Why Testing in Continuous Integration Actually Matters

Continuous Integration (CI) has become essential to modern software development. Its real strength lies in how it improves software testing. CI isn’t just about testing more often. It’s about changing how teams view and manage software quality. By making testing a core part of the CI pipeline, errors are caught early. This creates a faster feedback loop and helps developers deliver more reliable software. This proactive approach to quality is key for today’s development workflows.
The Impact of Early and Frequent Testing
Traditional testing often happens late in the development cycle. These manual processes are time-consuming and allow bugs to accumulate. This makes them more difficult and expensive to fix later. CI testing, however, encourages early and frequent testing. Every code change triggers automated tests, giving developers immediate feedback. This prevents defects from spreading throughout the system, saving significant time and money on bug fixes.
Think of it like building a house. If inspections only happen at the end, any structural issues require extensive rework. Late-stage software testing presents the same challenges. Testing in CI is like having continuous inspections throughout the building process. Each component is checked before moving on to the next, guaranteeing a solid foundation. This illustrates the proactive nature of CI testing.
Transforming Team Dynamics and Development Speed
Continuous integration testing significantly impacts team dynamics. It promotes shared responsibility for quality. Developers become more involved in testing and accountable for their code. This reduces friction between developers and testers, creating a more collaborative and productive environment.
Faster feedback loops in CI testing also enable faster development. Developers get immediate notifications about failing tests, allowing them to address issues quickly, while the code is still fresh in their minds. This simplifies debugging and reduces troubleshooting time. Industry trends confirm this observation. The adoption of CI testing has increased dramatically in recent years. By 2025, an estimated 70% of development teams will use automated tests as a core part of their CI/CD process. This widespread adoption is driven by the demand for quicker and more dependable software deployments. Early detection of issues within the development cycle minimizes the risk of problems after deployment. For more in-depth statistics, check out this resource: Test Automation Statistics.
Building a Solid CI/CD Foundation
Simply adding automated tests to a CI pipeline is not enough. Effective CI testing requires careful planning, strategic test selection, and a robust automation framework. For a comprehensive guide on building a strong CI/CD foundation, see this article: CI/CD pipeline best practices. This resource provides valuable insights into implementing and optimizing CI/CD workflows. It helps teams understand how to deliver high-quality software and achieve faster release cycles. Mastering these key principles is essential to fully leveraging the benefits of testing in continuous integration and achieving development excellence.
