Level Up Your Code Quality with Regression Testing Best Practices
Delivering high-quality app updates quickly is crucial. Regression testing ensures new code doesn’t introduce bugs or break existing features. This listicle provides seven regression testing best practices to mitigate risks, reduce downtime, and improve software quality. Learn how to optimize your testing strategy with techniques like risk-based testing, automated suite maintenance, test selection, CI integration, data-driven testing, reporting metrics, and visual regression testing. These practices empower React Native developers, DevOps, QA, security teams, and product managers to ship reliable software efficiently.
1. Risk-Based Regression Testing
Risk-based regression testing is a crucial best practice that elevates the efficiency and effectiveness of your regression testing efforts. Instead of treating all test cases equally, this approach prioritizes them based on the potential impact a failure would have on critical business functions, the likelihood of failure occurring, and the feature’s past defect history. This targeted strategy ensures that the most critical areas of your application receive the most thorough testing, especially valuable when time and resources are limited. This makes it an essential best practice for regression testing.
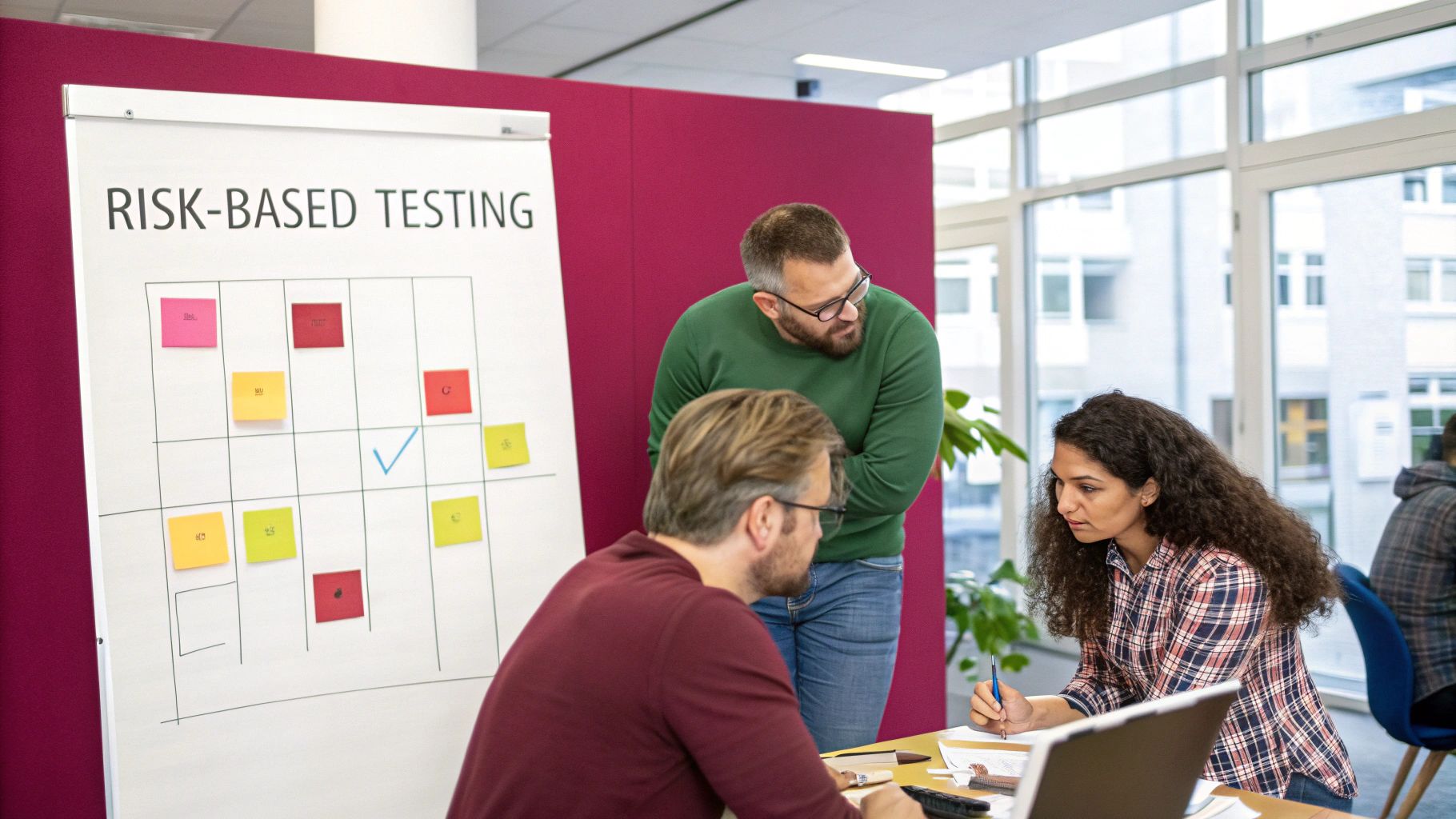

Risk-based regression testing involves a systematic process. First, a thorough risk assessment is conducted for each feature or module. This assessment often utilizes a prioritization matrix that combines the potential impact of a failure with the likelihood of that failure occurring. A weighted scoring system is then used to determine the priority of each test case. This allows teams to focus their limited resources on the most critical areas – those with the highest potential for disruption and greatest impact on business operations.
For React Native app developers, DevOps and release engineers, and QA teams, this method offers a practical approach to managing the complexity of regression testing, particularly in rapidly iterating environments. Security-conscious enterprise organizations will appreciate the emphasis on testing high-risk areas, helping mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Product managers seeking real-time insights will find the data-driven approach valuable in understanding areas needing attention and optimizing resource allocation.
Features of Risk-Based Regression Testing:
- Systematic risk assessment: Each feature/module is evaluated for its potential impact and failure likelihood.
- Prioritization matrix: Combines impact and likelihood to create a clear visualization of risk.
- Weighted scoring: Assigns a numerical score to each test case based on its risk level, streamlining prioritization.
