In today’s competitive mobile landscape, a flawless user experience is no longer a luxury, it’s a requirement. Users expect apps to be fast, secure, and reliable, regardless of their device or network connection. A single critical bug can lead to negative reviews, uninstalls, and significant brand damage. This is where a robust testing strategy becomes paramount.
However, simply running a few automated scripts is not enough. Effective mobile app testing requires a multi-faceted approach that covers everything from platform-specific nuances to real-world performance bottlenecks. This guide presents seven crucial mobile app testing best practices that modern development teams must adopt to stay ahead.
We will explore actionable strategies specifically tailored for React Native applications, covering the entire lifecycle from code deployment and automation to rigorous security and performance validation. For each best practice, we’ll provide concrete steps you can implement immediately. You will also see how modern tools like CodePushGo can streamline these complex processes, helping you deliver higher-quality apps faster and with greater confidence. Let’s dive into the essential practices that will upgrade your testing framework for 2025 and beyond.
1. Platform-Specific Testing
While cross-platform frameworks like React Native promote code reuse, treating iOS and Android as identical environments is a critical mistake. Platform-specific testing is a fundamental mobile app testing best practice that involves creating distinct test strategies for each operating system. This approach acknowledges that iOS and Android have unique UI/UX conventions, hardware configurations, API behaviors, and user expectations. A “one-size-fits-all” testing strategy will inevitably miss platform-exclusive bugs that can frustrate users and harm your app’s reputation.
The core principle is to validate that your application not only functions correctly but also feels native on each platform. This means respecting established design languages like Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines and Google’s Material Design. For instance, a user expects a swipe-to-delete gesture on an iOS list, while an Android user might look for a long-press context menu. Ignoring these nuances leads to a disjointed and unintuitive user experience.
Why It’s a Best Practice
Platform-specific testing directly addresses the fragmentation of the mobile ecosystem. It ensures your app integrates seamlessly with native features, such as push notifications, camera APIs, and permission handling, which often behave differently across OS versions and manufacturers. This detailed approach improves stability, enhances usability, and significantly boosts user satisfaction by delivering a polished, platform-aware experience. Adopting this practice is a key component of a robust quality assurance process, much like those found in agile mobile app development.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Create Platform-Specific Test Matrices: Develop detailed matrices that map features against specific OS versions, device models (e.g., iPhone 15 vs. Samsung Galaxy S24), and screen sizes. This helps organize test execution and ensures comprehensive coverage.
- Leverage Native Testing Frameworks: For deep integration testing, supplement your React Native tests with platform-native tools. Use XCTest for iOS to verify interactions with native iOS components and Espresso for Android to test intricate UI logic and system integrations.
- Document Separate Acceptance Criteria: Your product and QA teams should define and document distinct acceptance criteria for each platform. For example, the criteria for handling notifications on iOS 17 should differ from those for Android 14 due to their unique system-level controls and user permissions.
2. Real Device Testing
While simulators and emulators are invaluable for early-stage development and rapid iteration, they cannot fully replicate the complexities of real-world usage. Real device testing is an essential mobile app testing best practice that involves executing tests on physical hardware. This approach is critical for validating an app’s performance, stability, and compatibility under authentic conditions, including varying network strengths, battery levels, hardware limitations, and unique manufacturer OS customizations.

The core principle behind real device testing is to uncover issues that are impossible to simulate. For example, a banking app’s fingerprint authentication must be tested on different sensor types, and a ride-sharing app like Uber needs to verify GPS accuracy across various device chipsets. Similarly, an AR-heavy app like Pokémon GO must validate its camera overlay features on a wide range of hardware. Relying solely on virtual environments means these critical, hardware-dependent interactions go untested, leading to production failures.
Why It’s a Best Practice
Real device testing provides unparalleled accuracy for performance and user experience validation. It allows you to measure an app’s true CPU, memory, and battery consumption, and to test its response to real-world interruptions like incoming calls or low-battery alerts. By running tests on actual devices, you ensure your app works flawlessly for your target audience, from those with the latest flagships to those on older, less powerful models. This practice bridges the gap between development theory and user reality, which is a key goal in any comprehensive beta testing strategy.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Build a Prioritized Device Lab: Maintain an in-house lab of physical devices, prioritizing models based on your user analytics data. Focus on the most popular devices and OS versions within your target market to maximize the impact of your testing efforts.
