Understanding What Is a Test Group: The Foundation of Smart Testing

A test group is a select group of individuals or items chosen to participate in a study or experiment. This group is exposed to a specific treatment or condition, enabling researchers or businesses to observe the effects. The data gathered from the test group is then compared against data from a control group – a group that does not receive the treatment. This comparison helps determine the treatment’s impact and effectiveness, a process fundamental to understanding cause and effect. Think of it like baking a cake: the test group is the cake with the new ingredient, while the control group is the original recipe.
Why Are Test Groups So Important?
Test groups are vital for data-driven decision-making. They provide concrete evidence, moving us beyond assumptions and gut feelings. Imagine launching a new feature in your React Native app. A test group lets you observe how real users interact with the feature before releasing it to your entire user base. This can save you time, resources, and potentially prevent negative feedback. It’s a crucial approach for understanding how modifications impact user experience.
The selection process for creating a test group is critical to the experiment’s success. A poorly selected test group can skew your results, leading to inaccurate conclusions. For instance, if a test group isn’t representative of the target audience, the findings might not be applicable to the broader population. This is especially important for CodePushGo users who need to ensure their over-the-air (OTA) updates enhance the user experience for all app users.
A/B Testing and Test Groups
The concept of a test group is particularly relevant in A/B testing. Here, the test group receives a new variable, while the control group remains unchanged. This direct comparison of two variations helps businesses measure performance. Consider mobile A/B testing with CodePushGo: the test group could experience a new app version with modified features, while the control group uses the standard version. This generates valuable data on the update’s effectiveness. Historically, companies like Google have used A/B testing extensively, even testing 41 shades of blue on their search results page to optimize click-through rates. For more information on test groups and control groups, see this helpful resource: Learn more about test groups and control groups.
Building an Effective Test Group
Several factors contribute to a successful test group. First, the group should be representative of the larger population being studied. This ensures your results are generalizable. Second, the size of the test group must be suitable for the specific research. Too small a group can yield unreliable results, while too large a group can be resource-intensive. Finally, maintaining the test group’s integrity throughout the experiment is paramount. This involves minimizing attrition (participants leaving the study) and preventing contamination (outside influences). By carefully considering these elements, developers using CodePushGo can optimize testing strategies for more efficient and reliable results, leading to confident deployments and a smoother user experience.
Getting Your Test Group Size and Composition Right
Finding the right test group is crucial for successful experiments. It’s not about the largest group, but the right one. A test group is the subset of participants who receive the treatment or modification being tested. This group is essential for understanding how changes affect user behavior and product performance. This section explores the statistical principles behind effective test group creation, focusing on practical application rather than complex formulas. We’ll discuss equal splits, sample size, and adaptive sequential design.
Balancing Your Test Group: The Power of Equal Splits
The simplest approach is often the best. Equally dividing your test group between control and treatment simplifies analysis and interpretation. This 50/50 split establishes a clear baseline, making it easier to identify statistically significant differences. For example, if you’re A/B testing a new feature in your React Native app with CodePushGo, an equal split provides a balanced view of the update’s impact.
Determining the Right Sample Size: Quality Over Quantity
A larger test group isn’t always better. The ideal sample size is large enough to detect meaningful changes but manageable within your resources. A balance between statistical power and practical limitations is key. A small test group might miss subtle effects, while an excessively large one becomes costly and time-consuming. Further reading: How to master Android Continuous Integration.