- Focus on business-critical functionality: Ensures that core features are thoroughly tested, minimizing business disruption.
Pros:
- Maximizes test coverage with limited resources.
- Ensures business-critical functions receive adequate testing.
- Reduces overall regression testing time.
- Provides better ROI on testing effort.
Cons:
- Requires a detailed risk analysis, which can be time-consuming.
- May miss defects in lower-priority areas.
- Effectiveness depends on the accuracy of the risk assessment.
- Needs regular reassessment as the application evolves.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Microsoft adopted risk-based regression testing for Windows OS updates, leading to a 30% reduction in testing time while maintaining quality.
- Barclays, a financial services company, implemented this approach for their trading platforms, concentrating on high-risk transaction components.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Create a comprehensive risk matrix: Combine business impact and technical complexity to create a detailed risk profile for each feature.
- Collaboration is Key: Involve both business stakeholders and the technical team in the risk assessment process for a holistic understanding of risk.
- Learn from the past: Review defect history to identify historically problematic areas that may require more attention.
- Stay updated: Reassess risk priorities after major releases or significant changes to the application.
Risk-based regression testing is a highly effective approach popularized by organizations like the ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board) and influential figures such as James Bach and Cem Kaner. By adopting this best practice, development teams can optimize their regression testing process, ensuring that critical functionalities are rigorously tested while maximizing resource utilization and minimizing potential business risks. It deserves its place in this list due to its proven ability to enhance testing efficiency and effectiveness, especially crucial in today’s fast-paced development environments.
2. Automated Regression Test Suite Maintenance
Maintaining a healthy automated regression test suite is paramount to achieving efficient and reliable regression testing best practices. This involves a continuous process of reviewing, updating, and refining your automated tests to ensure they remain aligned with the evolving application and provide accurate, actionable feedback. Without regular maintenance, your test suite can become bloated with obsolete and flaky tests, leading to increased test debt, slower execution times, and decreased confidence in the results. This ultimately undermines the very purpose of regression testing: ensuring software quality and stability.