Choosing the Right Tests for Your CI Pipeline
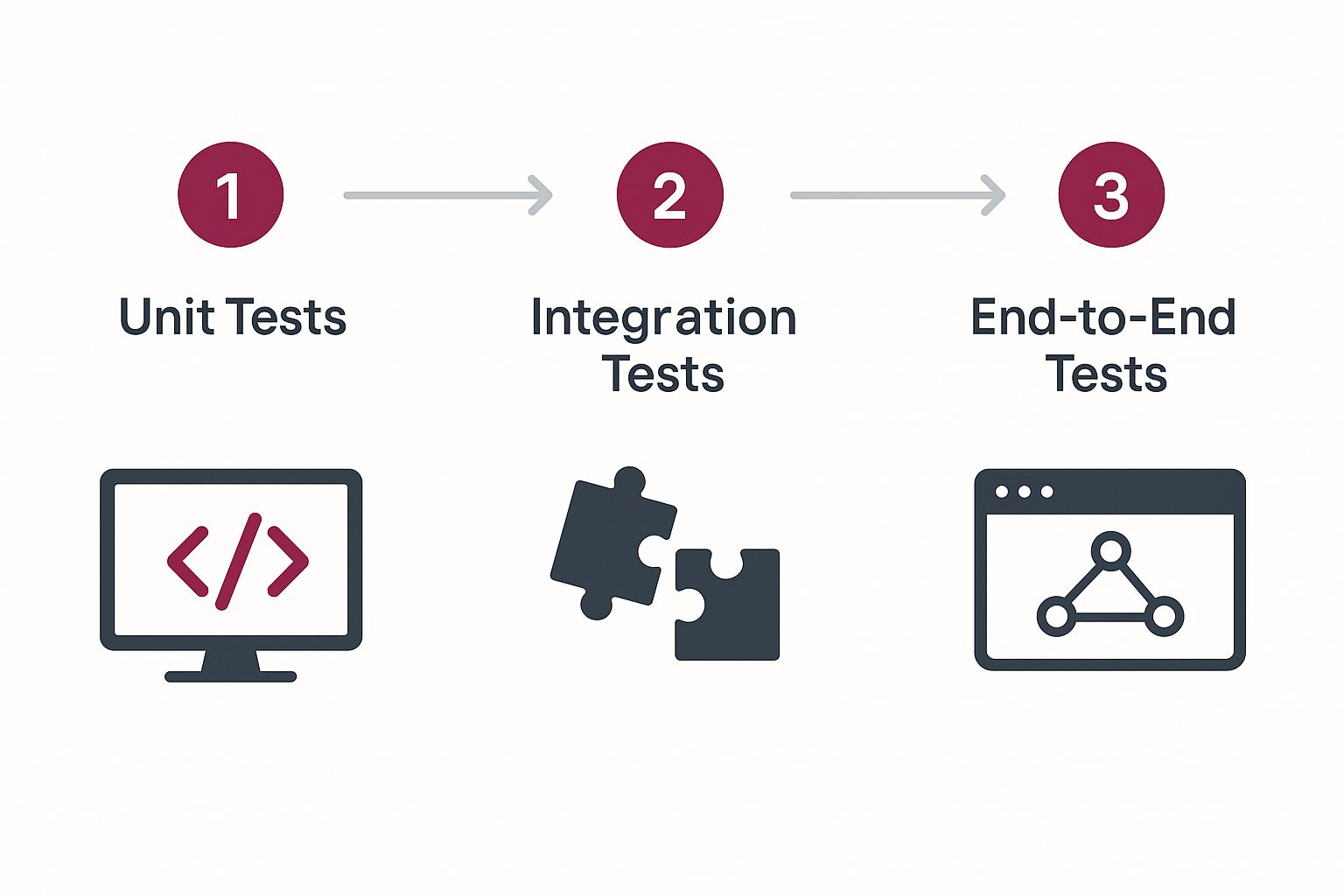
This infographic illustrates the typical progression of tests in a CI pipeline. It begins with Unit Tests, proceeds to Integration Tests, and culminates in End-to-End Tests. This layered approach, where each stage builds on the last, ensures rapid feedback and comprehensive test coverage.
Understanding which tests deliver the greatest value in CI is critical. By prioritizing the correct tests, teams gain quick feedback and robust validation without slowing down the development process. This allows them to address issues rapidly and consistently deliver high-quality software.
Balancing Speed and Coverage With the Right Test Mix
Effective CI testing hinges on striking a balance between different test types. Unit tests, which isolate and verify individual components, form the foundation. These fast tests are excellent for catching basic errors early. This rapid feedback is crucial for developers, enabling quick identification and resolution of issues.
Integration tests come next. They verify the interactions between different modules or services, ensuring they function together harmoniously. More complex than unit tests, they catch a wider range of issues that may arise from component interaction.
Finally, end-to-end (E2E) tests simulate real-world user scenarios, validating the complete application flow. While offering the most comprehensive validation, they are also the slowest and most resource-intensive. However, they are essential for ensuring the application functions as expected from the user’s perspective.
The following table offers a detailed comparison of these tests and their roles within a CI pipeline. It highlights their speed, resource needs, ideal placement within the pipeline, key benefits, and common tools used for implementation.
Test Types That Deliver Results in CI Pipelines
| Test Type | Execution Speed | Resource Requirements | Pipeline Stage | Key Benefits | Popular Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Tests | Fast | Low | Every commit | Early error detection, quick feedback | JUnit, NUnit, Jest |
| Integration Tests | Moderate | Moderate | Branch builds, pre-merge | Validates component interaction | Selenium, Cypress, Rest-Assured |
| End-to-End (E2E) Tests | Slow | High | Staging, pre-release | Verifies complete application flow, user perspective | Selenium, Cypress, Playwright |
As you can see, each test type plays a specific role in ensuring code quality. By selecting the appropriate tools and integrating them effectively into your CI pipeline, you can significantly improve the quality and reliability of your software.