The following infographic illustrates the increased reliability when using a test group:
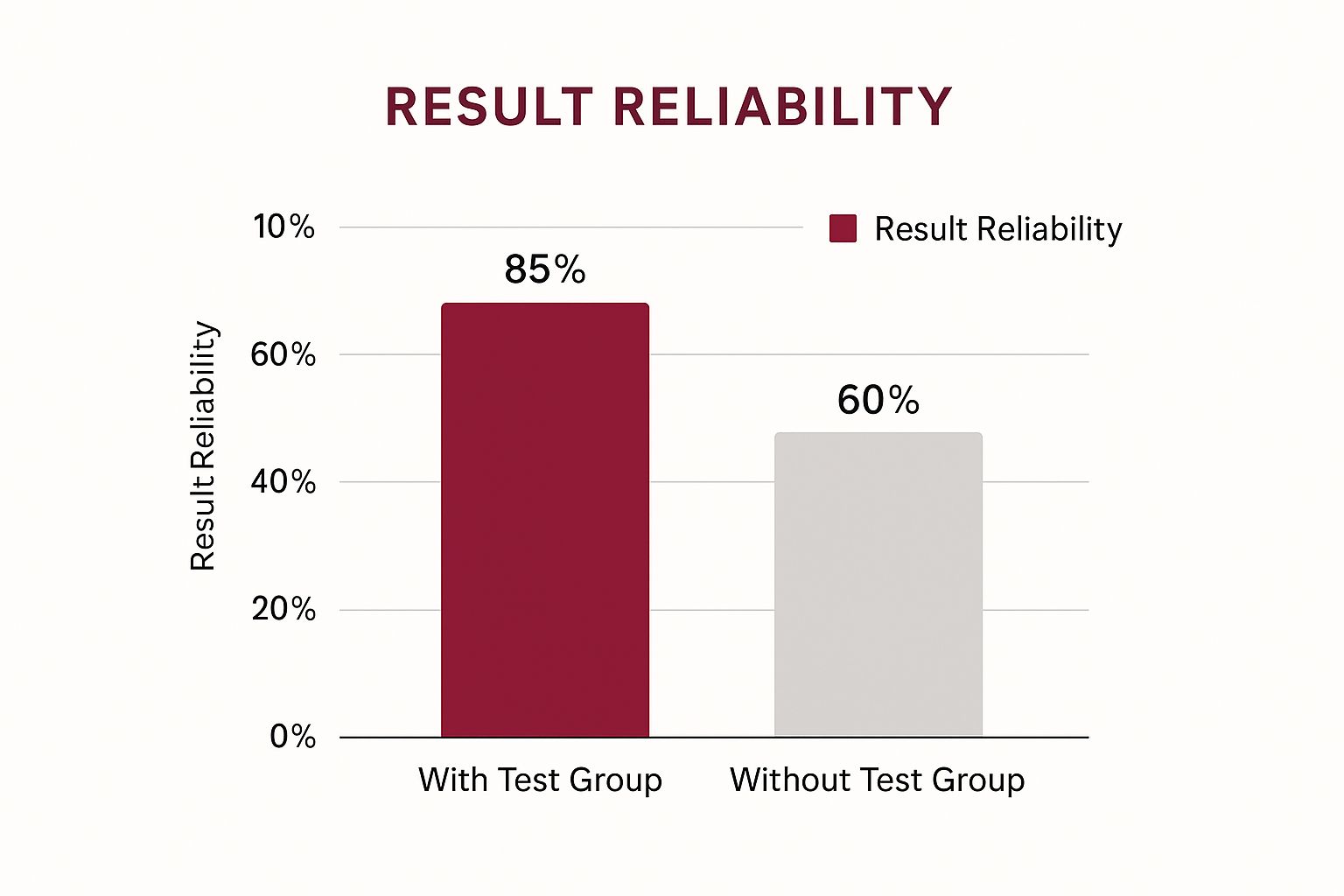
The infographic demonstrates that using a test group raises reliability to 85%, compared to 60% without one. This highlights the importance of incorporating a test group in your testing strategies. The size and composition significantly influence experiment outcomes. Often, test groups are split equally between control and treatment. For example, when testing a new marketing strategy, a company might divide its test group into two equal segments, with one receiving the new strategy and the other remaining with the existing one. This helps identify important differences for informed decision-making.