Automated regression test suite maintenance encompasses several key activities: periodic review and cleanup of test scripts, identification and remediation of flaky tests (tests that produce inconsistent results), refactoring of test code for improved maintainability, meticulous version control for test assets, and keeping test asset documentation up-to-date. These practices are crucial for ensuring the long-term health and effectiveness of your regression testing efforts. For example, identifying and fixing flaky tests drastically reduces false positives and negatives, improving the reliability of your CI/CD pipeline and increasing team confidence in the test results. Refactoring test code enhances readability and maintainability, making it easier for team members to understand, modify, and extend the test suite. Version control enables efficient tracking of changes and facilitates collaboration among team members.
Successful implementation of automated regression test suite maintenance can be seen in companies like Google, who prioritize immediate removal or fixing of flaky tests to maintain the reliability of their continuous integration and delivery pipelines. Spotify utilizes quarterly regression test maintenance sprints to ensure their test suites remain efficient and relevant to the current state of their application. These examples highlight the importance of dedicating time and resources to maintaining your automated tests.
Here are some actionable tips for implementing effective automated regression test suite maintenance:
- Schedule Regular Maintenance Windows: Allocate dedicated time, either monthly or quarterly, for test suite review and cleanup.
- Track Test Quality Metrics: Monitor key metrics like false positives/negatives and test execution time to identify areas for improvement.
- Implement Test Ownership: Assign ownership of specific tests to developers or QA engineers, fostering responsibility and accountability.
- Use Test Analytics: Leverage test analytics tools to identify problematic or redundant tests that require attention.
- Apply Code Review Standards: Hold test code to the same rigorous code review standards as production code.
While maintaining a test suite requires dedicated time and resources, the benefits far outweigh the costs. A well-maintained suite results in faster test execution, reduced long-term maintenance costs, and significantly increased confidence in the reliability of your test results. This also ensures that the tests remain relevant to the current state of the application, providing accurate feedback and preventing regressions. Conversely, neglecting maintenance can lead to a rapid accumulation of technical debt, impacting the efficiency and effectiveness of your regression testing process. Therefore, incorporating regular maintenance is essential for any team striving for robust and sustainable regression testing best practices.
For further exploration, you might find this article relevant: Learn more about Automated Regression Test Suite Maintenance. This practice, championed by thought leaders like Martin Fowler and Angie Jones and supported by organizations like Atlassian, is a cornerstone of effective software development.
3. Regression Test Selection Techniques
Regression test selection techniques are crucial for optimizing your regression testing best practices. These techniques help identify the specific subset of test cases that need to be executed after code modifications. By analyzing code changes, dependencies, and test coverage, these techniques pinpoint the tests most likely to uncover defects related to the recent updates, effectively reducing testing time without sacrificing quality. This is especially important for React Native app developers, DevOps and release engineers, and QA teams working in fast-paced environments.
The infographic above visualizes the process flow for regression test selection. It starts with “Code Changes,” then moves to “Impact Analysis” utilizing both static and dynamic techniques. Next, it branches into “Test Case Prioritization” based on factors like code coverage and historical data, before finally leading to the “Execution of Selected Tests.” The importance of this sequence lies in its ability to systematically narrow down the required tests, optimizing testing efforts and resource allocation. The visualization highlights how targeted testing can lead to faster feedback cycles and quicker identification of potential issues, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and stability of React Native applications.
Features like code change analysis, test-to-code traceability mapping, impact analysis (both static and dynamic), history-based selection, and even machine learning algorithms are employed to predict the most effective test subsets. This approach offers significant advantages, including a dramatic reduction in regression testing time, focused testing efforts on areas most susceptible to defects, and the facilitation of more frequent regression testing cycles, seamlessly integrating with continuous integration workflows. This allows for incremental application and adaptability as code changes occur, ensuring product managers seeking real-time insights get the feedback they need quickly. For example, Facebook utilizes its Sapiens tool for intelligent regression test selection, reportedly reducing test execution by up to 95%, while Microsoft’s FATE system selects regression tests based on file and function dependencies.
