The latest React Native version is 0.82, and it’s a big one. This release is a landmark because it operates entirely on the framework’s New Architecture, officially sending the old Legacy Architecture into retirement. This isn’t just an update; it’s a fundamental shift in how React Native works under the hood.
Understanding This Milestone Release
Think of this update less like a fresh coat of paint and more like swapping out a car’s traditional engine for a high-performance electric one. The outside looks the same, but the internal mechanics have been completely re-engineered for better speed, efficiency, and responsiveness. That’s exactly what the New Architecture delivers.
For those of us who have been in the trenches with React Native, this means we can finally say goodbye to the old “bridge.” That bridge often felt like a bottleneck, slowing down communication between our JavaScript code and the native side. The new system creates a much more direct, seamless connection, and the performance gains are immediately noticeable. If you’re just starting out, our getting started with React Native guide is a great place to build your foundation before jumping into these newer concepts.
Key Architectural Shifts
The release of React Native 0.82 in October 2025 marks a real turning point for the framework. This new architecture is built around two core components: TurboModules and the Fabric Renderer. These aren’t just fancy names—they deliver real, tangible benefits that users can actually feel.
For instance, benchmark data is showing that apps are now consistently hitting 60 fps, which is the gold standard for a buttery-smooth user experience.
The full adoption of the New Architecture is the most significant change since React Native’s inception. It addresses long-standing performance limitations and solidifies its position as a top-tier cross-platform solution.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what this means for the apps you’re building:
- Faster Startup: Apps are loading much faster. We’re seeing startup times improve by up to 40%.
- Optimized Memory: Memory usage has been trimmed down by 20–30%. This makes apps run better, especially on lower-end devices.
- Enhanced UI Responsiveness: Animations are smoother, and user interactions just feel snappier and more fluid.
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a summary of the major enhancements in this release.
Key Improvements in the Latest Version at a Glance
| Feature/Metric | Improvement Details | Impact on Apps |
|---|---|---|
| New Architecture | The Legacy Architecture is officially deprecated; TurboModules and Fabric are now standard. | Eliminates the JS-to-Native bridge bottleneck, resulting in faster and more direct communication. |
| Startup Time | Initial app load times have been reduced by up to 40% in benchmark tests. | Users get into the app quicker, improving first impressions and reducing bounce rates. |
| Memory Usage | Optimized memory footprint, with a 20–30% reduction across various scenarios. | Apps are more stable and perform better on a wider range of devices, including those with less RAM. |
| UI Performance | Frame rates consistently achieve 60 fps, even during complex animations. | Delivers a fluid, native-like feel with smooth transitions and immediate responsiveness to user touch. |
These improvements aren’t just incremental; they represent a significant step forward in what’s possible with the framework.
For businesses aiming to build high-performance applications, partnering with top React development services can be a smart move to take full advantage of this powerful ecosystem. Ultimately, this update gives developers the tools to create apps that are not only faster but also more reliable and ready for the future.
Inside the New Architecture and Its Impact
The biggest story with the latest react native version is, without a doubt, the full-on adoption of the New Architecture. This isn’t just some under-the-hood tweak; it’s a fundamental overhaul of how React Native works, aimed squarely at crushing the performance bottlenecks we’ve all wrestled with. It completely changes how your JavaScript code communicates with the native side of a device.
Think of the old system—the Legacy Architecture—like a slow, asynchronous message queue. Your JavaScript would bundle up a command, send it over a “bridge,” and then wait for the native side to eventually process it and send something back. It worked, but it was slow and clunky, especially for complex UIs.
The JSI Direct Connection
The New Architecture throws that old bridge out. In its place, we get a direct, synchronous connection called the JavaScript Interface (JSI). Now, instead of passing messages, your JavaScript can call native functions directly, as if it’s all one big, happy codebase. This instant communication is the secret sauce that makes everything else possible.
This shift means no more lag waiting for the bridge to catch up. The result? Far more responsive and complex user interfaces become a reality.
