In modern React Native development, speed and stability are not just goals; they are requirements. Teams are under constant pressure to deliver new features faster without introducing bugs or disrupting the user experience. This is where feature flags, also known as feature toggles, transform the development lifecycle from a high-stakes gamble into a controlled, strategic process. By decoupling code deployment from feature release, teams can ship code to production with confidence, knowing new functionality remains hidden until it is ready.
This guide presents eight essential feature flags best practices, specifically tailored for React Native teams leveraging over-the-air (OTA) update platforms like CodePushGo. Following these guidelines helps ensure your feature flag implementation is scalable, secure, and easy to maintain.
We will move beyond the basics, offering actionable strategies for everything from naming conventions and lifecycle management to security protocols and data-driven rollouts. The goal is to help you build a robust and scalable feature flagging system that accelerates innovation while safeguarding your application’s stability. By the end of this article, you will have a clear framework for implementing a feature management strategy that empowers your team to release with confidence and precision.
1. Start Simple and Evolve Gradually
Adopting feature flags doesn’t require an immediate leap into complex, multivariate testing systems. One of the most effective feature flags best practices is to start with a simple, foundational approach and allow your processes and team expertise to mature over time. This methodology prioritizes building confidence and establishing a solid operational baseline before introducing more advanced techniques.

Begin with basic boolean flags, which act as simple on/off switches for new functionality. For a React Native team using CodePushGo, this could mean wrapping a new component, like a promotional banner, in a conditional statement controlled by a single flag. This initial step allows your team to familiarize themselves with the core concepts of flag creation, implementation, and removal without the overhead of complex targeting rules.
Why This Approach Works
This gradual evolution, popularized by thought leaders like Martin Fowler and pioneering engineering teams at Flickr and GitHub, minimizes risk and cognitive load. By focusing on simple use cases first, you can iron out your internal processes, from naming conventions to lifecycle management, in a low-stakes environment. For instance, GitHub famously uses feature flags to release new UI changes to its own internal teams first, gathering feedback before a wider rollout. This “dogfooding” process is built on a foundation of straightforward toggles.
Actionable Tips for a Gradual Rollout
To implement this practice effectively, follow these steps:
- Target Non-Critical Features: Your first feature flag should not control a mission-critical user flow. Instead, apply it to a minor enhancement or a new, low-impact UI element.
- Establish Naming Conventions Early: Create a consistent naming system from day one, such as
[feature-name]-[type]-[status], to ensure clarity as your flag inventory grows. - Document Everything: For each flag, document its purpose, owner, expected lifespan, and what “success” looks like when it’s enabled. This creates an essential knowledge base.
- Train Your Team: Ensure every developer understands the full lifecycle of a feature flag, from creation to its eventual cleanup and removal from the codebase. This prevents technical debt.
2. Implement Proper Flag Lifecycle Management
A feature flag left in your codebase indefinitely ceases to be a tool and becomes technical debt. One of the most critical feature flags best practices is to establish a clear and robust lifecycle management process. This ensures that every flag has a defined purpose, owner, and, most importantly, a plan for its eventual removal, preventing code bloat and maintaining application health.
This systematic approach treats flags not as permanent fixtures but as temporary instruments. For a React Native team using CodePushGo, this means that when a new feature, like a redesigned checkout flow, is fully rolled out and stable, the flag controlling it is methodically cleaned up. This prevents the accumulation of dead code paths, which can confuse future development and introduce unforeseen bugs.
Why This Approach Works
Without a defined lifecycle, your flag inventory will inevitably grow out of control, creating a complex web of dependencies that is difficult to manage and reason about. Pioneering companies like Etsy and Facebook recognized this early on, implementing automated systems to manage flag retirement. Etsy, for example, developed tools to automatically alert teams about flags that have been 100% enabled for an extended period, prompting their removal. This proactive cleanup is essential for long-term code maintainability.
Actionable Tips for Flag Lifecycle Management
To implement this practice effectively, follow these steps:
- Set Mandatory Expiration Dates: Assign a target retirement date to every flag upon its creation. This sets a clear expectation that the flag is temporary and must be addressed.
