Why Your Deployment Rollback Plan Is Your Career Insurance

Imagine this: It’s Friday evening, you’ve just used CodePushGo to push what seemed like a small update to your React Native app. Then, bam - your production environment goes down in flames. Angry user reviews flood in. Your boss wants answers. All eyes are on you. This, my friend, is where your deployment rollback plan comes in. Is it your lifeline, or just another forgotten file?
A good rollback plan isn’t just about technical stuff; it’s about peace of mind for your team and, let’s be honest, protecting your career. Think of the hidden costs of a bad deployment: lost revenue, reputation damage, and the soul-crushing weekend spent on emergency fixes. These are the things that burn people out. A solid rollback plan can prevent all that.
The Real Cost of Downtime
Downtime hurts everyone, not just your users. Think of an e-commerce app crashing during Black Friday. Every minute of downtime equals lost sales and unhappy customers. A quick rollback can minimize the damage and get things back on track.
The deployment process itself is always a little risky. Bugs sneak through testing, systems have weird quirks, and performance issues pop up out of nowhere. I’ve seen new features cause crashes, slow down response times, and even create security holes. A fast rollback is crucial in these cases. Ignoring rollback strategies can be disastrous. Think extended outages, data loss, security breaches, and a damaged reputation. Learn more about the vital role of a solid rollback plan here.
Turning Disasters into Learning Experiences
Good deployment rollback plans aren’t just about putting out fires; they’re about understanding why the fire started in the first place. A well-documented rollback lets you analyze what went wrong, figure out the root cause, and make your development and testing better. It’s all about continuous improvement and more reliable deployments down the line.
Building a Culture of Confidence
Maybe the best part of a solid deployment rollback plan is the confidence it gives your team. Knowing there’s a safety net makes it easier for developers to try new things, move faster, and ship features more often. This creates a great cycle: more frequent deployments give you more chances to refine your rollback process, boosting confidence and reducing the fear of failure. This contributes to a healthier, more resilient team. A good rollback strategy, especially with the quick deployments CodePushGo offers, can turn potential catastrophes into valuable lessons and strengthen your entire development process.
Building Your Rollback Strategy From Real-World Experience
Creating a solid rollback plan isn’t about following some generic online template. It’s about deeply understanding your app, your team, and, most importantly, your users. It’s about knowing precisely what to do when things go south, even if your star engineer is on a beach somewhere with no cell service. Trust me, I’ve seen enough “deploy and pray” scenarios go disastrously wrong to know that a robust rollback plan isn’t just documentation—it’s peace of mind.
Identifying Your Rollback Triggers
Let’s talk about what actually triggers a rollback. It’s not always about catastrophic crashes. Sometimes, a subtle performance dip or a quirky UI glitch can be enough to justify hitting the reverse button. You need clear, measurable criteria. For instance, a 20% spike in error rates or a 10-second lag in critical user flows might be your red flags. The key is to define these triggers before you deploy. This takes the emotion out of what can quickly become a high-pressure situation.
In my experience working with React Native apps and CodePushGo, integrating these triggers directly into our monitoring system has been invaluable. This enables automated rollback initiation, which can save you precious time. It doesn’t replace human oversight, but it buys you valuable breathing room while you get your team together.