- Utilize Cloud-Based Device Farms: For comprehensive coverage without the overhead of a physical lab, use cloud services like AWS Device Farm, BrowserStack, or Sauce Labs. These platforms provide access to hundreds of real device models and configurations on demand.
- Test Under Realistic Network Conditions: Don’t just test on a stable office Wi-Fi connection. Use real devices to test your app’s behavior on fluctuating 4G/5G networks, in low-signal areas, and during transitions between Wi-Fi and cellular data.
- Document and Categorize Device-Specific Bugs: When a bug is found only on a specific device (e.g., a OnePlus running a custom version of Android), document it meticulously with the model, OS version, and steps to reproduce. This helps isolate issues related to manufacturer-specific software skins.
3. Performance Testing
A functional app is only half the battle; a slow, resource-hungry app will quickly be uninstalled. Performance testing is a critical mobile app testing best practice that evaluates an application’s responsiveness, speed, stability, and resource consumption under various conditions. This process goes beyond simple functionality checks to measure key metrics like app launch times, CPU and memory usage, battery drain, and network efficiency. The goal is to ensure a smooth, snappy user experience, regardless of the user’s device or network quality.
For example, an e-commerce app must render product lists instantly, while a social media app like Facebook meticulously optimizes News Feed loading to minimize perceived latency. Similarly, streaming services like Netflix rigorously test video playback performance across fluctuating network conditions to prevent buffering. These scenarios highlight how performance directly impacts user retention and satisfaction. Neglecting this stage can lead to a sluggish app that frustrates users and earns negative reviews.
Why It’s a Best Practice
Performance testing is essential for delivering a high-quality mobile experience in a fragmented device market. It helps identify and eliminate bottlenecks, memory leaks, and excessive battery consumption that can render an app unusable, especially on older or lower-end devices. By simulating real-world usage scenarios, such as poor connectivity or low battery, you ensure the app remains reliable and efficient. A strong performance testing strategy is a cornerstone of effective quality assurance and is closely tied to the principles outlined in application performance monitoring best practices.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Establish Clear Performance Benchmarks: Define and document acceptable performance targets before testing begins. For example, specify that the app must launch in under 2 seconds on a mid-range Android device or that scrolling a list should not exceed 50% CPU usage.
- Utilize Profiling Tools: Leverage built-in and third-party profiling tools to pinpoint performance issues. Use Instruments for iOS to analyze CPU, memory, and energy usage, and Android Studio Profiler for Android to detect memory leaks and CPU spikes in your React Native app.
- Test Under Adverse Conditions: Don’t just test on a high-end device with a stable Wi-Fi connection. Simulate real-world stress by testing on devices with low battery, limited storage, and throttled network speeds (e.g., 3G) to uncover performance degradation.
- Automate and Monitor Continuously: Integrate performance tests into your CI/CD pipeline to catch regressions early. Use automated scripts to measure key metrics with every build and monitor performance in production to identify issues affecting real users.
4. Network Condition Testing
Users access mobile apps from everywhere: a crowded subway with spotty Wi-Fi, a remote area with a weak 3G signal, or during a seamless switch from Wi-Fi to cellular data. Network condition testing is a crucial mobile app testing best practice that simulates these real-world connectivity challenges. It involves validating an app’s behavior under various network scenarios, including slow speeds, high latency, intermittent connections, and complete offline mode. Ignoring these conditions leads to crashes, data loss, and a frustrating user experience that can quickly drive users away.
The primary goal is to ensure the application remains stable, functional, and user-friendly regardless of network quality. This means gracefully handling connection timeouts, providing clear feedback to the user (e.g., loading indicators or offline notifications), and ensuring data integrity is maintained. For instance, an app like Google Drive must be able to pause an upload when a connection drops and seamlessly resume it once connectivity is restored, preventing data corruption or duplicate files.