To further illustrate the relationship between experiment type and required sample size, let’s examine the following table:
Test Group Size Requirements by Experiment Type
| Experiment Type | Minimum Sample Size | Confidence Level | Expected Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| A/B Test (Website Button Color) | 200 | 95% | Small |
| User Survey (Product Satisfaction) | 300 | 90% | Medium |
| Multivariate Test (Landing Page Elements) | 500 | 95% | Small |
This table provides a general guideline; specific requirements may vary. Notice how the sample size increases with the complexity of the experiment and desired confidence level. A larger effect size can allow for smaller sample sizes.
Advanced Techniques: Adapting and Optimizing
For complex experiments, consider adaptive sequential design. This technique dynamically adjusts the control and treatment group proportions based on real-time data. Unlike traditional A/B testing with fixed group sizes, adaptive designs optimize resource allocation by directing participants towards the better-performing treatment. This results in faster, more efficient insights, essential for rapid iteration. With adaptive sequential design, the proportions may shift based on ongoing results for more efficient testing. Learn more about test groups at Analytics Toolkit.
Practical Considerations: Balancing Budget and Impact
Effective test groups are possible even with limited resources. Prioritize quality over quantity by selecting a representative sample of your target audience. By thoughtfully considering these factors – from equal splits to advanced techniques – you can create experiments that yield reliable, actionable insights, regardless of budget constraints.
The Fascinating History Behind Modern Test Group Methods

Understanding user behavior and product performance relies heavily on test groups. The history of these groups is more complex than many realize, offering key insights into effective testing practices. Exploring this evolution reveals why certain methods succeed while others don’t.
Early Innovations: From Pooled Samples to Powerful Insights
The journey begins in the 1940s with statistician Robert Dorfman. During World War II, Dorfman’s work revolutionized testing. He pioneered group testing to efficiently screen soldiers for syphilis. This resource-efficient technique involved testing pooled samples rather than individual ones.
This innovation proved invaluable for large-scale screenings, saving significant time and resources. The method eventually expanded to other fields like medicine and engineering, optimizing resource use and speeding up identification processes. More recently, digital platforms have leveraged online experiments for rapid data collection and analysis globally. Learn more about group testing here.
The Rise of A/B Testing: Refining the Process
Dorfman’s work laid the foundation for modern A/B testing, a core component of digital experimentation. A/B testing compares two versions of something – a webpage, app feature, or advertisement – to determine which performs better. One version serves as the control, and the other as the test group, providing clear data on the impact of changes.
This shift from pooled samples to direct comparison enabled more nuanced insights. For those interested in mastering testing within continuous integration, check out this resource: How to master testing in continuous integration.
Modern Applications: From Netflix to Amazon and Beyond
Today, A/B testing, fueled by sophisticated algorithms and vast amounts of data, informs decisions across diverse industries. Companies like Netflix use test groups to optimize recommendations and personalize user experiences. Amazon also utilizes A/B testing to refine its checkout process and boost conversion rates. These applications showcase the power of test groups in driving business growth. The evolution from wartime efficiency to personalized user experiences demonstrates the enduring value of test groups.
The Digital Age: Real-Time Testing and Continuous Improvement
Platforms like CodePushGo now empower developers to deploy over-the-air (OTA) updates. This allows for instant data gathering from test groups, enabling rapid iteration and continuous improvement. This real-time feedback loop facilitates quick adjustments and smoother user experiences, proving invaluable for agile development. This constant evolution highlights the continued importance of test groups in understanding user behavior and driving product success.
Test Group vs Control Group: Mastering the Critical Partnership
Think of test groups and control groups as two integral parts of any successful experiment. Understanding their distinct roles is vital for getting reliable results. A test group (also known as the experimental group) is exposed to the change or treatment being studied. The control group, however, remains unchanged, acting as a baseline for comparison. This comparison reveals the actual impact of the modification, whether it’s a new app feature or a revised marketing campaign.
To understand this further, we will compare the Test and Control group further below.
Why You Need Both: The Power of Comparison
Imagine testing a new landing page design. The test group sees the new design, while the control group sees the original. By analyzing metrics like conversion rates for both groups, you can isolate the impact of the design change. Without a control group, there’s no reference point to determine if the new design genuinely performed better.