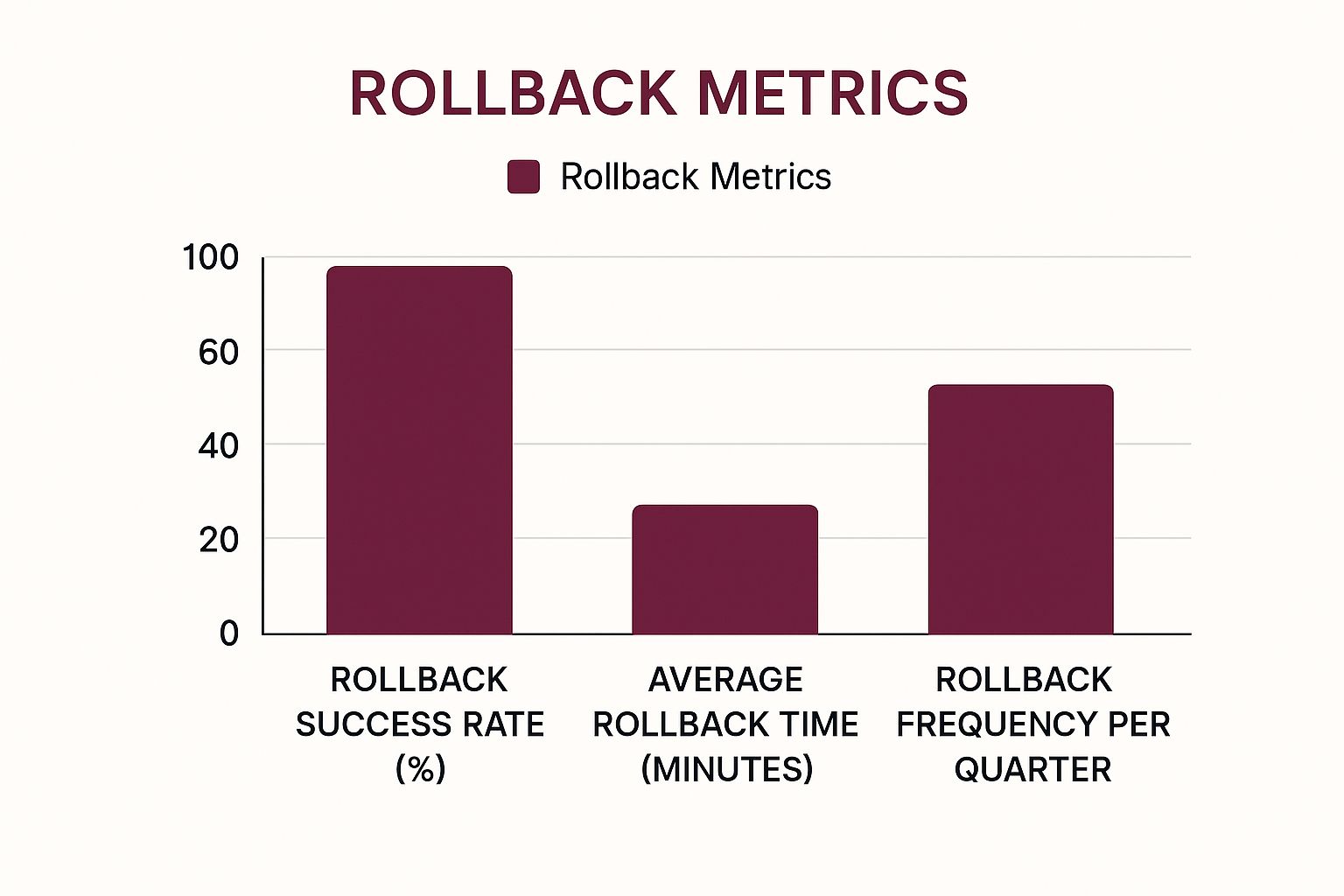
This chart tracks key rollback metrics: success rate, average rollback time, and frequency per quarter. Notice how, while rollback frequency has stayed fairly consistent, our focus on streamlining the process has dramatically improved success rates and significantly reduced rollback time.
Choosing the Right Rollback Strategy
Now, for the strategy itself. A simple redeployment might be fine for small tweaks, but for bigger changes, a blue-green deployment using CodePushGo might be a safer bet. This lets you test the new version in a staging environment before shifting all user traffic. If problems crop up, switching back is fast and easy. For even finer control, canary releases allow you to incrementally roll out changes to a small group of users.
The complexity of your app’s architecture also matters. Microservices, for example, demand a more sophisticated approach than a monolithic app. Consider dependencies and the potential for cascading failures. Your rollback plan needs to address every component. A good first step is thoroughly documenting your current deployment architecture and identifying potential bottlenecks before they become major headaches.
Making Your Documentation Accessible
Here’s the hard truth: the most brilliant rollback plan is worthless if your team can’t find it in a crisis. Don’t bury it in some obscure wiki page. Create a dedicated “Emergency Procedures” document that’s readily available to everyone. Keep it short, sweet, and focused on actionable steps. Include contact info for key personnel (and backups, just in case someone’s unavailable).
Checklists are invaluable under pressure. They guide your team step-by-step, minimizing errors even when stress levels are high. This isn’t just about tech; it’s about human psychology. Tired, stressed engineers make mistakes. Checklists help reduce that risk.