Why It’s a Best Practice
Effective network condition testing is a cornerstone of building a resilient and reliable mobile application. It ensures your app doesn’t just work in the ideal conditions of your office Wi-Fi but performs predictably in the unpredictable environments your users face daily. This practice is vital for maintaining user trust, especially for apps that handle critical data or transactions. By proactively identifying and addressing how your app handles poor connectivity, you prevent negative reviews, reduce user churn, and build a reputation for dependability and quality.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Test Critical Journeys Under Duress: Identify and prioritize critical user flows, such as login, checkout, or data submission. Systematically test these journeys on simulated 2G, 3G, and “flaky” network profiles to ensure they don’t fail catastrophically.
- Implement and Verify Retry Logic: Ensure your app has robust error handling and intelligent retry mechanisms for failed network requests. Test that these mechanisms work as expected without spamming your server or draining the user’s battery.
- Validate Caching and Offline Functionality: Confirm that data is correctly cached for offline access and that the app provides a meaningful experience even without a connection. For example, Spotify’s offline playback must function flawlessly. Test the synchronization logic that updates local data once the connection is re-established.
- Use Network Simulation Tools: Employ tools to create repeatable and controlled test scenarios. Apple’s Network Link Conditioner (for iOS) and Android Studio’s emulator settings allow you to simulate various network profiles, including specific bandwidth, packet loss, and latency, making this a core part of your mobile app testing best practices.
5. Security Testing
In an era where data breaches are common, security cannot be an afterthought; it must be a core component of your mobile app testing best practices. Security testing is a comprehensive process designed to uncover vulnerabilities, threats, and risks in your application. It involves a systematic evaluation of data storage, user authentication, session management, and API communications to ensure the application is resilient against malicious attacks. Forgetting this step exposes your users, and your business, to significant harm, from data theft to reputational damage.
The goal is to proactively identify and fix security flaws before they can be exploited. This means going beyond basic functionality checks to simulate real-world attack scenarios. For example, a banking app must not only validate that transactions work but also ensure that transaction data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, and that strong multi-factor authentication prevents unauthorized access. Similarly, a messaging app like Signal must rigorously test its end-to-end encryption protocols to guarantee user privacy.
Why It’s a Best Practice
Comprehensive security testing is critical for building user trust and protecting sensitive information. A single vulnerability can lead to catastrophic consequences, including financial loss, legal penalties, and a complete loss of customer confidence. By integrating security testing throughout the development lifecycle, you can identify weaknesses early, making them cheaper and easier to fix. This proactive approach ensures compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA and demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding user data, which is a powerful competitive differentiator. For a deeper exploration of this topic, consider reading about effective mobile app security testing.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Test for OWASP Mobile Top 10: Familiarize your team with the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Mobile Top 10 list. Systematically test your app for these common vulnerabilities, such as insecure data storage, improper platform usage, and insecure authentication.
- Perform Static and Dynamic Analysis (SAST & DAST): Use Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools to scan your source code for potential vulnerabilities before compilation. Complement this with Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST), which tests the app in its running state to find vulnerabilities that only appear during execution.
- Conduct Penetration Testing: Hire independent security experts to perform penetration testing. These “ethical hackers” will simulate real-world attacks to identify weaknesses that automated tools and internal teams might miss, providing an unbiased assessment of your app’s defenses.
6. Usability Testing
While functional tests confirm that your app works, usability testing answers a more critical question: is it easy and enjoyable to use? This mobile app testing best practice focuses on evaluating the user experience (UX) from the perspective of a real user. It goes beyond technical correctness to assess the intuitiveness of navigation flows, the clarity of the interface design, and the overall satisfaction a user feels while interacting with the application. A technically flawless app can still fail if users find it confusing, frustrating, or inefficient.

The fundamental goal is to uncover friction points in the user journey. For example, Airbnb invests heavily in usability testing to refine its booking flow, ensuring users can find and reserve a property with minimal effort. Similarly, Apple’s commitment to accessibility testing for features like VoiceOver ensures its products are usable by everyone. These efforts highlight that a smooth, intuitive experience is not an accident but the result of deliberate and user-centric testing.
