous monitoring offers valuable insights into your app’s performance, enabling iterative improvements and a smoother user experience. The continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) market is growing rapidly. It was valued at USD 3.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 16.9 billion by 2032. Explore this topic further.
Real-World Implementation Stories and Benefits
By adopting these strategies, mobile teams have dramatically reduced release cycles, sometimes from weeks to hours. This not only speeds up delivery but also improves quality and reduces team burnout. Automated processes free developers to focus on building features instead of managing complex releases.
These streamlined workflows lead to more frequent releases, faster feedback, and a better product for your users. This automated and efficient approach empowers teams to deliver high-quality Android apps at a sustainable pace.
Conquering the Android CI Challenges No One Talks About
Beyond the perfect scenarios often presented, real-world hurdles can seriously impact your Android CI implementation. Let’s tackle these challenges directly, beginning with the common issue of excessive build times.
Taming Lengthy Build Times: Optimization Techniques
Long build times are a frequent problem for many Android CI pipelines. This can lead to developer frustration and decreased productivity. Fortunately, proven optimization techniques can drastically reduce these times. One such technique is caching. Just like saving files on your computer for faster access later, caching in CI saves intermediate build artifacts, preventing unnecessary recompilation. This dramatically speeds up subsequent builds.
Another valuable technique is parallelization. Imagine multiple chefs working together to prepare a meal at the same time. By distributing build tasks across multiple machines or processor cores, you can considerably shorten the overall build time. For example, Duolingo optimized their Android and iOS CI builds, including upgrading their build machines and implementing caching, which led to a 68% reduction in build times, from 50 minutes to 16 minutes. This resulted in happier developers and faster release cycles.
Managing the Android SDK Dependency Maze
The Android SDK presents its own set of dependency challenges. Maintaining consistent SDK versions across various build environments is vital for reproducible builds. A practical solution is using a dependency management tool like Gradle. Gradle streamlines dependency definition and resolution, ensuring the proper versions are downloaded and used in each build. This prevents version conflicts and annoying build errors.
Furthermore, consider using a dedicated build machine or a container image with a pre-configured Android SDK. This avoids the need to repeatedly download and install the SDK for every single build, further optimizing the CI process. This also guarantees environment consistency, minimizing the risk of unexpected problems stemming from differing SDK configurations.
Handling Large Binary Assets Efficiently
Large binary assets, such as images, videos, and audio files, can inflate your repository size and slow down your CI pipeline. Storing these assets externally is one effective strategy. Consider a dedicated asset storage service or a cloud storage solution. Your CI configuration can then download the required assets during the build, reducing the overall repository size and boosting pipeline speed.
An alternative approach is using Git Large File Storage (LFS). Git LFS replaces large files in your repository with simple text pointers, storing the actual files on a separate server. This keeps your repository lean while still allowing you to manage binary assets within your version control system.
Secure Credential Management for CI/CD
Protecting your signing keys and other sensitive credentials is paramount in any CI/CD environment. Storing credentials directly in your repository is a significant security risk. Instead, utilize secret management tools offered by your CI platform. These tools securely store and inject credentials during the build, safeguarding them from unauthorized access.
For instance, GitHub Actions provides encrypted secrets, and Jenkins offers the Credentials Binding plugin. These features guarantee that sensitive information is never exposed as plain text, bolstering the security of your CI pipeline.
Fostering Team Adoption and Managing Change
Shifting to Android CI can sometimes face resistance. Addressing team concerns and cultivating a collaborative environment are key. Start with a pilot project to showcase the benefits of CI and gather valuable feedback. Provide sufficient training and documentation to assist your team in adapting to the new workflows.
Open communication and ongoing discussions are essential. Explain the reasons behind the change, highlighting the positive effects on productivity and product quality. Celebrate early wins to build momentum and demonstrate the tangible value of Android continuous integration. This creates shared understanding and ensures a smooth transition. Consider incorporating tools like CodePushGo into your CI/CD pipeline to optimize the release process and encourage team buy-in.
The Future of Android CI: Trends Reshaping Mobile DevOps

The Android continuous integration (CI) landscape is in constant motion. To stay competitive, understanding the key trends shaping mobile DevOps is essential. These advancements promise greater efficiency, reliability, and security for Android CI.
AI-Powered CI: Practical Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) is making tangible improvements in CI systems. AI offers practical advantages in areas like build optimization, test selection, and code quality assessment. For example, AI algorithms can analyze historical build data to anticipate potential issues or pinpoint areas for improvement. This can significantly reduce build times and optimize resource allocation.
AI can also intelligently select which tests to run based on code changes. This ensures comprehensive test coverage without unnecessary overhead, speeding up the CI process and providing faster feedback for quicker iteration cycles.
Integrating Security Testing into the CI Pipeline
Security is paramount in software development. Leading teams are integrating security testing directly into their Android CI pipelines, a practice known as “shift left.” This approach identifies vulnerabilities early in the development process.
Tools like static application security testing (SAST) and dynamic application security testing (DAST) can be integrated into the CI workflow. These tools provide automated security checks with every build, reducing the risk of security breaches and creating more secure applications.
Containerization and Cloud-Native Approaches
Containerization, using technologies like Docker, tackles the challenge of environment consistency in Android builds. Containers package the application and its dependencies, ensuring consistent execution across different machines. This solves the “works on my machine” problem and leads to reliable and reproducible builds.
Cloud-native approaches offer flexible and scalable CI workflows. Cloud-based CI platforms provide on-demand resources, allowing teams to scale their build infrastructure as needed. This bypasses the limitations of on-premise infrastructure and improves team efficiency.
Feature Flags and Progressive Delivery
Feature flags enable controlled feature releases without deploying new code. This allows for testing in production and offers a quick rollback option if problems arise.
Combined with progressive delivery, feature flags enable gradual feature rollouts to a subset of users. This allows teams to gather feedback and iteratively improve features before full deployment. This risk-averse approach minimizes the impact of bugs and enhances user experience.
Implementing Advanced Practices: Actionable Guidance
Adopting these practices doesn’t require a complete system overhaul. Start small, perhaps by integrating security testing or experimenting with feature flags.
Gradually incorporate these techniques into your workflow, building on your team’s skills and experience. CodePushGo can enhance Android CI/CD processes, enabling smooth and secure over-the-air (OTA) updates. Incremental changes and continuous improvement will unlock the full potential of Android CI, creating a more efficient and reliable development process.