However, it’s important to be aware of the potential drawbacks. Regression test selection techniques might miss defects arising from indirect or unforeseen dependencies, and they require sophisticated tooling for accurate impact analysis. The initial setup for test-to-code mapping can also be resource-intensive, and the effectiveness can be limited in highly interconnected codebases.
This approach is invaluable when you need faster feedback cycles and optimized testing, especially after frequent code changes. It’s particularly beneficial for security-conscious enterprise organizations where thorough testing is paramount, but time is of the essence. Starting with a simple static analysis of changed files/methods and gradually implementing code coverage analysis to understand test-code relationships is a good starting point. Tracking test effectiveness metrics allows you to continuously refine selection algorithms, and combining multiple selection techniques often yields the best results. Remember to periodically run the full test suite to catch any regressions that might have slipped through the cracks. The work of researchers like Gregg Rothermel and Mary Jean Harrold, who developed key test selection algorithms, and presentations at the Google Test Automation Conference (GTAC) have significantly popularized and advanced this field.
Tips for Implementing Regression Test Selection:
- Start with simple static analysis of changed files/methods.
- Implement code coverage analysis to understand test-code relationships.
- Track test effectiveness metrics to refine selection algorithms.
- Combine multiple selection techniques for better results.
- Periodically run the full test suite to catch missed regressions.
Learn more about Regression Test Selection Techniques
By understanding and implementing regression test selection techniques, development teams can significantly improve their testing efficiency and ensure the quality and reliability of their software, making it a vital best practice in the world of regression testing.
4. Regression Testing in Continuous Integration
Regression testing is a crucial aspect of software development, ensuring that new code changes don’t introduce unintended side effects or break existing functionality. One of the most effective ways to implement regression testing is by integrating it directly into your Continuous Integration (CI) pipeline. This best practice, known as Regression Testing in Continuous Integration, empowers teams to detect and address regressions early in the development cycle, fostering higher quality software and faster release cycles.
This approach works by automatically triggering a suite of regression tests every time code is committed or merged into the main branch. These tests can encompass various levels, from quick smoke tests verifying core functionalities to comprehensive full regression suites covering the entire application. By automating this process, teams gain immediate feedback on the impact of code changes, preventing the accumulation of bugs and reducing the time it takes to identify and fix them.
Features that facilitate effective Regression Testing in CI include:
- Automated Test Execution: Tests are automatically triggered by code commits or merges.
- Multi-level Test Execution: Different test suites (smoke, critical path, full regression) can be executed based on the context of the code change.
- Parallel Test Execution: Running tests concurrently significantly reduces overall testing time, providing faster feedback.
- Test Result Reporting and Notification Systems: Automated reports and notifications alert developers to test failures and provide detailed diagnostics.
- Test Failure Analysis and Triage Automation: Tools and processes to automatically analyze test failures and assign them to the appropriate developers for resolution.
The advantages of integrating regression testing into your CI pipeline are numerous:
- Provides Immediate Feedback on Potential Regressions: Developers receive immediate notification of any regressions introduced by their code changes.
- Prevents Accumulation of Regression Issues: Regular testing prevents regressions from accumulating, making them easier and less costly to fix.
- Reduces Time Between Introducing and Fixing Bugs: Early detection through CI allows for faster bug fixing, minimizing the impact on development timelines.
- Enables More Frequent Releases with Confidence: Automated regression testing provides the confidence to release software more frequently and with reduced risk.
- Creates a Safety Net for Refactoring Activities: Comprehensive regression tests provide a safety net for refactoring, ensuring existing functionality remains intact.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Requires Significant Upfront Investment in Test Automation: Implementing robust automated tests requires time and resources.
- Can Slow Down CI Pipeline if Tests are Not Optimized: Inefficient tests can significantly increase the overall CI pipeline execution time.
- False Positives Can Reduce Developer Confidence in Tests: Unreliable tests that generate false positives can erode developer trust in the testing process.