Why It’s a Best Practice
Usability testing provides direct, qualitative insights that quantitative metrics alone cannot capture. It reveals why users are dropping off at a certain screen or why a new feature is being ignored. By observing real user behavior, you can identify design flaws, confusing copy, and unintuitive layouts that automated tests would miss. This proactive approach reduces the risk of post-launch redesigns, increases user retention, and builds a loyal user base that appreciates an app designed with them in mind.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Recruit Diverse User Groups: Ensure your test participants represent your target demographics, including varying levels of technical proficiency, age groups, and accessibility needs. A feature that is clear to a tech-savvy user might be confusing to another.
- Use Task-Based Scenarios: Instead of giving vague instructions, create specific, goal-oriented tasks. For example, ask a user to “add three items to the cart and apply a discount code.” This helps evaluate specific user flows and pinpoint exact areas of difficulty.
- Combine Qualitative and Quantitative Data: Record user sessions (with permission) and encourage them to “think aloud” to capture qualitative feedback. Supplement this with quantitative data like task completion times, error rates, and analytics to get a comprehensive view of the user experience.
- Implement Accessibility Checks: Use tools like accessibility scanners and manual testing with screen readers (e.g., VoiceOver on iOS, TalkBack on Android) to ensure your app complies with WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) and is usable by people with disabilities.
7. Automated Testing Integration
Manual testing alone cannot keep pace with the rapid release cycles of modern mobile app development. Automated testing integration is a critical best practice that involves embedding comprehensive, automated test suites directly into your development workflow. This approach systematically executes unit, integration, and UI tests across various devices and platforms without manual intervention. By automating these checks, teams can catch regressions, validate new features, and ensure consistent quality with every code commit.