Prioritizing Tests for Different Pipeline Stages
Strategic test placement in your CI pipeline optimizes feedback and efficiency. Running every test type at each stage would cause unnecessary delays. Instead, structure your test suite to provide the most relevant feedback at each point.
Unit tests, being fast and lightweight, should execute on every commit, giving developers immediate feedback. Integration tests can run less frequently, perhaps on a specific branch or before a merge, allowing for deeper testing without affecting every commit’s speed. End-to-end tests, being more complex and slower, are best suited for staging or pre-release environments, minimizing the chance of releasing software with critical user-facing defects.
Managing Long-Running Tests Effectively
Long-running tests, particularly E2E tests, pose a unique challenge in CI and can create bottlenecks. However, their comprehensive coverage is essential.
Parallelization, running tests concurrently on multiple machines or virtual environments, significantly reduces execution time. Running a subset of critical E2E tests in the CI pipeline, with the full suite executed less frequently (perhaps nightly), is another strategy.
Optimizing the test environment is also important. A staging environment closely mirroring production reduces unexpected behavior and enhances test reliability. These strategies help balance comprehensive testing with the need for rapid feedback in your CI pipeline.
Building Test Automation That Actually Works
Effective testing in continuous integration (CI) involves more than just running tests. It requires building robust, maintainable automation that delivers reliable results and adapts as your product grows. This can be challenging, but the right strategies can prevent a legacy of unwieldy tests.
Structuring Test Code for Long-Term Success
Well-structured test code is crucial for maintainability. Think of your test suite as a well-organized library. Each test should have a clear purpose and be easy to find. Descriptive names that clearly explain the functionality under test are essential. This improves understanding of each test’s scope and purpose.
Grouping related tests into logical units enhances organization and readability. For example, group tests related to user authentication or specific API endpoints. This modular approach simplifies navigation and maintenance of your growing test suite.
Implementing Assertions That Catch Real Issues
Assertions are at the core of your tests, verifying that the software behaves as expected. However, poorly designed assertions can lead to false positives or overlook critical bugs. Focus assertions on core functionality and expected outcomes.
Avoid getting caught up in checking minor details that don’t affect the user. For example, verify if a UI element is visible and interactive, rather than its exact pixel position. This makes tests more robust and less likely to break due to minor UI updates.
Designing Stable Tests Despite UI Changes
UI changes often break tests, causing frustration and undermining confidence in the CI process. One solution is to minimize direct UI interaction within tests. Focus on testing the underlying logic and data flow, rather than the visual aspects.
When UI interaction is unavoidable, use stable locators. For instance, prioritize unique IDs or data attributes over XPath. This decouples test cases from the visual layer, reducing maintenance. Consider visual regression testing tools like Percy to detect unexpected UI changes automatically.
Successfully building test automation requires continuous attention. The move toward automation has significantly impacted software testing. By 2025, many organizations anticipate a 40% reduction in manual testing. This allows testers to focus on more complex and critical aspects of development. For more insights, check out these detailed statistics.
Managing Test Data and Environments for Consistent Results
Consistent results depend on careful management of test data and environments. Dedicated test environments ensure tests run in a controlled setting, isolated from external factors. Effectively managing test data ensures tests have the necessary information without compromising sensitive data.
Techniques like data masking and synthetic data generation can help achieve this. Using containerization technologies like Docker ensures consistent execution across different pipeline runs by creating reproducible and isolated test environments. This eliminates environment-specific inconsistencies, promoting test stability.
This approach to CI automation builds a test suite that is both effective and maintainable. Focusing on well-structured code, meaningful assertions, robust test design, and managed environments creates a CI testing process that truly supports your development goals.
Creating Reliable Test Environments That Scale

Inconsistencies in testing environments often cause more issues in continuous integration (CI) pipelines than actual code errors. This highlights the critical need for dependable and scalable test environments for successful CI testing. These environments must deliver consistent results without becoming a management burden. Building effective test automation means adhering to established automated testing best practices.