- Maintenance Overhead Increases with Test Suite Size: As the test suite grows, so does the effort required to maintain and update it.
Real-world examples demonstrate the power of this practice. Netflix, for example, runs thousands of regression tests in parallel on their CI platform, enabling them to deploy multiple times per day. Similarly, Amazon’s CI system automatically selects and runs regression tests based on the risk profile of code changes, optimizing testing efficiency while maintaining high quality.
To effectively implement Regression Testing in CI, consider these tips:
- Implement a multi-stage testing approach with fast feedback loops: Start with quick smoke tests and progressively run more comprehensive suites.
- Optimize tests for stability and execution speed: Ensure tests are reliable and execute quickly to avoid slowing down the CI pipeline.
- Set up intelligent test distribution for parallel execution: Distribute tests across multiple machines or containers to maximize parallelism.
- Establish clear ownership of test failures: Assign clear responsibility for addressing test failures to ensure prompt resolution.
- Configure actionable notifications with diagnostics data: Provide developers with detailed information about test failures to facilitate debugging.
Influential figures like Martin Fowler, a strong advocate of continuous integration, and Jez Humble, co-author of Continuous Delivery, have popularized this approach. Platforms like Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitHub Actions provide robust support for integrating regression testing into CI workflows.
Learn more about Regression Testing in Continuous Integration
This approach is particularly valuable for React Native app developers, DevOps and release engineers, QA and beta testing teams, security-conscious enterprise organizations, and product managers seeking real-time insights into application stability. By incorporating regression testing into your CI/CD pipeline, you can build a more robust, reliable, and higher-quality software product. This practice deserves its place among the best practices for regression testing because of its ability to provide continuous feedback, prevent the accumulation of bugs, and enable faster, more confident releases.
5. Data-Driven Regression Testing
Data-driven regression testing is a crucial best practice for ensuring the stability and reliability of your software, especially for React Native apps and complex enterprise systems. It earns its place among regression testing best practices by significantly boosting test coverage while keeping test scripts concise and maintainable. This approach separates test logic from test data, allowing you to execute the same test scripts with multiple data sets. This means that instead of writing a new test script for every single input variation, you create one script that can handle a range of data inputs defined externally. This is incredibly valuable for DevOps and release engineers looking to streamline their pipelines and for QA and beta testing teams who need to thoroughly validate functionality across a wide array of scenarios.
How It Works:
The core principle behind data-driven testing lies in externalizing the test data. This data, representing different input values, expected outcomes, and other test parameters, can be stored in various formats like CSV, Excel, XML, or even a database. Your test scripts are then parameterized to read and consume this data during execution. Data generation tools can further enhance this process by automatically creating variations in your test data, covering a broader spectrum of possible scenarios, including valuable boundary value testing. Data-driven assertion capabilities then compare the actual results of your test against the expected outcomes defined in your data set, providing a comprehensive validation of your application’s behavior.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Large-scale applications frequently leverage data-driven testing. Salesforce, for example, uses this technique to validate their CRM platform across thousands of different customer configurations, ensuring consistent performance regardless of individual settings. Similarly, Intuit’s TurboTax employs data-driven regression testing to verify the accuracy of tax calculations across a diverse range of financial scenarios, ensuring compliance and minimizing errors.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Design for Boundary Conditions: Focus your test data design on edge cases and boundary conditions to catch potential issues at the limits of your application’s functionality.
- Leverage Data Generation Tools: Utilize data providers that can generate random and edge case data automatically, saving time and expanding test coverage.
- Track Failing Data Sets: Maintain clear references to which specific data sets caused test failures for easier debugging and faster issue resolution. This is especially valuable for product managers seeking real-time insights into application stability.
- Version Control Test Data: Treat test data with the same importance as your test code. Use version control to track changes and ensure consistency.