The goal of this practice is to create a safety net that provides rapid, reliable feedback. When properly integrated into a Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline, automated tests act as gatekeepers, preventing faulty code from reaching production. For example, Netflix runs extensive automated test pipelines to verify streaming quality and UI behavior across hundreds of device types, ensuring a stable user experience with each app update. This level of rigor is a hallmark of mature mobile app testing best practices.
The infographic below summarizes the core pillars of an effective automated testing strategy, including the test pyramid model and CI/CD integration.
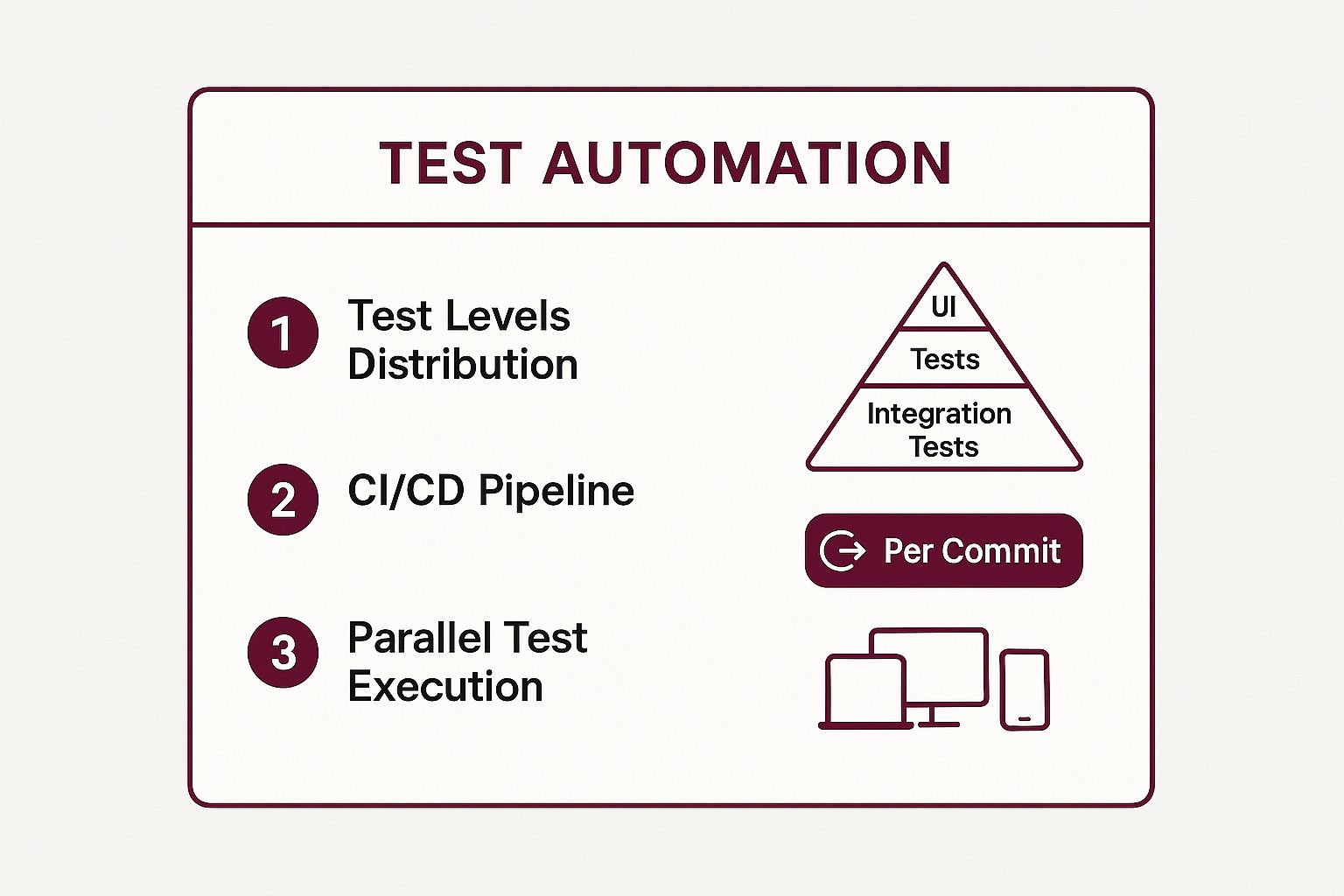
This visualization highlights how a balanced test suite, triggered automatically and run in parallel, forms the backbone of an efficient and scalable quality assurance process.
Why It’s a Best Practice
Automated testing integration fundamentally accelerates the development lifecycle while increasing confidence in code quality. It allows developers to identify and fix bugs early, when they are cheapest and easiest to resolve. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tests, it frees up QA engineers to focus on more complex exploratory testing and edge-case analysis. This practice is essential for maintaining velocity in agile environments and ensuring your application remains stable and reliable as it evolves. To learn more about how this fits into your workflow, you can explore the principles of testing in continuous integration.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Implement the Test Pyramid Strategy: Structure your test suite according to the test pyramid model popularized by Martin Fowler. Focus on a large base of fast, isolated unit tests, a smaller layer of integration tests to check component interactions, and a very small number of slow, brittle end-to-end UI tests.
- Start with Critical User Journeys: Don’t try to automate everything at once. Prioritize automating the most critical user paths, such as user login, the checkout process, or core feature interactions. This delivers the highest return on investment early on.
- Integrate Tests into Your CI/CD Pipeline: Configure your CI server (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions) to automatically trigger the relevant test suite on every commit or pull request. A failed test should immediately block the merge, preventing bugs from entering the main codebase.
- Use the Page Object Model (POM): For UI automation, implement the Page Object Model design pattern. This practice separates test logic from UI element locators, making your tests more readable, maintainable, and resilient to UI changes.