This infographic breaks down the core benefits that spring from this new approach.
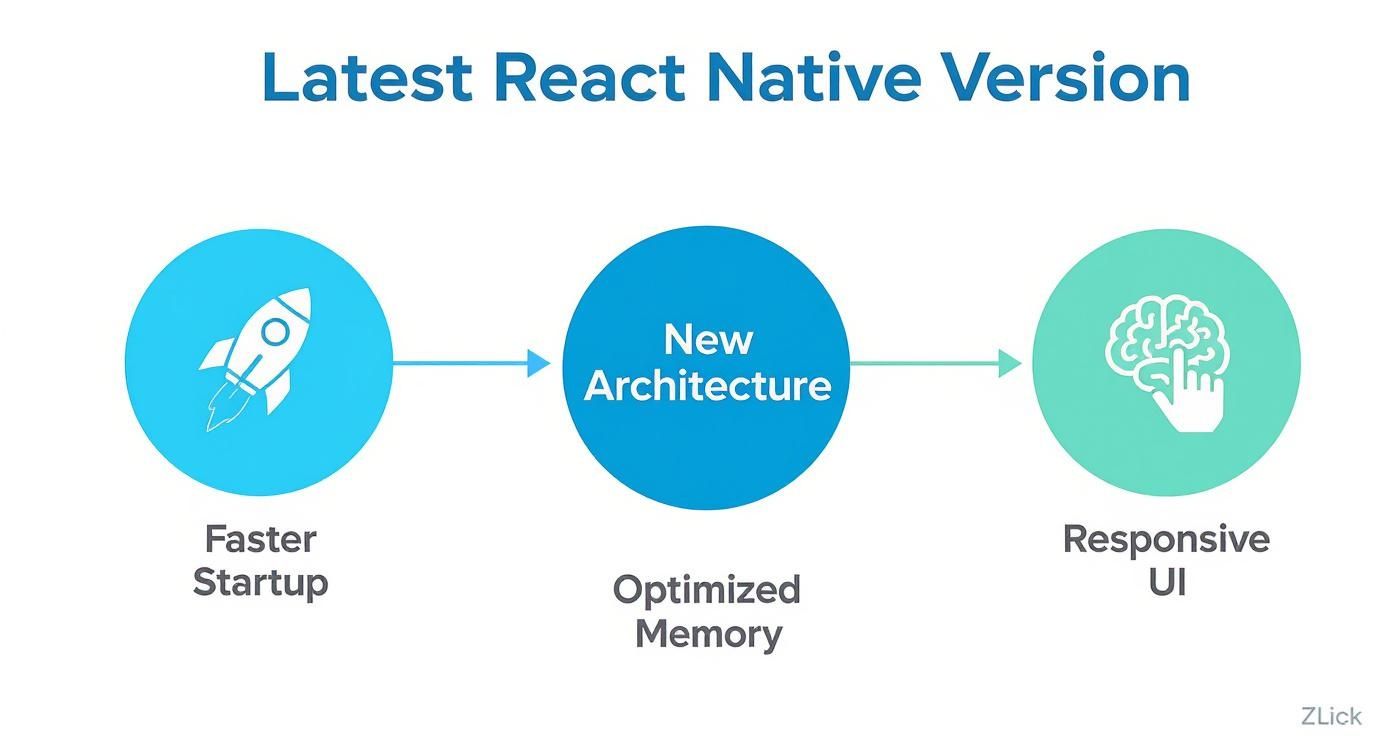
As you can see, the direct results are faster app startup times, better memory management, and a UI that feels incredibly snappy.
Key Components: Fabric and TurboModules
Sitting on top of the JSI are two other game-changers: TurboModules and Fabric. They work together to deliver some serious performance gains.
- TurboModules: Think of these as the smarter, faster successors to the old Native Modules. In the past, every native module had to be initialized the moment your app launched, whether you needed it or not. TurboModules, on the other hand, are loaded lazily—only when they’re actually used. This simple change can slash initial app startup times by up to 40%.