Strategies For Isolated and Disposable Environments
Isolated and disposable environments are essential for dependable CI testing. Isolation prevents test interference and ensures consistent outcomes. Containerization with technologies like Docker offers a streamlined method for packaging applications and their dependencies into isolated containers. These containers are easily created and removed, providing disposable environments for every test run.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform allow for declarative management of test environments. This ensures consistency across various environments and simplifies the creation and management process. This combined approach guarantees tests run in predictable and reproducible settings.
Practical Approaches To Test Data Management
Effective test data management is crucial for CI reliability. Tests require realistic data to accurately simulate real-world conditions. However, using production data poses significant security risks. Data masking, which obscures sensitive information while preserving data structure, is one solution.
Synthetic data generation is another valuable technique, creating realistic yet fabricated data. This completely eliminates privacy concerns. Using these strategies allows your tests to utilize representative data without compromising sensitive information.
Handling External Dependencies In CI Testing
External dependencies, such as APIs or databases, can create difficulties in CI. These services might be unavailable or behave unpredictably, resulting in unreliable tests. Service virtualization offers a solution by simulating the behavior of external dependencies, providing a controlled and consistent testing environment.
Contract testing focuses on interactions between services, ensuring they adhere to agreed-upon contracts. This prevents changes in one service from disrupting others. Intelligent mocking allows for simulated dependency behavior based on specific scenarios, offering greater control over the testing environment.
Implementing Parallel Test Execution
Parallel test execution drastically reduces feedback time in CI. Running tests concurrently speeds up the testing process. However, improper parallelization can lead to resource conflicts and unreliable test results. Implementing proper locking mechanisms and resource allocation strategies is key to preventing conflicts.
Designing tests to be independent and avoid shared states ensures they don’t interfere with each other during parallel execution. This approach maximizes the advantages of parallelization, maintaining test reliability and creating a highly efficient CI process with fast, dependable feedback.
Measuring What Matters: Beyond Basic Coverage

While code coverage is a common metric in continuous integration testing, focusing only on achieving a specific percentage can be misleading. True effectiveness lies in understanding which metrics genuinely reflect the quality of your software. This involves moving beyond simple coverage numbers and embracing a more holistic approach.
Understanding Different Coverage Types and Their Significance
Code coverage comes in various forms, each offering unique insights. Line coverage, for instance, measures the percentage of lines of code executed during testing. While straightforward to calculate, it doesn’t guarantee the quality of the tests. A high line coverage percentage might still overlook critical logical branches within your codebase.
Branch coverage addresses this by measuring the percentage of code branches exercised during testing. This provides a more comprehensive view of code execution paths, helping to identify gaps in test coverage. Condition coverage goes even further, assessing the completeness of testing for various logical conditions within the code. This can reveal areas where edge cases or complex logic might not be fully validated.
Relying on a single metric provides a limited perspective. Combining these coverage types offers a much richer understanding of your test suite’s effectiveness.
To illustrate the various coverage metrics and their significance, let’s examine the following table:
Introduction to the table: The following table presents various test coverage metrics that teams can track in their CI pipelines, explaining what each metric measures, how to interpret the results, and recommended target values. It also highlights the limitations of each metric, encouraging a balanced approach to test coverage.
| Coverage Metric | What It Measures | Interpretation Guide | Recommended Targets | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Coverage | Percentage of lines of code executed by tests | Higher percentage generally indicates better coverage, but doesn’t guarantee test quality | 80-90% (depending on project complexity) | Doesn’t capture all execution paths or logical conditions |
| Branch Coverage | Percentage of code branches (if/else statements, loops) executed by tests | Captures more execution paths than line coverage, highlighting gaps in testing logic | 70-85% (can be higher for critical applications) | May not fully cover all possible combinations of conditions within branches |
| Condition Coverage | Percentage of boolean sub-expressions evaluated to both true and false | Ensures all logical conditions within the code are thoroughly tested | 80-95% (especially important for complex logic) | Can be challenging to achieve 100% and may require specialized testing techniques |
Key insights from the table: While high coverage percentages are generally desirable, focusing solely on achieving a specific number can be counterproductive. Instead, teams should strive for a balance across different coverage metrics, considering the project’s complexity and risk tolerance.