Planning for Partial Rollbacks
Sometimes, a complete rollback is overkill. Maybe only one specific feature needs reverting. This is where feature flags shine. They let you remotely toggle individual features on or off without a full redeployment. This gives you granular control and minimizes disruption for your users. Think of it as a precision strike instead of nuking your entire app. This level of control is especially helpful for complex React Native projects.
Let’s look at a quick comparison of different rollback strategies:
Rollback Strategy Comparison Matrix Comparing different rollback approaches including redeployment, blue-green, canary rollback, and feature flags with their complexity, speed, and use cases
| Strategy Type | Implementation Time | Rollback Speed | Complexity Level | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redeployment | Fast | Fast | Low | Minor updates, bug fixes |
| Blue-Green Deployment | Moderate | Fast | Moderate | Major version releases, significant changes |
| Canary Release | Moderate | Moderate | High | Introducing new features, A/B testing |
| Feature Flags | Fast | Fast | Low | Toggling specific features, quick fixes |
This table summarizes the key trade-offs between different rollback strategies. As you can see, each approach has its strengths and weaknesses, so choose the one that best fits your specific needs.
Understanding The Modern Deployment Rollback Landscape
The deployment world is always changing. Staying on top of current trends is essential for building a smart deployment rollback plan. The rise of continuous deployment has dramatically shifted how we approach rollbacks, affecting companies big and small. Planning for rollbacks isn’t just a technical to-do list anymore; it’s a real competitive advantage.
Continuous Deployment and the Changing Rollback Landscape
With the move towards continuous deployment, software updates are released much more frequently, sometimes multiple times a day. This increased pace demands a rock-solid rollback strategy that can quickly revert changes if things go south. Just having a plan isn’t enough anymore. It needs to be automated, efficient, and baked into your existing workflow. Think of it like the emergency brake in a race car – you need to know it works perfectly, even at top speed. For a deeper dive into this, check out this article on Blue-Green Deployment Strategy.
The need for reliable deployment solutions, especially robust rollback plans, is reflected in the market. The continuous delivery market was worth USD 4.27 billion in 2024 and is expected to exceed USD 17.8 billion by 2034. This impressive growth highlights how important reliable deployment strategies are, with solid rollback plans at the center. Discover more insights.
Industry Adaptations and Emerging Patterns
Different industries approach rollbacks in their own ways. In finance, for example, even a tiny hiccup can have major consequences, so rollback procedures are incredibly strict and thoroughly tested. On the other hand, a gaming company might be more flexible about small bugs, prioritizing rapid updates and new features. Grasping these industry-specific nuances is key to tailoring a deployment rollback plan that fits your unique situation.
Budget and Market Pressures
Let’s face it, budget matters. Investing in a robust rollback infrastructure takes resources, both in terms of tools and people. But the cost of not having a solid rollback plan is often much higher. Think about the potential damage of a big outage: lost revenue, unhappy customers who leave, and a damaged reputation. A strong rollback plan isn’t just another cost; it’s an investment in stability and keeping your business running smoothly.
Market competition also shapes your rollback strategy. In fast-moving industries, a quick rollback can be the difference between keeping customers and losing them to the competition. This pressure to deliver smooth user experiences is driving innovation in rollback technology, including automated solutions and advanced monitoring tools.
From Requirement to Competitive Edge
Deployment rollback plans used to be just a box to tick. Now, they’re a crucial differentiator. Companies with reliable rollback systems are better equipped to handle unexpected problems, maintain customer trust, and ultimately, win in a competitive market. It’s about making your whole system resilient, making sure you can quickly adapt and bounce back from any challenge. This proactive approach allows you to not just survive disruptions, but actually thrive in spite of them.
Implementing Rollback Procedures That Work Under Pressure

This screenshot shows the pillars of the AWS Well-Architected Framework, a great resource for anyone building reliable systems. Notice how much it emphasizes operational excellence. That’s really key for any deployment rollback plan. A solid rollback procedure isn’t about theory; it’s about what happens when everything’s on fire in production and you’re running on fumes. It’s about having procedures your team can execute perfectly, even at 3 AM. So, let’s get into the practicalities.