- Establish Clear Ownership: Every flag must have a designated owner or team responsible for its monitoring and eventual removal. This accountability prevents flags from becoming orphaned.
- Create Retirement Checklists: Develop a standard operating procedure for removing a flag. This should include steps like removing the flag from the management dashboard (e.g., CodePushGo), deleting the conditional logic from the codebase, and cleaning up any related tests.
- Use Automation for Alerts: Implement automated systems to flag long-lived or stale flags that have been fully rolled out or disabled for a significant time. Exploring automation tools for DevOps can provide valuable insights into building these workflows.
3. Use Consistent and Descriptive Naming Conventions
As your use of feature flags expands, a haphazard naming approach can quickly lead to confusion, technical debt, and costly errors. Establishing and enforcing a standardized naming pattern is one of the most critical feature flags best practices for maintaining a clean and understandable system. Good conventions act as self-documenting code, immediately communicating a flag’s purpose, scope, and context to anyone who encounters it.
A well-designed naming convention prevents ambiguity and makes it easier for developers, QA engineers, and product managers to manage flags across different environments and lifecycles. For a React Native team using CodePushGo, this means a developer can instantly recognize if a flag controls a new checkout button, a user profile experiment, or a temporary kill switch, simply by reading its name.
The following infographic outlines a simple, three-step process for creating a robust feature flag name.
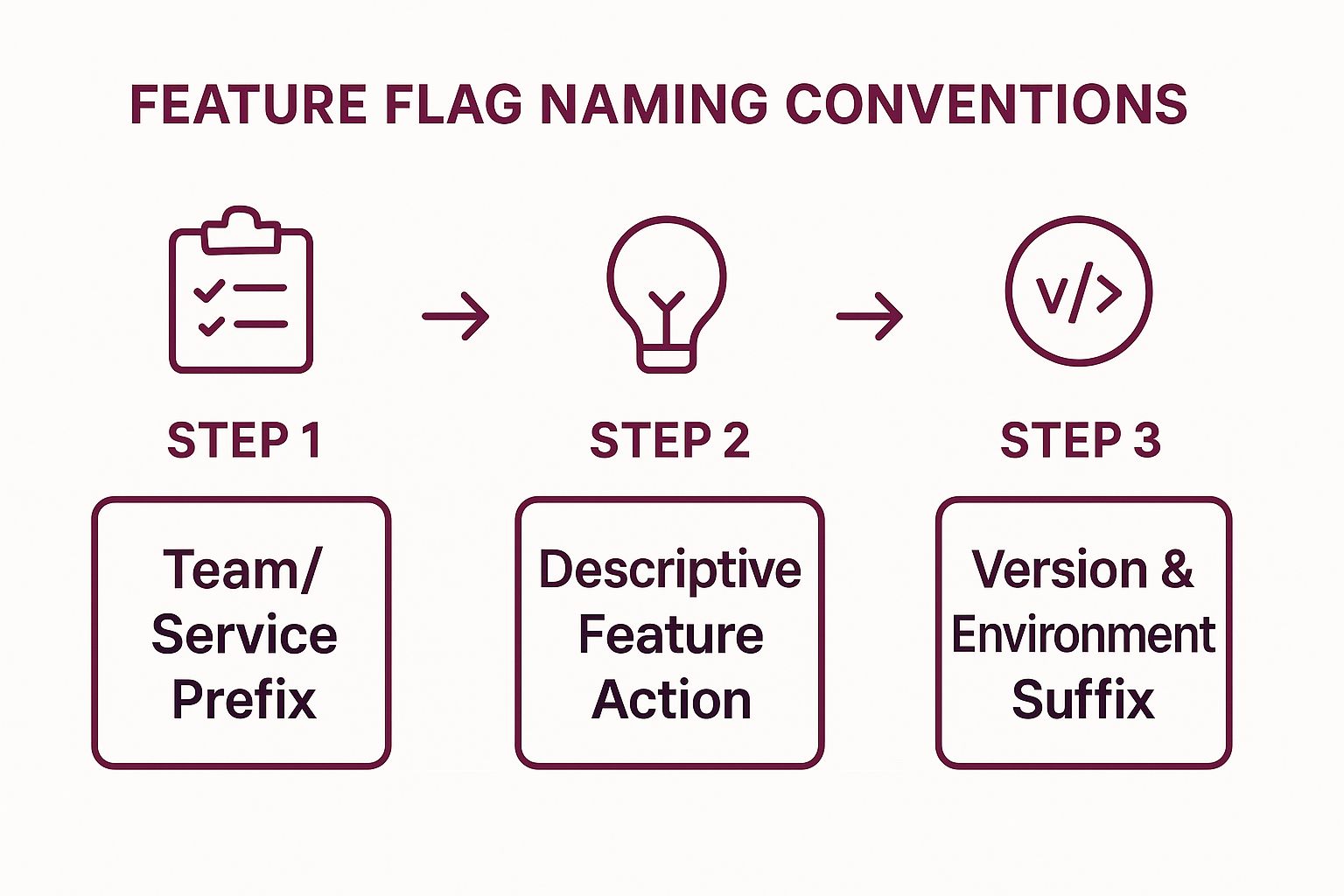
This structured approach ensures every flag name is immediately informative, reducing the need to look up documentation for basic context.