Beyond Code Coverage: A Holistic View of Quality
Effective testing in continuous integration goes beyond just code coverage. Engineering leaders also incorporate other quality signals for a complete picture of their software’s health. One such signal is the defect escape rate, which measures how many bugs make it into production. Tracking this metric helps pinpoint weaknesses in the testing process.
Test reliability is also crucial. Flaky tests that yield inconsistent results undermine confidence in the CI process. Monitoring test reliability and promptly addressing flaky tests is vital for maintaining a healthy CI pipeline.
Finally, focusing on user-impacting issues found during testing, regardless of coverage metrics, directly measures the impact on the end-user experience. This user-centric approach emphasizes the real-world consequences of defects and prioritizes areas for improvement.
Implementing Coverage Gates Strategically
Coverage gates, which require a minimum coverage level before merging code, can be useful tools. However, they should be implemented strategically to avoid becoming bureaucratic obstacles. Tie coverage gates to meaningful metrics aligned with your overall quality goals. Blindly enforcing arbitrary percentages without understanding the context can hinder progress without improving quality.
Regularly review and adjust your coverage gate thresholds based on project needs and historical data to ensure their continued relevance and positive impact. CodePushGo offers seamless CI/CD integration for React Native developers, further enhancing the benefits of coverage gates by streamlining the release process.
Visualizing Quality Trends Over Time
Visualizing testing metrics over time provides valuable insights into trends and patterns. Tracking metrics like code coverage, defect escape rates, and test reliability allows teams to monitor progress and identify areas needing attention. This data-driven approach enables proactive problem identification and facilitates continuous improvement of testing practices.
For instance, if defect escape rates increase while code coverage remains stable, it might indicate a need to reassess the effectiveness, not just the quantity, of your test cases. These insights are critical for continuously refining your testing strategies within continuous integration and ensuring your CI pipeline delivers high-quality software.
Building a Test-Driven Culture That Delivers
Building a successful continuous integration (CI) testing strategy isn’t simply about having the right tools. It’s about cultivating a culture where quality is everyone’s responsibility. This shift in perspective changes how teams approach software development, integrating quality from the beginning rather than treating it as an afterthought.
Breaking Down Silos Between Development and Testing
Traditional software development often creates divisions between developers and testers. This can lead to disagreements and slow down the feedback process. A test-driven culture breaks down these walls and promotes shared ownership of the test suite. When developers actively participate in testing, they gain a better understanding of how their code affects the entire system. This shared responsibility leads to better collaboration and a united focus on delivering high-quality software. For example, pairing developers and testers together to create and maintain test cases can encourage a more collaborative work environment.
Establishing Processes That Balance Speed With Quality
Balancing rapid feature delivery with maintaining high quality is a constant challenge. Effective CI testing helps teams achieve this balance. Automating tests and integrating them into the CI pipeline gives teams quick feedback on code changes without sacrificing quality. This speeds up the development process and reduces the chances of releasing software with bugs. Implementing quality gates at different stages of the pipeline ensures that code meets predefined standards before moving forward.
Prioritizing Tests for Maximum Impact
Prioritizing tests based on risk and impact ensures that the most important areas of the software are thoroughly checked. This strategic approach recognizes that not all tests are equally important. Tests that cover essential functions and user-facing features should be prioritized. This makes sure the most critical parts of the application are thoroughly tested. For example, tests for login functionality or key API endpoints should be prioritized over tests for less important features.
Handling Long-Running Tests and Managing the Test Pyramid
Long-running tests, such as end-to-end tests, can slow down CI. Strategies like parallelization and optimizing test environments minimize this impact. Running tests simultaneously on multiple machines significantly reduces the overall testing time. Optimizing the test environment to closely resemble the production environment also improves the reliability of tests and reduces unexpected issues. Managing the test pyramid effectively is also essential. This means focusing most of the testing effort on fast, isolated unit tests, then a smaller number of integration tests, and finally, a minimal set of slower, more complex end-to-end tests.