From Database to Infrastructure: Rollback Approaches That Actually Work
Different problems need different rollback solutions. A simple database rollback might just mean reverting a schema change or restoring from a backup. This is often automated with scripts as part of your deployment rollback plan. But infrastructure reversions can be trickier. Sometimes, you need to redeploy entire server configurations. From my experience, having a good infrastructure-as-code setup with tools like Terraform is really important here. This makes rollbacks reproducible and reliable, minimizing manual work and the risk of human error when the pressure is on.
There’s a world of difference between theory and practice. I once saw a rollback plan that looked perfect in a meeting, but completely bombed in a real outage because the network connection it depended on was down. Always test your plan under realistic conditions.
The Human Factor: Building Rollback Procedures for Real People
Even the best engineers mess up when they’re stressed and tired. Your deployment rollback plan has to take this into account. Clear, concise checklists are essential. They give step-by-step guidance, making things easier for your team during those high-pressure moments. I’ve seen checklists transform chaotic rollbacks into smooth, controlled operations.
Here are a few things to consider including in your checklists:
- Verification steps before starting the rollback
- Clear communication protocols within the team
- Escalation procedures if things don’t go to plan
These steps might seem basic, but they’re lifesavers in a crisis.
Automation and Override: Finding the Right Balance
Automated rollback triggers are fantastic. They can catch issues before anyone even notices, automatically reverting to a stable version. This is especially helpful with monitoring systems like Datadog or New Relic that track performance and errors. For example, if error rates spike, an automated rollback can kick in immediately. Speaking of automation, check out our guide on Continuous Integration if you’re looking to optimize your CI pipeline.
But you can’t automate everything. There will always be edge cases. That’s why manual overrides are so important. They let experienced engineers step in if the automated rollback isn’t working or a unique situation needs a different approach. This balance between automation and human control is key for a robust deployment rollback plan.
Coordinating Rollbacks Across Complex Architectures
Things get really interesting with distributed systems and microservices. Rolling back one service might trigger problems in others if it’s not coordinated. In these cases, your rollback plan needs to be more than just a document; it needs to be a well-orchestrated process.
Think about using techniques like:
- Phased rollbacks: Rolling back changes bit by bit across different services.
- Rollback dependencies: Clearly defining which services need to be rolled back and in what order.
- Communication channels: Setting up clear communication between the teams responsible for different services.
A successful rollback in these complex architectures is like conducting an orchestra. Every instrument (service) has to play its part at the right time for a harmonious (and stable) outcome. Ignoring these dependencies can make things much worse. And this leads to another crucial point: testing. But that’s a topic for another section.
Testing Your Rollback Plans Like Lives Depend On Them
Having a rollback plan you haven’t tested is a bit like having a fire extinguisher you’ve never checked. Sure, it looks good hanging on the wall, but will it actually work when you need it? Let’s talk about testing your deployment rollback plan thoroughly – because sometimes, your app’s survival really does depend on it.
Beyond Smoke Tests: Real-World Rollback Drills
Basic smoke tests are a starting point, but they won’t cut it in a real crisis. You’ve got to test your rollback under realistic failure conditions. Think about a database connection crashing mid-rollback, or a crucial dependency suddenly vanishing. These are the messy, complicated scenarios you need to simulate. I’ve personally seen companies lose millions because their rollback plan only worked in perfect conditions – conditions that never exist in the real world of production environments.
Leading tech companies run regular rollback drills, much like fire drills. They deliberately introduce failures into their systems to see how their rollback procedures perform under pressure. This even extends to chaos engineering – intentionally breaking things to observe the consequences. It might sound extreme, but it’s the best way to truly validate your recovery processes.
Simulating Real Failure Scenarios: Not Just the Easy Stuff
Consider your absolute worst-case scenarios. What if your primary server crashes and burns? What if your API goes completely silent? Your rollback tests should be designed to mimic these specific situations. This becomes especially important with the rapid deployment cycles that tools like CodePushGo enable. A quick rollback is essential, but only if it actually works when everything’s going haywire. For more insights on optimizing your monitoring setup, check out this article on Performance Monitoring Best Practices.
From Automated Tests to Disaster Recovery Exercises
Automating your rollback testing and integrating it into your CI/CD pipeline is a game-changer. Every code change can then trigger a rollback test, allowing you to catch potential issues early on. Tools like CodePushGo simplify this process with their one-click rollback feature. However, don’t underestimate the importance of manual testing. Consider running full-scale disaster recovery exercises involving your entire team, not just the engineers. These exercises test not only your technical infrastructure but also your team’s ability to respond effectively under stress.