Why This Approach Works
This practice, championed by engineering leaders at Google, Airbnb, and Microsoft, brings order to the potential chaos of a large flag inventory. A clear system prevents naming collisions and makes it simple to search, filter, and audit flags. For instance, Airbnb’s convention, like web_booking_flow_v2_experiment, clearly defines the platform, feature, version, and type of flag. This level of detail is invaluable during incident response or when performing cleanup of obsolete flags. It turns the flag name from a simple identifier into a rich piece of metadata.
Actionable Tips for Naming Conventions
To implement this practice effectively, follow these guidelines:
- Prefix with Team or Service: Start the flag name with the responsible team or microservice, such as
[checkout-team]-[feature-name]or[auth-service]-[feature-name]. This clarifies ownership instantly. - Use Descriptive Actions: Clearly state what the feature does. Use verbs for action-based features, like
enable-new-cart-summaryinstead of a vaguecart-update. - Add Version and Environment Suffixes: For iterative features or experiments, include a version number (
_v2,_v3). For flags specific to an environment, a suffix like_devor_stagingcan prevent accidental production changes. - Document the Convention: Make your naming standard part of your team’s official documentation or wiki. Ensure it is accessible to all stakeholders and included in new developer onboarding.
- Avoid Ambiguous Abbreviations: Steer clear of unclear acronyms or abbreviations. What
nps-fbmeans might be obvious today but will be confusing to a new team member in six months. Spell it out:enable-nps-feedback-modal.
4. Implement Gradual Rollouts and Canary Releases
Deploying a feature to your entire user base at once is inherently risky. A more strategic and safer method, a core tenet of feature flags best practices, is to implement gradual rollouts and canary releases. This involves incrementally exposing new functionality to small, controlled segments of users before a full-scale launch, allowing you to monitor for issues and validate performance in a live environment.

With a tool like CodePushGo, a React Native team can easily configure a feature flag to be active for just 1% of its user base. As the team gains confidence in the feature’s stability and performance, they can increase that percentage to 5%, 25%, 50%, and eventually 100%. This controlled exposure minimizes the blast radius of any potential bugs, crashes, or performance degradation, turning a high-stakes release into a manageable, data-driven process.
Why This Approach Works
Pioneered by engineering giants like Facebook, Google, and Netflix, this methodology de-risks software delivery. Facebook famously uses a phased rollout strategy for major features, starting with a tiny fraction of users and scaling up as metrics remain healthy. This allows them to catch unforeseen issues at a small scale before they impact the entire platform. By adopting a similar approach, your team can make informed decisions based on real user data rather than relying on internal testing alone. For more insight, you can explore the detailed mechanics of a canary deployment strategy on codepushgo.com.
Actionable Tips for Gradual Rollouts
To execute gradual rollouts effectively, follow these key steps:
- Start Internally: Begin by releasing the feature to your own team or a dedicated group of beta testers. This provides an initial layer of real-world feedback.