- Fabric Renderer: This is the new rendering engine. It gives JavaScript the power to create native views synchronously, which is huge for eliminating the stutter and “jank” you sometimes see during heavy animations or screen transitions. Fabric keeps the UI thread free and responsive.
JSI provides the direct line of communication, TurboModules ensure we only load what we need, and Fabric makes the UI rendering instantaneous. Together, they create a system where high performance is built-in, not something you have to fight for.
If you want to really get into the weeds, you can learn more about how the React Native New Architecture works and what it means for your day-to-day coding. This is the stuff that finally allows React Native to deliver an experience that feels truly native, closing the gap with apps built from the ground up in Swift or Kotlin.
What Else Is New? Features and Enhancements You Need to Know
While the New Architecture is grabbing all the headlines, this latest React Native version is also loaded with other critical features that will immediately improve your day-to-day workflow and your app’s performance. Think new debugging tools, better APIs, and a much smoother developer experience.
Let’s dig into what’s new.

One of the biggest leaps forward is in performance monitoring. For years, web developers have had a treasure trove of tools to measure and diagnose performance right in the browser. Mobile development, on the other hand, often felt like flying blind, forcing us to rely on clunky, platform-specific profilers.
This release finally starts to bridge that gap by bringing powerful, web-inspired diagnostics straight into the React Native world.
Introducing Web Performance APIs
The latest React Native version brings in a subset of the Web Performance APIs, something many of us have been wanting for a long time. This gives developers a level of visibility into app runtime behavior that was simply out of reach before—we’re talking millisecond-level precision.
For anyone working on large-scale apps, this is a huge deal. Teams can now collect real-world performance data, catch regressions before they ship, and benchmark new features using familiar patterns. You can get more details on these APIs over at the official React Native blog.
Here’s a quick look at what’s included:
- High Resolution Time: Get incredibly precise, sub-millisecond timestamps for accurate measurements.
- Performance Timeline: See a chronological log of all performance-related events happening in your app.
- User Timing API: Create your own custom performance marks and measures to track specific user flows.
- Event Timing API: Measure the latency of critical events, like the time from a button press to a screen update.
- Long Tasks API: Automatically flag any tasks that block the main thread and cause that dreaded UI jank.
This toolkit lets you move away from guesswork and pinpoint exactly what’s slowing your app down with hard data.
Modernizing the Developer Tooling
Beyond just performance, the everyday developer experience has gotten some much-needed upgrades. The tools you rely on are now faster, smarter, and more in line with modern JavaScript standards. For a broader look at the ecosystem, check out our guide on essential React Native development tools.
A key change is the new Strict TypeScript API. This is an opt-in feature that gives you more accurate and safer types for the core React Native library. Turning this on means you’ll catch more errors during development, not after you’ve shipped to users, which leads to far more stable code.
By embracing stricter type safety and providing better diagnostic tools, the framework is really growing up. These changes are all about helping us build more reliable applications at scale, cutting down on bugs and making debugging less of a headache.
This release also cleans up how JavaScript interacts with native components. Deep imports from the react-native package are now deprecated, which nudges everyone toward using a more stable and predictable public API. This small change prevents your app from breaking unexpectedly when you upgrade React Native in the future.
These might seem like minor tweaks, but together they create a much more professional and stable development environment, making it that much easier to build great apps.
Navigating Breaking Changes and Deprecations
Alright, let’s talk about the tricky part of any major upgrade: breaking changes. It’s never fun when something that used to work suddenly doesn’t, but there’s a good reason for it. Think of it like a city upgrading its old infrastructure—it’s disruptive for a bit, but the end result is a more efficient and reliable system for everyone.
These changes are intentional and crucial for the long-term health of React Native. The core team is cleaning up the codebase, pushing for better development patterns, and paving the way for the New Architecture to really shine. It might feel like a headache at first, but getting through these updates is what will make your app more stable and ready for the future.
Here’s your no-nonsense guide to what’s been removed or changed, why the team made these calls, and how you can get your code updated without pulling your hair out.