- Obfuscate Sensitive Data: If your test data includes sensitive information, implement data obfuscation techniques to protect user privacy and maintain security, a crucial consideration for security-conscious enterprise organizations.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Significantly increases test coverage without increasing script count, leading to more efficient testing and quicker release cycles.
- Improves maintainability of tests through separation of concerns, making updates and modifications easier to manage.
- Enables non-technical stakeholders, such as product owners or business analysts, to contribute test scenarios directly via the data sets.
- Simplifies the testing of locale-specific behaviors and internationalization features through data variations.
- Facilitates comprehensive edge case testing, improving the robustness of your application.
Cons:
- Requires more upfront design and development effort to establish the data-driven framework.
- Can be slightly harder to debug when failures occur due to the indirect relationship between test logic and data.
- May increase overall test execution time depending on the size and complexity of the data sets.
- Requires careful data management to prevent test data corruption and ensure data integrity.
When and Why to Use Data-Driven Testing:
Data-driven testing is particularly effective when:
- Dealing with complex business logic that behaves differently based on various inputs.
- Testing applications that require a wide range of input variations, like e-commerce platforms or financial applications.
- Automating repetitive test cases where only the input data changes.
- Requiring non-technical team members to participate in the testing process.
By adopting data-driven regression testing as a best practice, development teams, particularly those working with React Native and in enterprise environments, can significantly improve the quality and reliability of their applications while optimizing their testing efforts. It’s an investment that pays off in terms of reduced defects, faster release cycles, and increased user satisfaction.
6. Regression Testing Metrics and Reporting
Effective regression testing isn’t just about running tests; it’s about understanding what those tests tell you. Regression Testing Metrics and Reporting is a crucial best practice that provides the visibility needed to assess the health, efficiency, and impact of your regression testing efforts. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and generating insightful reports, teams gain a data-driven perspective on their testing process, allowing for continuous improvement and demonstrable value to stakeholders. This is particularly important for React Native app developers, DevOps and release engineers, QA and beta testing teams, security-conscious enterprise organizations, and product managers seeking real-time insights.
This practice works by systematically collecting data during the regression testing process and analyzing it to extract meaningful information. This data includes details such as test execution time, the number of passed and failed tests, code coverage percentages, and the number of regression defects found. By aggregating and analyzing these metrics, teams can identify trends, pinpoint bottlenecks, and ultimately optimize their regression testing strategy.
Features of Effective Regression Testing Metrics and Reporting:
- Test execution metrics: Track pass/fail rates, test duration, and the number of tests executed.
- Coverage analysis: Measure code coverage, requirements coverage, and feature coverage to ensure comprehensive testing.
- Defect metrics: Monitor the number of regression defects found versus missed, providing insight into test effectiveness.
- Trend analysis: Analyze metrics across multiple test cycles to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
- Real-time dashboards: Offer up-to-the-minute visibility into test status and progress.
Pros:
- Provides objective measurement of regression testing effectiveness.
- Identifies bottlenecks and opportunities for optimization.
- Helps justify testing investments to management.
- Enables data-driven decisions about test strategy.
- Creates transparency across development and QA teams.
Cons:
- Can lead to “metric obsession” at the expense of genuine testing quality.
- Requires additional tooling and integration effort.
- May add overhead to the testing process.
- Some metrics can be misleading without proper context.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Microsoft’s Azure DevOps: Utilizes comprehensive test analytics to continuously optimize their regression test suite, demonstrating the power of data-driven testing.
- Atlassian: Employs a quality dashboard that tracks regression effectiveness across all their products, providing a centralized view of testing performance.
Actionable Tips for Implementing Regression Testing Metrics and Reporting:
- Focus on a small set of actionable metrics: Don’t get bogged down trying to track everything. Start with a few key metrics that align with your testing goals.
- Combine quantitative metrics with qualitative assessment: Numbers tell a story, but don’t forget the importance of human observation and feedback.
- Establish baselines and improvement targets: Setting clear goals provides direction and helps measure progress over time.
- Automate metric collection and reporting: Automation streamlines the process and reduces manual effort.