To provide a clear overview, we’ve created a detailed comparison table:
To better understand the differences between these two groups, let’s look at a side-by-side comparison:
| Aspect | Test Group | Control Group | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure to Treatment | Receives the treatment or intervention | Does not receive the treatment or intervention | Provides a baseline |
| Variables | Exposed to the independent variable | Independent variable is held constant | Isolates the effects of the independent variable |
| Measurement | Measured for changes after exposure to the treatment | Measured to determine the baseline and any changes unrelated to the treatment | Comparing the two groups reveals the impact of the treatment |
| Purpose | To determine the effect of the independent variable | To serve as a comparison group, demonstrating what happens without the treatment | To draw accurate conclusions about the treatment’s efficacy |
This table highlights the key distinctions between the test and control groups, emphasizing how they work together to provide a comprehensive understanding of a treatment’s impact. The control group’s role as a benchmark is vital for accurately assessing the treatment’s effects.
Avoiding Pitfalls: Selection Bias and Group Crossover
Two common issues can affect your experiment’s validity: selection bias and group crossover. Selection bias arises when the test and control groups aren’t comparable. For example, if your test group includes only tech-savvy users, while the control group includes those less familiar with technology, any differences might be due to those pre-existing characteristics, not your treatment. You might find this article on regression testing best practices helpful.
Group crossover occurs when individuals switch between groups, complicating the results. If some control group users access the new landing page designed for the test group, it becomes difficult to isolate the design’s true effect.
Building Clean Comparisons: Practical Techniques
Maintaining clear group separation is crucial. When A/B testing with platforms like CodePushGo, ensure the control group receives the current version of your React Native app, while the test group gets the update. Randomly assigning participants to groups helps minimize selection bias, creating statistically similar groups.
Real-World Examples: From Marketing to User Experience
Test and control groups are used in numerous scenarios. Marketing teams might test a new ad campaign with a test group, while the control group sees the old ads. Product teams can launch a new feature to a test group first, collecting data before a wider release. UX designers test different interfaces, analyzing user interactions in each group to optimize usability.
Ensuring Reliability: Practical Tips for Success
Here are key takeaways for effective test and control groups:
- Randomization: Randomly assigning participants minimizes differences.
- Representative Samples: Ensure both groups reflect your target audience.
- Clear Separation: Prevent any interaction between groups.
- Appropriate Size: Use a sample size large enough to detect meaningful differences.
By following these principles, you’ll gain reliable results and make informed decisions based on solid data. Using both groups strengthens your testing strategy, providing concrete information for effective decision-making, whether you’re refining a landing page, launching a new app feature, or enhancing your overall marketing approach.
Real-World Applications: How Modern Businesses Use Test Groups

Businesses rely on test groups to inform their decisions with real-world data. These groups offer crucial insights into user behavior and preferences, helping companies optimize everything from website design to new product development. This data-driven approach minimizes risk and maximizes the potential for success.
Optimizing User Experience: Refining Digital Products and Services
Major e-commerce players frequently use test groups to fine-tune their online platforms. For instance, a company might test different checkout processes with two groups. One group experiences a single-page checkout, while the other navigates a multi-page process. Analyzing key metrics like conversion rates and cart abandonment reveals which checkout flow delivers a better user experience and higher sales. You might be interested in learning more about app engagement metrics: How to master app engagement metrics.
Similarly, Software as a Service (SaaS) companies use test groups to improve their onboarding processes. By presenting different onboarding tutorials or in-app guidance to separate groups, and subsequently analyzing user engagement and feature adoption, these companies identify the most effective onboarding strategies for increased user retention and satisfaction.
Marketing and Advertising: Targeting the Right Audience
Test groups are essential for targeted marketing campaigns. A company testing different ad creatives with various groups can track click-through rates and conversions to determine which ad resonates best. This targeted approach optimizes ad spend and improves campaign performance.