Key Deprecations to Address
One of the first things you’ll likely run into is the deprecation of the built-in <SafeAreaView> component. This component was always a bit of a workaround, originally built just for iOS. In today’s world of edge-to-edge Android screens, it just doesn’t cut it anymore.
If you’re using it, you’ll start seeing warnings light up your console. The fix is simple and actually a big improvement:
- Switch to
react-native-safe-area-context: This is the library pretty much everyone uses anyway. It’s powerful, works flawlessly on both iOS and Android, and gives you fine-grained control over how your UI handles notches, punch-holes, and dynamic islands. It’s a must-have.
The other big shift is the removal of the built-in JavaScriptCore (JSC) engine. For a long time, Hermes has been the default and far superior JavaScript engine for React Native. Now, it’s official—JSC has been moved out of the core and into a community-run package.
The message from the core team is loud and clear: they’re doubling down on modern, high-performance tools. Standardizing on Hermes and promoting best-in-class libraries like
react-native-safe-area-contextmakes the framework leaner and the entire ecosystem stronger.
If for some reason your project is still tied to JSC, you’ll need to manually install the community package to keep it running. Honestly, though, this is the perfect nudge to finally make the switch to Hermes. You’ll see real, noticeable gains in startup time and memory usage.
Understanding Important Breaking Changes
Beyond components being removed, a few other changes will require you to tweak your code. A big one is that deep imports from the react-native package are now a no-go. You’ll get warnings if you’re doing something like import View from 'react-native/Libraries/Components/View/View'.
This change is all about creating a stable public API. By preventing developers from reaching into the framework’s internal files, your app is less likely to break when you upgrade in the future. The rule is simple: always import directly from the react-native package itself.
On the tooling side, the minimum version requirements have also been updated. You’ll need to make sure your development environment is up to spec:
- Node.js: Now requires version 20 or higher.
- Xcode: Now requires version 16.1 or higher.
Get your local machine and your CI/CD pipelines updated to these baselines. It’s a small step that prevents a world of build-related headaches down the line and ensures you’re on a secure, fully supported toolchain.
How to Upgrade to the Latest React Native Version
Let’s be honest, upgrading your React Native app can feel like a major chore. But with a solid game plan, you can sidestep the usual headaches and get your project running on the latest version smoothly. This is your roadmap to tackling the upgrade process with confidence.

Before you touch a single line of code, preparation is everything. From my experience, almost every upgrade nightmare stems from an outdated dependency. So, the first thing you need to do is a full audit of your project’s libraries to see what’s compatible.
Pre-Upgrade Preparation Checklist
A little planning upfront saves hours of debugging later. Seriously, don’t skip these steps.
- Audit Your Dependencies: Open up your
package.jsonand start checking the compatibility of every single library. Pay close attention to the big ones—navigation, state management, and anything that hooks into native code. - Commit Your Code: Make sure every last change is committed to Git or your version control system. You absolutely need a stable, clean checkpoint to revert to if things go sideways.
- Read the Changelog: Head over to the official release notes for the new version. This is your bible. It will detail all the breaking changes, deprecations, and new requirements you need to be aware of.
Upgrading isn’t just about chasing shiny new features. It’s about keeping your app secure, fast, and easier to maintain down the road. The prep work is non-negotiable.
Using the Upgrade Helper Tool
Once your prep is done, your best friend for the actual upgrade is the official React Native Upgrade Helper. It’s a fantastic web tool that gives you a side-by-side comparison of the template files from your current version and the new one.
This isn’t a magic script that does it all for you; think of it as a detailed guide. You’ll need to go through and manually apply the changes it shows to your own native configuration files, like build.gradle for Android or your Podfile for iOS. This hands-on process is actually a good thing, as it forces you to understand exactly what’s changing under the hood. For a much deeper look into potential gotchas and advanced fixes, our comprehensive React Native upgrade guide has you covered.