- Monitor Key Metrics: Closely watch application performance metrics (APM), error rates, and business KPIs for the user segment exposed to the new feature.
- Define Success Criteria: Before starting the rollout, clearly define what “success” looks like. This could be a specific conversion rate, a reduction in support tickets, or a stable crash-free rate.
- Prepare a Rollback Plan: Always have a clear, tested procedure to disable the feature flag instantly if a critical issue is discovered. Automated alerts can trigger this process.
5. Maintain Flag Configuration Security and Access Control
Feature flags are powerful tools that directly control application behavior in production, making them a high-value target for unauthorized changes. A critical feature flags best practices is to treat your flag configuration system with the same level of security as your production database or deployment pipeline. This involves implementing robust access controls, detailed audit trails, and secure storage to prevent accidental or malicious modifications.
For a React Native team, this means ensuring that only authorized personnel can toggle features that might impact revenue, user data, or system stability. Using a service like CodePushGo, this involves setting up role-based access control (RBAC) where developers might create flags in a staging environment, but only a senior engineer or product manager can approve changes for production. This creates a necessary separation of duties.
Why This Approach Works
This security-first mindset is standard practice in highly regulated industries and large enterprises. Companies like Stripe and PayPal, which handle sensitive financial transactions, build stringent controls around their feature flag management to meet compliance standards like SOX. Microsoft’s enterprise development lifecycle incorporates strict access controls for any tool that can alter production behavior. By securing who can change a flag and logging every modification, you prevent catastrophic errors, such as a junior developer accidentally enabling an unfinished feature for all users.
Actionable Tips for Securing Your Flags
To implement robust flag security, follow these essential steps:
- Implement Least-Privilege Access: Grant team members the minimum level of access they need to perform their jobs. A QA engineer might only need view-access in production, while a developer may only have edit-access in a development environment.
- Require Approval Workflows: For production environments, mandate an approval step for any flag change. This ensures a second set of eyes reviews the modification, reducing the risk of error.
- Set Up Real-Time Alerts: Configure alerts for any changes to critical feature flags. Notifications via Slack or email can provide immediate visibility into modifications, allowing for a swift response if something goes wrong.
- Audit Access Permissions Regularly: Periodically review who has access to your feature flag system and what permissions they hold. This helps enforce your security policies and aligns with comprehensive app security standards.
6. Design Fail-Safe Default Behaviors
Your feature flag system should enhance reliability, not introduce a single point of failure. A critical feature flags best practices is to design your application with sensible default behaviors that activate when the flag service is unreachable. This resilience engineering approach ensures that a network blip or service outage on your flag provider’s end doesn’t cascade into a full-blown application failure for your users.

The core principle is to code your feature flag checks to “fail closed” or “fail safe”. For a React Native app using CodePushGo, this means your code shouldn’t crash if it can’t fetch the latest flag configuration. Instead, it should gracefully fall back to a known, stable state. For instance, if a flag controls a new, experimental checkout flow, the default behavior during a service error should always be to render the old, battle-tested checkout process.
Why This Approach Works
This practice, rooted in Amazon’s fault tolerance principles and Netflix’s pioneering work in resilience engineering, treats the feature flag service as an enhancement, not a dependency. It decouples your application’s core functionality from the flag management system’s availability. Shopify, for example, ensures its critical checkout flows default to the most stable, known-good version if flag evaluations fail, preventing revenue loss. Similarly, Twilio’s APIs fall back to conservative, safe rate limits during configuration retrieval issues, maintaining system stability.
Actionable Tips for Building Resilience
To implement fail-safe defaults effectively, integrate these steps into your development process:
- Choose the Safest Path: When implementing a conditional, the default or
elseblock should always contain the most stable and tested code path. - Implement Local Caching: Use the SDK’s built-in caching capabilities. For a mobile app, this means storing the last known good flag configuration on the device, ensuring a seamless user experience even when offline.
- Log and Monitor Failures: Your application should log every instance where it fails to retrieve a flag configuration. This data is invaluable for monitoring the health of your flag service integration.
- Test Default Behaviors: Actively test your fail-safe mechanisms. Use staging environments to simulate flag service outages and verify that your app behaves as expected.