Personalizing marketing messages also benefits from test group insights. By sending tailored emails or promotional offers to different customer segments and analyzing response rates, businesses can identify which messaging leads to higher engagement and conversion.
Product Development: Iterating and Innovating
Before a new product or feature launch, test groups offer valuable feedback. This allows companies to identify and address potential usability issues early in the development cycle, ultimately leading to a superior final product. For example, a company developing a mobile app might release a beta version to a test group using CodePushGo. The resulting feedback helps refine the app before its official release.
The Tools of the Trade: Making Testing Accessible
A range of platforms and tools simplify test group management and data analysis. From basic A/B testing tools to more sophisticated solutions with advanced segmentation and behavioral tracking, these resources empower businesses of all sizes to incorporate testing into their operations.
Integrating Experimentation: A Culture of Continuous Improvement
Successful businesses often integrate experimentation into their standard workflows. This continuous testing and iteration cultivate a culture of data-driven decision making, driving ongoing optimization and growth. Regular testing of different ideas and approaches fosters a constant cycle of learning and improvement. This is especially valuable for React Native developers, who can use CodePushGo to release updates quickly, gather real-time feedback from test groups, and iterate rapidly. This agile development process ensures the final product truly meets user needs. By embracing experimentation and tools like CodePushGo, businesses can stay competitive in today’s market.
Building Test Groups That Actually Work: Your Step-by-Step Guide
Creating effective test groups is vital for gathering reliable data and making informed decisions. This guide offers a practical, step-by-step framework to design and execute experiments that deliver real business outcomes. We’ll cover essential principles such as randomization, sample size calculation, and bias prevention, drawing on insights from seasoned professionals. We’ll also delve into best practices for participant recruitment, data collection, and strategies for navigating unforeseen challenges.
Step 1: Define Your Objectives and Metrics
Before launching any experiment, it’s crucial to clearly define your goals. What specific questions are you trying to answer? Are you aiming to increase user engagement, boost conversion rates, or improve app performance? Once you’ve established your objectives, identify the key metrics that will measure success. These could include click-through rates, conversion rates, retention rates, or specific in-app actions.
Step 2: Randomization and Group Formation
Random assignment is a cornerstone of effective testing. This ensures your test and control groups are as similar as possible, minimizing the risk of selection bias. Use a random number generator or specialized software to assign participants to either group. If using CodePushGo for A/B testing, randomly distribute users between the group receiving the updated app version and the group using the current version.
Step 3: Calculate the Right Sample Size
The sample size of your test group (the group experiencing the change) is crucial for obtaining statistically significant results. A sample that’s too small might overlook subtle effects, while an excessively large sample can be unnecessarily resource-intensive. Use online calculators and statistical formulas to determine the appropriate sample size based on factors like the desired confidence level and expected effect size.
Step 4: Mitigate Potential Biases
Bias can inadvertently skew results and lead to inaccurate conclusions. Beyond selection bias, be wary of confirmation bias, where you might interpret data to confirm pre-existing beliefs. Implementing blinding techniques, where participants and even researchers are unaware of group assignments, helps minimize these biases.
Step 5: Recruiting and Onboarding Participants
Attracting and retaining participants is essential for any successful experiment. Clearly communicate the study’s purpose and benefits to potential participants. If offering incentives, ensure they don’t unduly influence user behavior. For app testing with CodePushGo, use in-app messaging or push notifications to inform users about participation opportunities.
Step 6: Data Collection and Analysis
Throughout the experiment, diligently collect data related to your predefined metrics. Use analytics platforms, in-app tracking, or survey tools. Once the experiment concludes, analyze the data, comparing results between the test and control groups. Look for statistically significant differences to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of your treatment or change. For more insights, check out this article: How to master automatic app updates.
Step 7: Addressing Challenges and Adapting
Real-world experiments rarely go perfectly. Participants may drop out, technical issues may arise, or unexpected external factors could influence results. Prepare for these by establishing clear protocols for handling dropouts, troubleshooting technical problems, and documenting external influences. You might need to adjust the experimental design or extend the study duration to account for unforeseen circumstances.