- Review metrics regularly with both QA and development teams: Collaboration is key to interpreting results and making informed decisions.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Regression Testing Metrics and Reporting is essential whenever you’re performing regression testing. This practice is particularly valuable when:
- Dealing with complex software systems with a large number of test cases.
- Working in Agile or DevOps environments with frequent releases.
- Needing to demonstrate the value of testing to stakeholders.
- Seeking to continuously improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your regression testing process.
This practice deserves its place in the list of regression testing best practices because it provides the necessary feedback loop to ensure that regression testing is achieving its intended purpose. Without metrics and reporting, it’s difficult to assess the true impact of regression testing and identify areas for improvement. Learn more about Regression Testing Metrics and Reporting. This article, while focused on OTA updates, provides valuable insights into tracking success metrics that can be adapted for broader regression testing contexts. By adopting this best practice, teams can move beyond simply running tests and begin leveraging data to optimize their testing strategy and deliver higher-quality software.
7. Visual Regression Testing
Visual regression testing is a crucial part of modern regression testing best practices. It automates the process of detecting unintended visual changes in user interfaces (UIs) by comparing screenshots taken before and after code changes. This approach complements traditional functional regression testing, which verifies that the application’s features work as expected. While functional tests ensure the functionality remains intact, visual regression testing ensures the appearance remains consistent, catching issues like layout shifts, font changes, color mismatches, and rendering errors that might not trigger functional test failures but can significantly impact the user experience.

Visual regression testing tools typically work by capturing screenshots of the application’s UI at various stages, such as before and after a code deployment. These screenshots are then compared using either pixel-by-pixel or DOM-based comparison algorithms. Configurable similarity thresholds determine whether a difference between screenshots constitutes a visual regression. When a difference exceeds the threshold, a visual diff is generated, highlighting the changes for easy identification and review. This is particularly helpful for React Native app developers, as UI changes can subtly break across platforms.
Features of Visual Regression Testing Tools:
- Automated Screenshot Comparison: Automates the comparison of screenshots across different browsers and devices. This is crucial for DevOps and release engineers ensuring consistent cross-platform rendering.
- Pixel-by-pixel or DOM-based Comparison: Offers flexibility in how differences are detected, catering to different needs and levels of sensitivity.
- Configurable Similarity Thresholds: Allows teams to fine-tune the sensitivity of change detection, reducing false positives.
- Visual Diff Highlighting: Provides clear visual representations of the changes, simplifying defect identification for QA and beta testing teams.
- Responsive Design Testing: Supports testing across different viewport sizes, ensuring consistent UI across devices.
Pros:
- Catches UI regressions that functional tests miss: This is vital for design-intensive applications where visual consistency is paramount.
- Reduces manual visual verification effort: Frees up QA teams to focus on more complex testing scenarios.
- Provides visual evidence of changes: Facilitates stakeholder review and sign-off on UI changes.
- Protects brand consistency: Ensures a consistent brand experience across application updates.
Cons:
- Prone to false positives from dynamic content and animations: Requires careful configuration and management of dynamic elements.
- Requires baseline management and regular updates: Baselines need to be updated with every intended visual change.
- Can be computationally intensive for large applications: Requires appropriate infrastructure and optimization strategies.
- May need environment consistency for reliable results: Inconsistencies in test environments can lead to false positives.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Airbnb developed and open-sourced Happo for their visual regression needs.
- BBC News uses BackstopJS to ensure consistent rendering across their global news platforms.
Tips for Effective Visual Regression Testing:
- Implement intelligent region ignore capabilities for dynamic content: This helps minimize false positives caused by dynamic elements like timestamps or ads.
- Run tests on consistent environments to minimize false positives: Containerization or dedicated testing environments can help achieve this.
- Consider component-level testing for faster feedback: Testing individual components can provide quicker feedback during development.
- Establish a baseline approval workflow for intended visual changes: This ensures that intended changes are properly documented and incorporated into the baseline.
- Combine with cross-browser testing for comprehensive coverage: Ensure consistent UI across different browsers and operating systems.