Measuring, Documenting, and Improving Your Rollback Capabilities
Testing isn’t a one-and-done deal; it’s an ongoing commitment. Keep track of critical metrics like rollback time, success rate, and error rates. Document every test thoroughly, noting what went right, what went wrong, and any unexpected behavior. Use this data to continually refine your deployment rollback plan. Just like athletes analyze their performance to improve, you need to analyze your rollbacks to enhance your system’s resilience.
Building a Culture of Rollback Readiness
The most effective rollback plans are part of a larger culture of preparedness. Regular drills, comprehensive documentation, and a focus on continuous improvement ensure your team is always ready for anything. Think of it like a pilot practicing emergency procedures in a flight simulator. Your team needs to practice rollbacks regularly to build confidence and make those stressful 3 AM incidents a little less… stressful.
To help you structure your testing, here’s a sample table you can adapt for your specific needs:
Before we dive into the table, keep in mind this is a starting point. You’ll need to customize it based on your application and infrastructure.
Rollback Testing Scenarios and Success Criteria Comprehensive testing scenarios for different rollback situations with expected outcomes and success metrics
| Test Scenario | Trigger Conditions | Expected Recovery Time | Success Criteria | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Database Failure | Database connection lost | < 5 minutes | Database restored to previous state, application functionality restored | High |
| API Outage | API unresponsive | < 10 minutes | API restored to previous version, application functionality restored | Medium |
| Network Connectivity Issues | Network connection lost | < 15 minutes | Application gracefully handles network interruption, rollback successful upon connection restoration | Medium |
| Critical Dependency Failure | Third-party service unavailable | < 30 minutes | Failover to backup service activated, rollback initiated if necessary | High |
| Partial Feature Failure | New feature causing errors | < 1 minute | Feature disabled via feature flag, application stability restored | Low |
The table above provides a framework for thinking through different failure scenarios. Remember, the objective isn’t simply to have a deployment rollback plan, but to have one you can rely on – one that’s been tested and proven effective. That confidence is invaluable when things inevitably go sideways.
Measuring and Optimizing Rollback Performance That Matters

Testing your deployment rollback plan is essential. But truly mastering it means understanding its performance inside and out. It’s not enough to just know it works. You need to know how effectively it works and, crucially, how to make it even better. This goes way beyond simple uptime checks. We’re talking about grasping the real-world business impact of your rollback strategy.
Key Metrics For Rollback Success
Sure, uptime is important, but it doesn’t tell the whole story. You also need to think about rollback duration. How long does it actually take to fully revert to the previous version? In a high-traffic app, every minute counts. Trust me.
Then there’s rollback frequency. A spike in rollbacks might signal problems in your development process. But it could also mean your rollback triggers are doing their job, catching issues early before they blow up into something much worse. Context is everything here. If a slight uptick in rollbacks prevents major outages, that’s actually a win.
Finally, never underestimate error rates after a rollback. Ideally, you want to restore the app to its pre-deployment stability, not create new problems. I learned this the hard way once. A buggy rollback script actually increased error rates after reverting. It made a bad situation even worse. Lesson learned: test rigorously and monitor everything closely.
In fact, metrics like rollback frequency become even more critical with advanced deployment strategies. Teams often compare rollbacks to total deployments to get a clear picture of their process. For example, 5 rollbacks out of 100 deployments equals a 5% rollback frequency. Check out AWS’s documentation for deeper insights into advanced deployment strategies.
Establishing Baselines and Identifying Trends
To know if your rollback plan is getting better, you need a solid baseline. Track those key metrics over time and look for telling trends. Are rollback times trending down? Are error rates staying low post-rollback? These trends show you whether your efforts are paying off. They can also highlight underlying issues. For instance, a creeping increase in rollback time might mean your application is becoming more complex, requiring some architectural attention.
For more on streamlining your update process, take a look at our guide on Automatic App Updates.
Optimizing Your Entire Deployment Process
A truly effective deployment rollback plan isn’t just about fixing problems after they occur; it’s about preventing them in the first place. Your rollback data is a goldmine of information. Are certain types of changes more likely to trigger rollbacks? Are there specific parts of your app that are more fragile than others? This data can inform better testing, more thorough code reviews, and ultimately, fewer headaches down the road. I’ve seen teams cut their rollback frequency by over 50% just by analyzing rollback data and proactively addressing the root causes of deployment issues.