- Document the Fallback: For every feature flag, your documentation should explicitly state what the application’s behavior will be if the flag cannot be evaluated.
7. Monitor Flag Performance and Business Impact
Deploying a feature behind a flag is only the first step; understanding its real-world effect is what unlocks true value. One of the most critical feature flags best practices is to implement comprehensive monitoring to track how flags affect system performance, user behavior, and key business metrics. This data-driven approach transforms feature flags from simple toggles into powerful tools for informed decision-making.
For a React Native team using CodePushGo, this means connecting flag states to your analytics and observability platforms. When you roll out a new checkout flow to 10% of users, you must be able to correlate that segment with conversion rates, API response times, and app crash rates. This practice allows you to quantify a feature’s success or failure objectively.
Why This Approach Works
This practice, central to the operational models of data-centric companies like Google, Meta, and Netflix, ensures that product decisions are based on evidence, not assumptions. Netflix, for instance, famously uses its experimentation platform to test everything from UI layouts to video compression algorithms, meticulously measuring the impact on user engagement and streaming quality. This prevents negative user experiences and validates the business value of new development work before a full release.
Beyond technical metrics, effectively monitoring flag performance and business impact also involves robust strategies for analyzing customer feedback, providing deeper insights into feature success. Integrating these qualitative data points with quantitative metrics gives you a complete picture of a feature’s reception. To dive deeper into the technical side, explore these strategies for React Native performance monitoring.
Actionable Tips for Effective Monitoring
To implement robust flag monitoring, follow these steps:
- Define Key Metrics First: Before activating a flag, define the specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) you will track. This could be user retention, session length, crash-free rate, or revenue per user.
- Set Up Automated Alerting: Configure alerts in your monitoring tools (like DataDog or Sentry) to notify you of significant metric deviations correlated with a flag’s state. For example, get an alert if the crash rate for users with
new-login-flow-enabledincreases by 5%. - Use Statistical Significance: When running A/B tests, use statistical methods to ensure your results are not due to random chance. This builds confidence that the observed changes are a direct result of the feature.
- Create Stakeholder Dashboards: Build and share dashboards that clearly visualize the performance of features under flags. This keeps product managers, engineers, and other stakeholders aligned and informed.
8. Separate Deployment from Release
One of the most transformative feature flags best practices is to fundamentally decouple the act of deploying code from the act of releasing a feature. By using flags to hide new functionality, your team can merge and deploy code to production at any time, while the business retains precise control over when users see and interact with that new functionality. This separation mitigates deployment risk and empowers more strategic, data-driven release decisions.
With CodePushGo, a React Native team can deploy a new, complex checkout flow to 100% of users but keep it disabled by default. The code is live and running in the production environment, but it remains invisible behind its feature flag. This allows for thorough end-to-end testing in the actual production environment before a single customer is impacted, a concept championed by DevOps pioneers.
Why This Approach Works
This separation of concerns, a core tenet of Continuous Delivery, dramatically reduces the pressure and risk associated with “big bang” deployments. Pioneering companies like GitHub use this method, often called “dark launching,” to deploy major features weeks before they are publicly announced. This allows them to ensure stability and performance under real-world conditions. This practice fits perfectly within methodologies like the Dual Track Agile approach, where discovery and delivery streams can operate on different timelines but merge into a single, stable codebase.
Actionable Tips for Decoupling Deployment and Release
To effectively implement this practice, consider these steps:
- Plan Releases Independently: Schedule feature activations based on marketing campaigns, user feedback, or business milestones, not on engineering sprint cycles.
- Coordinate with Business Teams: Align with marketing, sales, and support teams well in advance of a planned feature release. Ensure they are prepared with documentation and communication plans.
- Test Inactive Features in Production: Use internal user segments or specific test accounts to validate that the deployed but hidden feature works as expected in the live environment.
- Monitor Post-Deployment Health: Before flipping the switch, closely monitor system performance and error rates to ensure the new, dormant code has not introduced any unintended side effects. For deeper insights, you can learn more about software deployment best practices on codepushgo.com.