Why Visual Regression Testing Deserves its Place in Regression Testing Best Practices:
For security-conscious enterprise organizations and product managers seeking real-time insights, visual regression testing provides an essential layer of quality assurance. It catches visual defects that could negatively impact the user experience and brand perception, ultimately saving time and resources by preventing issues from reaching production. This is particularly valuable in the fast-paced world of React Native development, where seemingly minor code changes can have unforeseen visual consequences across different devices.
Visual regression testing, championed by figures like Kevin Lamping and Garris Shipon (creator of BackstopJS), and popularized by services like Percy.io (now Browserstack Percy), has become an indispensable technique for maintaining the visual integrity and user experience of modern web applications. By incorporating visual regression testing into your regression testing best practices, you can ensure a polished and consistent user interface, ultimately contributing to a higher quality product and greater user satisfaction.
7 Best Practices Comparison Matrix
| Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk-Based Regression Testing | Medium to High: Requires detailed risk analysis | Moderate: Time and stakeholder involvement | Focused testing on high-risk areas, reduced test time | Time/resource-constrained projects focused on critical features | Efficient use of resources, high ROI |
| Automated Regression Test Suite Maintenance | Medium: Requires ongoing review & refactoring | Moderate to High: Dedicated maintenance time | Improved test relevance, reduced false positives/maintenance cost | Mature automation projects needing reliability and accuracy | Maintains test quality, reduces flakiness |
| Regression Test Selection Techniques | High: Needs sophisticated tools for code analysis | Moderate to High: Tooling and setup effort | Significant test time reduction, targeted test execution | Large, modular codebases with frequent changes | Fast, focused testing; supports CI workflows |
| Regression Testing in CI | High: Automation setup & pipeline integration | High: Automation infrastructure and tests | Rapid feedback on regressions, frequent release support | Continuous integration/delivery environments | Early bug detection, faster releases |
| Data-Driven Regression Testing | Medium to High: Requires framework and data design | Moderate: Test data management and tooling | Increased coverage with fewer scripts, better edge case testing | Complex business logic with variable inputs | High coverage, maintainable test scripts |
| Regression Testing Metrics & Reporting | Medium: Requires metric collection and analysis tools | Moderate: Setup and ongoing monitoring effort | Improved test process transparency and data-driven decisions | Teams aiming to optimize and justify regression testing efforts | Objective insight, test process improvement |
| Visual Regression Testing | Medium to High: Requires setup of visual comparison | Moderate: Test infrastructure and baseline management | Detects UI regressions missed by functional tests | UI/UX intensive applications needing visual consistency | Catches visual bugs early, reduces manual checks |
Ready to Elevate Your Regression Testing?
Mastering regression testing best practices is crucial for any development team aiming to deliver high-quality software. We’ve explored seven key areas: risk-based testing, automated test suite maintenance, effective test selection techniques, integration with continuous integration pipelines, data-driven testing, insightful metrics and reporting, and the power of visual regression testing. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of regressions, accelerate your release cycles, and ultimately build a more robust and resilient application. These best practices empower your team to confidently deploy changes, knowing that existing functionality remains intact and that new features perform as expected.
Beyond the technical aspects of regression testing, integrating it within a broader quality assurance strategy is essential. To further enhance your software quality, explore these comprehensive software quality assurance best practices covering everything from strategy to implementation. They provide a valuable framework for building a robust QA process that complements your regression testing efforts.
Remember that effective regression testing isn’t merely a checkbox; it’s an investment in the long-term health and success of your software. It’s about building a culture of quality and continuous improvement. By embracing these regression testing best practices, you are not just catching bugs, but fostering a development environment that prioritizes stability, performance, and user satisfaction.
For React Native developers seeking to streamline their OTA updates and regression testing cycles, consider exploring CodePushGo. CodePushGo facilitates faster and more efficient regression testing, enabling you to quickly identify and address issues introduced by code changes, ensuring a seamless user experience with each update.