Monitoring and Alerting for Rollback Events
You absolutely need comprehensive monitoring for rollback events. You need to know immediately when a rollback happens, how long it takes, and if it was successful. Tools like CodePushGo offer built-in rollback monitoring and alerting. This gives you real-time visibility into your deployment stability. Integrate these alerts into your communication channels, like Slack or email, so your team is always in the know.
Analyzing Rollback Data for Continuous Improvement
Regularly analyze your rollback data. Look for patterns, identify areas for improvement, and track the effectiveness of any optimizations you make. This continuous feedback loop is the secret sauce to building a truly resilient deployment process. Treat every rollback as a learning opportunity. Use those lessons to strengthen your deployment rollback plan and prevent future disruptions. This iterative approach makes sure your rollback strategy evolves alongside your application and remains your best defense against instability and unhappy users. It’s about being proactive, not reactive.
Your Rollback Success Roadmap
Alright, let’s get down to brass tacks. We’ve talked a lot about rollback plans, so how do you actually build one? This is your practical guide to creating a deployment rollback plan that scales with your React Native app and team. Whether you’re a tiny startup or a massive enterprise, this roadmap offers some real-world advice to get you moving.
Prioritized Recommendations for Different Stages
-
Startups: Keep it simple! Honestly, redeploying with CodePushGo might be all you need in the beginning. Seriously, write down clear documentation and checklists, even if your team is just you and your cat. Future you will be so grateful.
-
Growing Teams: As your team expands, put some resources into automated testing and basic rollback triggers. Look into blue-green deployments with CodePushGo to minimize user impact during rollbacks. Also, start thinking about using feature flags – they give you way more control.
-
Enterprises: At the enterprise level, with complex systems, chaos engineering becomes crucial. Regular rollback drills, advanced monitoring, and automated rollback procedures are key. Your rollback plan needs to be a well-oiled machine, fully integrated with your CI/CD pipeline.
Essential Checklists and Decision Frameworks
Checklists. I know, they seem boring. But they’re lifesavers. Use them for every single stage of your deployment rollback plan to avoid painful mistakes:
-
Pre-Deployment: Did all the tests pass? Are backups up-to-date? Is your rollback procedure current? Triple check everything.
-
Rollback Trigger: What exactly are the metrics that will trigger a rollback? Get specific!
-
Rollback Execution: Have clear, step-by-step instructions for reverting your app, database, and infrastructure. No room for error here.
-
Post-Rollback: How do you know the rollback was successful? What are your verification steps? How do you track error rates to make sure things are stable?
Decision frameworks can also help you through those tough calls. A simple decision tree can work wonders: If error rates exceed X, automatically rollback. If the database is affected, restore from backup Y. These frameworks remove the guesswork (and the panic) during critical moments.
Measuring Success and Justifying Investment
How do you know your rollback plan is actually working? Data. Track these metrics:
-
Rollback Frequency: If this is trending down, you’re catching problems earlier – a great sign!
-
Rollback Time: How quickly can you revert? Faster is better, obviously.
-
Error Rates Post-Rollback: Are you getting back to the stability you had before deployment?
These metrics are how you justify continued investment in your deployment rollback plan. Show your boss how a robust rollback strategy saves the company money by minimizing downtime, makes users happy, and ultimately boosts the bottom line. For further guidance on optimizing deployments, check out our article on deployment optimization.
Next Steps and Realistic Timelines
Don’t aim for perfection right away. Start small, focus on the most critical improvements, and iterate based on what your team can handle. Here’s a possible timeline:
-
Week 1: Write down your current rollback procedure (even if it’s a mess) and identify your top three risks.
-
Month 1: Implement automated testing for your most important features and set up basic rollback triggers.
-
Quarter 1: Dive into blue-green deployments with CodePushGo and start practicing those rollback drills.
This is a marathon, not a sprint. Celebrate the small victories, learn from your mistakes, and build a rollback system that actually works for your team.
Ready to supercharge your React Native deployments? CodePushGo gives you the tools and the confidence to release faster and rollback smarter. Give it a try and feel the peace of mind that comes with a reliable safety net.