Fostering Continuous Improvement in Testing
A test-driven culture embraces ongoing improvement. Regularly reviewing and refactoring test code prevents technical debt from building up. Like production code, test code needs continuous maintenance and refinement. Teams should implement regular code reviews for test cases and encourage refactoring to improve clarity and efficiency. This proactive approach ensures that tests remain effective and adaptable to changes in the software. It also promotes a long-term perspective for CI testing.
Building a test-driven culture requires consistent effort and dedication. However, the advantages are clear: faster delivery, higher quality, and improved team morale. By implementing the right processes, tools, and mindset, teams can maximize the benefits of testing in continuous integration. CodePushGo seamlessly integrates with your existing CI/CD pipeline, further empowering your team to adopt these best practices and deliver high-quality React Native applications. Learn more about how CodePushGo can enhance your CI/CD workflow at CodePushGo.
Overcoming Common Obstacles in CI Testing
Testing in continuous integration (CI) offers many advantages, but it also presents unique challenges. This section explores common roadblocks encountered in CI testing and offers practical solutions for navigating these complexities.
Tackling Flaky Tests
Flaky tests, which produce inconsistent results even without code changes, erode confidence in the CI process. Much like a traffic light that randomly changes colors, flaky tests create uncertainty and hinder development progress. The first step is to isolate and rerun these tests to pinpoint the root cause, which can stem from timing issues or inconsistent test data.
Addressing the root cause is essential. This could involve improving test isolation, using mock dependencies with tools like Mockito, or refining timeout settings. For instance, if a test relies on an external service, mocking that service ensures predictable behavior and eliminates external factors as a source of flakiness. Prioritizing fixes for flaky tests maintains CI reliability.
Reducing Test Execution Time
Long test execution times can create bottlenecks in the CI/CD pipeline. Minimizing this time without compromising test coverage is vital for maintaining development velocity. Parallelization, running tests concurrently, significantly increases speed. Think of it like having multiple chefs preparing different parts of a meal at the same time, reducing the overall cooking time.
Effective parallelization, however, requires careful management of dependencies between tests and shared resources. Optimizing individual tests for speed is also crucial. This includes removing unnecessary assertions and simplifying test setup and teardown processes.
Managing External Dependencies
External dependencies, such as third-party APIs or databases, introduce unpredictability into the CI process. These services might experience downtime or behave erratically during testing, impacting results. Service virtualization offers a solution by simulating the behavior of these dependencies, much like a flight simulator trains pilots without a real aircraft.
This allows tests to run consistently regardless of the external service’s status. Contract testing is another useful strategy, focusing on verifying interactions between services based on predefined agreements, ensuring changes in one service don’t disrupt integration with others.
Maintaining Test Code Quality
Test code, like production code, demands regular maintenance to prevent it from becoming unwieldy. Applying clean code principles to your test suite ensures long-term maintainability. This includes using clear and descriptive test names, structuring tests into logical modules, and following consistent coding conventions.
Regular refactoring of test code keeps it concise and understandable. Implementing design patterns, such as the Page Object Model for UI testing, enhances modularity and reduces code duplication. This proactive approach prevents technical debt within the test suite and ensures tests remain effective and easy to manage.
Optimizing CI Tool Configurations
Your CI tool, such as Jenkins or GitHub Actions, offers various configurations to fine-tune testing. Adjusting timeout settings prevents tests from hanging indefinitely due to external dependencies. Configuring appropriate logging levels provides valuable debugging information.
Optimizing the CI pipeline stages maximizes test efficiency. Running fast unit tests early provides rapid feedback to developers, while longer integration and end-to-end tests can run later. These configurations bolster the CI process’s effectiveness and provide valuable feedback.
Building Testing Expertise Across the Team
Cultivating shared responsibility for quality involves empowering your team with testing skills. Providing training and resources equips developers to write effective tests. Encourage knowledge sharing through code reviews and pair programming focused on testing best practices.
Cross-functional training helps developers and testers understand each other’s perspectives, improving collaboration and fostering a shared commitment to quality. This team-wide grasp of testing principles elevates the entire CI process.
By addressing these common challenges, teams can harness the full potential of CI testing. A well-maintained and efficient CI testing process significantly improves software quality and speeds up delivery.