Feature Flags Best Practices Comparison
| Approach | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start Simple and Evolve Gradually | Low 🔄 | Minimal ⚡ | Reliable initial deployment with simple toggles 📊 | Early-stage projects; teams new to feature flags | Faster deployments; easier debugging; low risk ⭐ |
| Implement Proper Flag Lifecycle Management | Medium 🔄 | Moderate ⚡ + tooling | Cleaner codebase; less technical debt 📊 | Teams managing numerous or long-lived flags | Prevents dead code; improves maintainability ⭐ |
| Use Consistent and Descriptive Naming Conventions | Low-Medium 🔄 | Low ⚡ | Clear flag purpose and scope; reduced errors 📊 | Large teams or multiple services | Improved communication; easier automation ⭐ |
| Implement Gradual Rollouts and Canary Releases | High 🔄 | High ⚡ + monitoring | Controlled feature exposure; early issue detection 📊 | Complex deployments; risk-sensitive releases | Risk mitigation; data-driven rollouts ⭐ |
| Maintain Flag Configuration Security and Access Control | Medium-High 🔄 | High ⚡ + security tooling | Secure flag management; compliance adherence 📊 | Regulated industries; security-critical apps | Prevents unauthorized changes; auditability ⭐ |
| Design Fail-Safe Default Behaviors | Medium 🔄 | Moderate ⚡ | System resilience during flag failures 📊 | High availability systems | Improved reliability; graceful fallback ⭐ |
| Monitor Flag Performance and Business Impact | Medium 🔄 | Moderate to High ⚡ + analytics | Data-driven insights; performance validation 📊 | Data-driven organizations; optimization focus | Better decision making; early regression alerts ⭐ |
| Separate Deployment from Release | Medium-High 🔄 | Moderate ⚡ + coordination | Safer deployments; flexible release timing 📊 | Continuous delivery pipelines; multi-team setups | Reduces risk; enables independent releases ⭐ |
Build Your Next Feature with Confidence
Adopting a robust feature flag strategy is a transformative step for any React Native development team. It marks a fundamental shift from a culture of high-stakes, anxiety-ridden deployments to one of confident, continuous innovation and iterative improvement. By moving through the practices we’ve outlined, you’ve seen how to build a powerful and scalable system that goes far beyond simple on/off toggles. This journey begins with establishing a solid foundation.
Mastering the basics is non-negotiable. Implementing proper flag lifecycle management ensures your codebase remains clean and free of technical debt, while consistent naming conventions provide clarity and prevent confusion as your system scales. These foundational elements create a predictable and manageable environment, which is the bedrock of any successful feature flagging practice. They turn chaos into order, making your system accessible and maintainable for everyone on the team, from junior developers to senior architects.
From Control to Strategic Advantage
With a stable foundation, you can unlock the true strategic power of feature flags. This is where your team can truly accelerate. Techniques like gradual rollouts and canary releases transform feature delivery from a monolithic event into a controlled, data-driven process. You can de-risk major launches by exposing new code to a small segment of users first, monitoring for issues before a full release.
This is amplified when you design for resilience with fail-safe default behaviors, ensuring that even if a flag service is unavailable, your application remains stable and functional for the end-user. Layering on comprehensive monitoring of both flag performance and business impact turns your releases into valuable experiments. You no longer have to guess the impact of a new feature; you can measure it directly, tying engineering effort to tangible business outcomes. By fully embracing the principle of separating deployment from release, you empower product managers and business stakeholders to control the user experience in real time, without requiring a new app store submission.
Ultimately, mastering these feature flags best practices empowers your team to build better products, faster. You reduce risk, increase deployment frequency, and create tight feedback loops that allow you to respond to user needs with incredible agility. This isn’t just about shipping code; it’s about building a resilient, innovative, and user-centric development culture. By integrating these principles into your daily workflow, you equip your team to handle the complexities of modern app development with confidence and precision, delivering value that delights your users and drives your business forward.
Ready to implement these best practices with a tool built for React Native? CodePushGo provides a complete solution for feature flagging and Over-The-Air (OTA) updates, giving you granular control over your releases. Start your free trial today and see how easy it is to deploy with confidence.