Best Practices Comparison of 7 Mobile App Testing Methods
| Testing Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform-Specific Testing | High - requires platform expertise and separate test plans | Moderate to High - needs multiple platform tools and environments | Detects platform-specific bugs; ensures UI/UX consistency | Apps needing optimized native experience per OS | Ensures app store compliance; platform-tailored validation |
| Real Device Testing | Medium - managing physical devices and setups | High - costly device procurement and maintenance | Accurate real-world behavior detection and performance metrics | Apps with hardware-dependent features or diverse devices | Reveals device-specific issues; authentic interaction testing |
| Performance Testing | High - specialized tools and expert analysis | Moderate - profiling tools and test time intensive | Identifies bottlenecks; optimizes resource consumption | Apps requiring responsiveness and resource efficiency | Prevents crashes; improves user retention and battery life |
| Network Condition Testing | High - complex network simulations | Moderate - needs network simulation tools | Validates app stability under varied network scenarios | Apps dependent on reliable network performance | Ensures data integrity; improves UX in poor connectivity |
| Security Testing | High - requires specialized knowledge | Moderate to High - security tools and expert time | Detects vulnerabilities; ensures data protection | Apps handling sensitive or financial data | Builds user trust; ensures regulatory compliance |
| Usability Testing | Medium - extensive user involvement | Moderate - recruiting diverse users and tools | Improves UI intuitiveness; identifies accessibility issues | Apps focused on user experience and accessibility | Enhances user satisfaction; provides actionable feedback |
| Automated Testing Integration | High - technical setup and maintenance overhead | Moderate to High - automation frameworks and CI/CD resources | Faster bug detection; consistent test execution | Projects emphasizing rapid delivery and repeatable tests | Reduces manual effort; supports continuous integration |
Streamline Your Testing and Deployment with CodePushGo
Navigating the complex world of mobile application development requires a steadfast commitment to quality. The mobile app testing best practices detailed throughout this guide, from platform-specific validation to rigorous security audits, form the bedrock of a successful app. Mastering these techniques is not merely about finding bugs; it is about building user trust, protecting your brand’s reputation, and delivering a seamless, reliable experience that keeps users engaged.
A truly effective testing strategy is comprehensive and layered. It acknowledges that a flaw in any single area, whether it’s poor performance on low-end devices, a security vulnerability, or a confusing user interface, can undermine the entire product. By embracing a holistic approach that combines automated checks with manual, real-world validation, you create a powerful quality assurance firewall.
Key Takeaways for Robust App Quality
Recapping our journey, several core principles stand out as non-negotiable for any serious development team:
- Embrace Real-World Conditions: Testing cannot happen in a vacuum. Simulating varied network conditions, testing on a diverse matrix of real devices, and understanding platform-specific nuances are essential for building an app that performs reliably for every user, everywhere.
- Automate Intelligently: Automation is your greatest ally for speed and consistency. Integrating automated tests into your CI/CD pipeline for regression, performance, and API validation frees up your QA team to focus on more complex, exploratory, and usability-focused testing.
- Prioritize Security from Day One: Security is not an afterthought. Implementing static and dynamic security testing (SAST/DAST) and regularly scanning for vulnerabilities in third-party libraries protects your users and your business from catastrophic breaches.
- Listen to Your Users: Usability and beta testing provide invaluable qualitative feedback. Observing real users interact with your app reveals friction points and opportunities for improvement that quantitative metrics alone cannot capture.
Bridging the Gap Between Testing and Production
Even with the most exhaustive testing protocols, the dynamic nature of mobile ecosystems means that post-release issues are inevitable. The critical differentiator is your ability to respond. This is where the synergy between testing and deployment becomes paramount. Your rigorous testing identifies issues, and your deployment mechanism determines how quickly you can resolve them.
This is precisely where a tool like CodePushGo transforms your workflow. It acts as the final, agile layer in your quality assurance strategy. When a critical bug slips through or an urgent performance fix is needed, you no longer need to endure the prolonged app store review cycle.
CodePushGo empowers React Native developers to deploy instant over-the-air (OTA) updates directly to users’ devices. By integrating it into your release process, you can leverage its channel-based system to support your testing efforts. For example, you can push a fix to a “beta-testers” channel first, validating the solution with a small, controlled group before rolling it out to your entire user base. This closes the loop, turning your deployment tool into an extension of your testing framework and ensuring you can maintain a high-quality user experience with unparalleled agility.
Ready to close the gap between finding bugs and fixing them instantly? Discover how CodePushGo can supercharge your React Native development lifecycle. Visit CodePushGo to learn how you can implement instant, targeted, and safe over-the-air updates to complement your mobile app testing best practices.