Post-Upgrade Verification and Debugging
After you’ve applied all the necessary changes, it’s time to test. And I mean really test. Don’t just see if the app boots up; you need to run through all your key user flows to spot any regressions that might have snuck in.
Here’s a quick checklist for the final stretch:
- Clean and Rebuild: Nuke your
node_modules,Pods, and build folders. Then, runnpm installandpod installto ensure you’re starting from a completely fresh slate. - Test on Both Platforms: Fire up your app on both iOS and Android simulators. Better yet, test on real physical devices if you have them.
- Watch for Warnings: Keep a close eye on the console. New warnings are often the first sign that you’re using a deprecated API that needs to be updated.
Keeping your app updated also keeps your skills sharp. The demand for React Native developers is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16.7% through 2033, largely because companies can save up to 40% on development costs. You can read more about the rise of React Native development to see how staying current puts you ahead of the curve.
Questions You Might Have About the Upgrade
Whenever a new version drops, especially one this big, questions are bound to pop up. It doesn’t matter if you’ve been working with React Native for years or are just getting started; it pays to look before you leap. Here, we’ll tackle some of the most common questions we’ve been hearing from the community about the latest React Native version.
Our goal is to give you clear, straightforward answers so you can make the right call for your projects.
Should I Upgrade Right Away?
This is the classic “it depends” question, but let’s break it down. The performance boosts from the New Architecture are no joke. We’re talking about apps seeing up to 40% faster startup times and a 20-30% reduction in memory usage. Those numbers alone are pretty convincing.
But here’s the catch: third-party library compatibility. While the big, popular libraries are mostly on board, some smaller or less frequently updated packages might not be ready yet. If you have a small, relatively simple app, go for it—the benefits are likely worth it. For a massive enterprise app loaded with dependencies, you’ll want to take a more cautious, phased approach. Test everything on a separate branch first.
How Does the New Architecture Affect My Libraries?
This is a big one. The New Architecture completely rethinks how JavaScript communicates with native code, and that has a direct impact on any third-party library with native modules. For a library to work seamlessly, it needs to be updated to support the new TurboModules and Fabric renderer.
The good news is the React Native team was smart about this. They created an interoperability layer called Bridgeless Mode, which lets many older libraries still function with the New Architecture. You just won’t get the full performance kick until those libraries are properly migrated.
Before you even think about upgrading, do this:
- Audit Your Dependencies: Go through the documentation for your most critical libraries and confirm they support the latest version.
- Hunt for Alternatives: If a key package is lagging, see if there are more modern, actively maintained alternatives you can swap in.
- Help Out: If you rely heavily on an open-source library, consider contributing to its upgrade process. It helps everyone.
What Are the Biggest Performance Wins I Can Expect?
Your mileage will vary depending on your app’s complexity, but the gains are significant pretty much everywhere. The real magic comes from the core components of the New Architecture.
- Quicker App Startup: TurboModules uses lazy-loading, meaning your app only spins up native code when it’s actually needed. This makes a huge difference in how fast your app gets up and running.
- Buttery Smooth Animations: The Fabric renderer handles UI updates synchronously. This gets rid of the slight lag or “jank” you might have seen with the old bridge, making animations and gestures feel incredibly responsive.
- Lighter Memory Load: The memory management is just plain better, which means fewer crashes and a smoother experience, especially for users on older or less powerful devices.
Does This Update Make React Native a Better Choice Than Flutter?
This release really does level the playing field. For a long time, Flutter’s high-performance rendering engine was its killer feature. With Fabric, React Native has effectively closed that performance gap, offering an experience that feels truly native.
Ultimately, the best choice still boils down to your team’s expertise. If your developers are already fluent in JavaScript and React, the latest React Native version is an absolute powerhouse. You get that near-native performance without having to learn an entirely new language like Dart. To get a better sense of which toolchain might suit your team, it’s worth exploring the differences between Expo versus React Native CLI development.
At CodePushGo, we help you deliver those updates and bug fixes instantly, without waiting for app store reviews. Ship faster and with more confidence today.