Building a Culture of Experimentation
Integrating these steps into your testing process allows you to build reliable test groups and generate actionable insights. Regular testing should be a cornerstone of your development cycle, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making. Whether you’re refining a user interface, launching a new feature, or optimizing your marketing strategies, well-designed test groups empower informed decisions based on evidence, not guesswork.
Key Takeaways
This section provides practical strategies for achieving test group success, based on proven methods and real-world examples. We’ll explore actionable steps for effective testing, realistic benchmarks, and advice on avoiding common pitfalls. Each takeaway offers immediately applicable insights, alongside clear indicators to track progress and measure success.
Essential Principles for Test Group Success
Before diving into the practicalities, let’s establish some fundamental principles. A successful test group hinges on several key factors:
-
Clear Objectives: Define precise goals before you begin. What do you hope to achieve? Are you aiming to increase conversions, enhance user engagement, or refine a specific feature? Well-defined objectives will guide your entire testing process.
-
Representative Sample: Your test group should accurately mirror your target audience. For instance, if testing a mobile game update with CodePushGo, ensure the test group reflects the demographics of your player base. This ensures your findings are applicable to the wider user population.
-
Adequate Size: The test group must be large enough to identify statistically significant differences. A small group might overlook subtle but important changes. Conversely, a very large group can strain resources. Utilize statistical tools like a sample size calculator to determine the optimal size for your experiment.
-
Clean Comparison: Maintain a clear distinction between your test group and your control group. Avoid any crossover or interaction that could skew your results. For example, if testing a new feature with CodePushGo, the control group should continue using the existing version.
Actionable Steps for Implementation
Now, let’s translate these principles into actionable steps. Implementing a successful test group involves:
-
Random Assignment: Randomly assign participants to either the test group or the control group. This minimizes pre-existing differences, leading to more reliable results. CodePushGo simplifies this by randomly distributing updates to designated user segments.
-
Data Collection: Meticulously collect data relevant to your pre-defined objectives. Use analytics platforms, in-app tracking, or surveys. CodePushGo offers real-time analytics, allowing you to track update success rates and monitor user engagement.
-
Iterative Approach: Treat testing as a continuous process. Analyze results, extract insights, and adjust your approach as needed. CodePushGo supports rapid iteration through its efficient deployment capabilities, allowing for swift testing and refinement.
Benchmarks and Measuring Progress
How do you know if your test is successful? Establish clear benchmarks and track relevant metrics.
-
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Monitor KPIs aligned with your objectives. If your goal is improved engagement, track metrics like daily active users or session duration.
-
Statistical Significance: Ensure observed differences between your test and control groups are statistically significant. This helps determine if changes are due to the treatment or simply random variation.
-
A/B Testing Best Practices: When conducting A/B testing with CodePushGo, follow best practices such as maintaining equal group sizes and running tests for an adequate duration. This helps capture a representative sample of user behavior.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
While planning your test, be mindful of these potential pitfalls:
-
Selection Bias: Ensure random assignment to avoid bias in group composition. A biased test group won’t accurately represent your target audience, leading to inaccurate results.
-
Contamination: Prevent interaction between your test and control groups. If control group participants access the treatment intended for the test group, it will compromise the results.
-
Insufficient Duration: Avoid concluding experiments prematurely. Run your tests for a sufficient period to gather enough data for robust conclusions.
Building a Culture of Experimentation
Testing should be an integral part of your development process. Integrate experimentation into your workflow. CodePushGo empowers this by facilitating quick deployments, allowing you to continuously test and improve your React Native applications. Cultivate a data-driven culture where testing and iteration are standard practice. This leads to better products and satisfied users.
Ready to explore the advantages of over-the-air updates and robust A/B testing? Begin your free trial with CodePushGo today: Get started with CodePushGo




